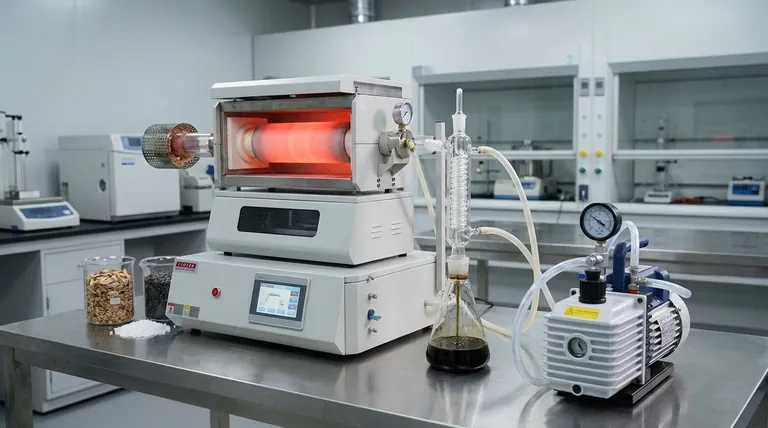
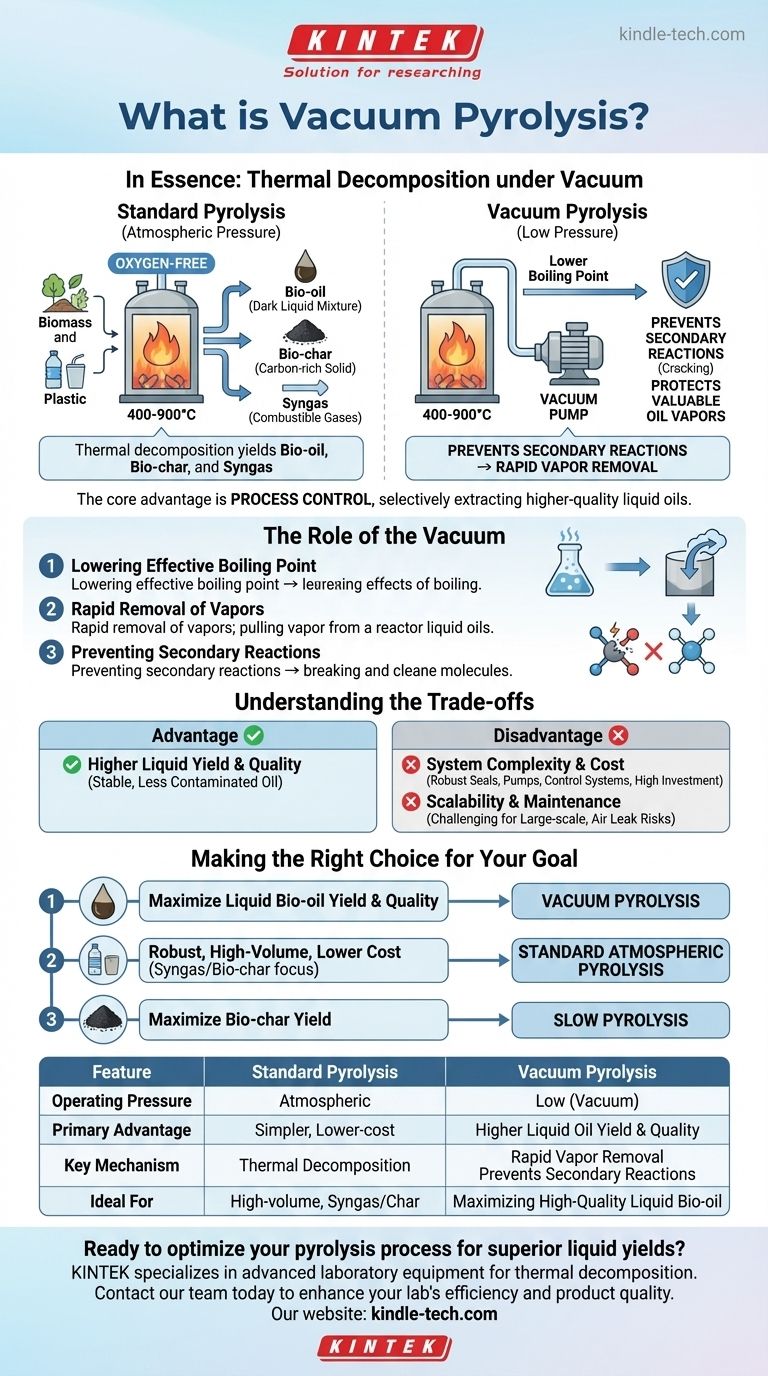
In essence, vacuum pyrolysis is a thermal decomposition process where materials like biomass or plastic are heated to high temperatures in a low-pressure, or vacuum, environment. Unlike standard pyrolysis, which occurs at atmospheric pressure, the vacuum significantly lowers the boiling point of the decomposition products. This allows valuable liquids and oils to be vaporized and removed from the reactor more quickly and at lower temperatures, preventing them from breaking down into less desirable gases and char.
