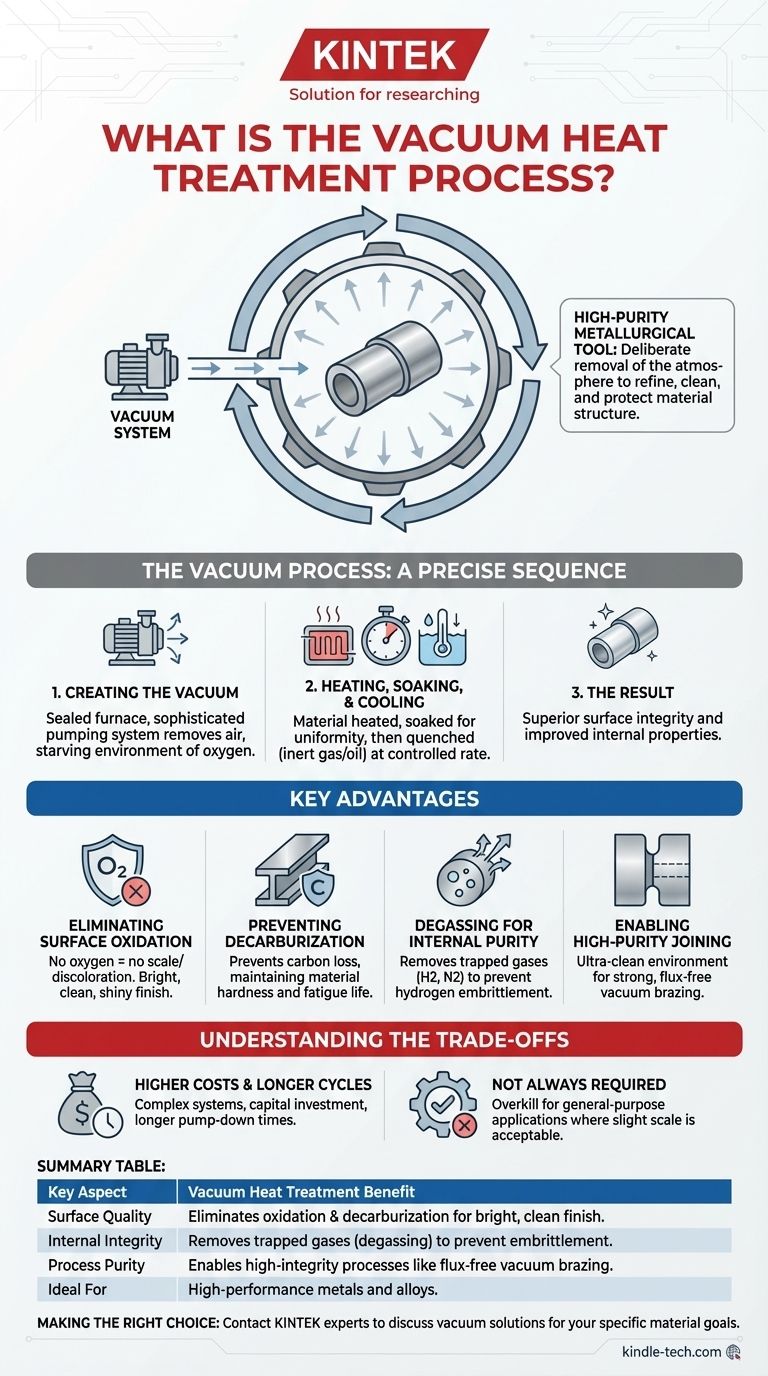
In essence, vacuum heat treatment is a process where materials, primarily metals, are heated and cooled in a highly controlled, low-pressure environment. By removing the atmosphere from the furnace chamber using a vacuum system, this method prevents unwanted surface reactions like oxidation and decarburization. The result is a component with superior surface integrity and improved internal properties.
The core advantage of vacuum heat treatment is not just the application of heat, but the deliberate removal of the atmosphere. This transforms the process from simple heating into a high-purity metallurgical tool that refines, cleans, and protects the material's surface and structure.
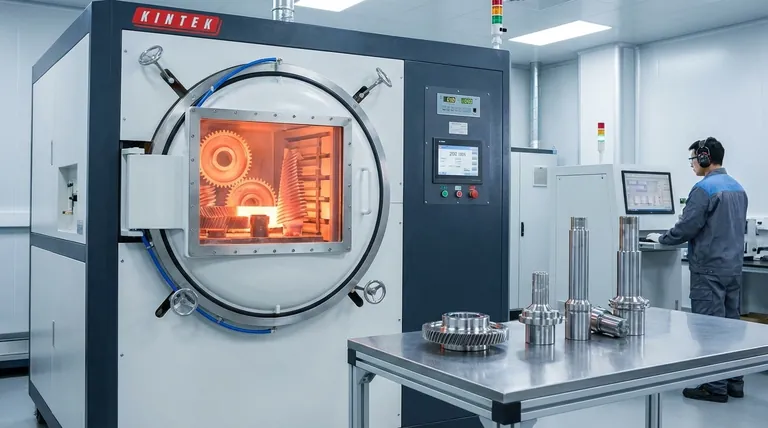

How the Vacuum Process Works
Vacuum heat treatment follows a precise, multi-stage sequence within a sealed furnace. Each step is critical for achieving the desired outcome.
The Principle: Creating the Vacuum
The process begins by placing the workpiece inside the furnace chamber and sealing it. A sophisticated vacuum pumping system then removes the air, reducing the internal pressure to a level far below that of the normal atmosphere.
This low-pressure state, or "vacuum," effectively starves the environment of oxygen and other reactive gases.
The Execution: Heating, Soaking, and Cooling
Once the target vacuum level is achieved, the material is heated to a specific temperature using internal heating elements. It is then held at this temperature for a predetermined period, known as soaking, to ensure the entire part reaches a uniform temperature.
Following the soak, the material is cooled, or quenched, at a controlled rate. This can be done using a high-pressure inert gas (like nitrogen or argon) or by transferring the part to a separate oil-quenching chamber, all while maintaining a controlled environment.
Key Advantages Over Traditional Methods
Choosing a vacuum environment provides several distinct benefits that are difficult or impossible to achieve with conventional atmospheric furnaces.
Eliminating Surface Oxidation
Without oxygen present, the oxidation that causes scale and discoloration on a metal's surface cannot occur. This results in a bright, clean, and shiny finish straight out of the furnace, often eliminating the need for post-process cleaning or machining.
Preventing Surface Decarburization
For many steels, heating in an oxygen-rich atmosphere can strip carbon from the surface layer, a defect known as decarburization. This softens the material and reduces its fatigue life. The inert vacuum environment completely prevents this.
Degassing for Internal Purity
The vacuum actively pulls trapped gases, such as hydrogen and nitrogen, out from within the metal itself. This degassing process is crucial for preventing issues like hydrogen embrittlement, a phenomenon that can cause catastrophic failure in high-strength components.
Enabling High-Purity Joining
Processes like vacuum brazing rely on this ultra-clean environment. The vacuum removes oxides and contaminants, allowing the brazing alloy to flow freely and create a strong, flux-free joint between components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum heat treatment is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Higher Equipment and Operational Costs
Vacuum furnaces, with their complex pumping systems, seals, and advanced controls, represent a significantly higher capital investment than standard atmospheric furnaces. The process cycle can also be longer due to the time required to pump down the chamber.
Not Required for All Applications
For many general-purpose applications where a slight amount of surface scale is acceptable or can be easily removed, the precision and cost of vacuum treatment may be unnecessary. A conventional furnace is often more cost-effective for lower-spec components.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right heat treatment method depends entirely on the required final properties of the component.
- If your primary focus is a pristine, bright finish with zero oxidation or decarburization: Vacuum treatment is the definitive choice for sensitive alloys and high-performance components.
- If your primary focus is maximum material integrity through degassing or creating a superior brazed joint: The controlled vacuum environment provides a level of purity and reliability that is difficult to achieve otherwise.
- If your primary focus is simple, cost-effective hardening where slight surface changes are acceptable: A traditional atmospheric furnace is often the more practical and economical solution.
By precisely controlling the treatment environment, vacuum heat treatment gives you unparalleled control over the final performance and quality of your material.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Vacuum Heat Treatment Benefit |
|---|---|
| Surface Quality | Eliminates oxidation and decarburization for a bright, clean finish. |
| Internal Integrity | Removes trapped gases (degassing) to prevent embrittlement. |
| Process Purity | Enables high-integrity processes like flux-free vacuum brazing. |
| Ideal For | High-performance metals and alloys requiring superior properties. |
Need to achieve a flawless finish and superior material properties?
For high-performance components in aerospace, medical, or tooling applications, the precision of vacuum heat treatment is critical. KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables, providing the reliable vacuum furnaces and expertise your laboratory needs to ensure material integrity and repeatable results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our vacuum solutions can enhance your heat treatment processes and meet your specific material goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What materials are used in a vacuum furnace? Selecting the Right Hot Zone for Your Process
- How to vacuum out a furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe DIY Maintenance
- Is heat Cannot travel in a vacuum True or false? Discover How Heat Crosses the Void of Space
- What does a vacuum furnace do? Achieve High-Purity Heat Treatment for Superior Components
- What is a vacuum furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Contamination-Free Thermal Processing



