The core advantage of vacuum pyrolysis is not just decomposition, but process control. By operating under reduced pressure, you can selectively extract higher-quality liquid oils and prevent the secondary reactions that degrade their value in standard pyrolysis systems.

How Standard Pyrolysis Works
The Core Principle: Thermal Decomposition
Pyrolysis is the process of heating an organic material, such as biomass, plastics, or old tires, to high temperatures (typically 400-900°C) in an environment completely devoid of oxygen.
Without oxygen, the material doesn't combust (burn). Instead, the intense heat breaks down the complex chemical bonds within the material, decomposing it into simpler, more valuable substances.
The Three Key Products
This decomposition typically yields three primary products:
- Bio-oil (or Pyrolysis Oil): A dark, liquid mixture of organic compounds that can be refined into transportation fuels or specialty chemicals.
- Bio-char: A stable, carbon-rich solid similar to charcoal. It can be used as a soil amendment, for filtration, or as a solid fuel.
- Syngas: A mixture of combustible gases (like hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and methane) that can be used to generate heat or power for the pyrolysis process itself.
The Role of the Vacuum in Pyrolysis
Lowering the Effective Boiling Point
The defining feature of vacuum pyrolysis is the introduction of a vacuum pump to continuously reduce the pressure inside the reactor.
Think of how water boils at a lower temperature on a high mountain. A vacuum has the same effect on the compounds produced during pyrolysis. They turn into vapor at a lower temperature than they would at normal atmospheric pressure.
Rapid Removal of Vapors
This low-pressure environment creates a powerful driving force that immediately pulls the newly formed vapors out of the hot reaction zone.
This rapid extraction is the key to the entire process. The vapors spend significantly less time exposed to the high temperatures inside the reactor.
Preventing Secondary Reactions
In standard pyrolysis, valuable oil vapors can linger in the hot reactor and "crack," or break down further, into less valuable permanent gases and more solid char.
By removing the vapors almost instantly, vacuum pyrolysis minimizes these secondary reactions. This preserves the integrity of the larger, more valuable liquid oil molecules.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Advantage: Higher Liquid Yield and Quality
The primary benefit of using a vacuum is a significant increase in the yield and quality of the liquid bio-oil. Because secondary cracking is prevented, the resulting oil is often more stable and less contaminated.
Disadvantage: System Complexity and Cost
Operating under a vacuum is technically demanding. It requires robust seals, powerful vacuum pumps, and more complex control systems to maintain the low-pressure environment. This increases both the initial capital investment and ongoing operational costs.
Disadvantage: Scalability and Maintenance
Maintaining a perfect vacuum in a large-scale industrial reactor can be challenging. Air leaks can compromise the entire process, requiring diligent maintenance and monitoring. This complexity can make scaling the technology more difficult than standard atmospheric systems.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use vacuum pyrolysis hinges entirely on your desired end-product.
- If your primary focus is maximizing the yield and quality of liquid bio-oil: Vacuum pyrolysis is the superior technical approach, as it protects valuable oil vapors from thermal degradation.
- If your primary focus is robust, high-volume processing at a lower cost: Standard atmospheric pyrolysis is often the more practical and economically viable choice, especially if syngas or bio-char are also desired products.
- If your primary focus is producing a high yield of bio-char: A different method, such as slow pyrolysis (often at atmospheric pressure), is typically preferred over the rapid vapor removal of a vacuum system.
Ultimately, choosing the right thermal decomposition method requires balancing the desired product slate against the inherent costs and complexities of the system.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Standard Pyrolysis | Vacuum Pyrolysis |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Pressure | Atmospheric | Low (Vacuum) |
| Primary Advantage | Simpler, lower-cost system | Higher liquid oil yield & quality |
| Key Mechanism | Thermal decomposition without oxygen | Rapid vapor removal prevents secondary reactions |
| Ideal For | High-volume processing, syngas/char focus | Maximizing high-quality liquid bio-oil production |
Ready to optimize your pyrolysis process for superior liquid yields?
KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment for thermal decomposition research and development. Whether you are developing a new bio-oil production method or scaling up your process, our experts can help you select the right pyrolysis system for your specific goals.
Contact our team today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your lab's efficiency and product quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-temperature electric furnace required for melting radioactive waste glass matrices? Expert Solutions
- What heat transfer happens in a vacuum? Master Thermal Radiation for Your Lab Equipment
- What is the main purpose of process annealing? Restore Workability and Eliminate Brittleness in Metals
- How do you maintain vacuum pressure? Master the balance between gas removal and gas load for stable performance.
- How do you control the temperature of a resistance furnace? Achieve Precise Thermal Control for Your Lab
- What is the role of a vacuum drying oven in Alloy 690TT preparation? Secure Flawless Data Baselines
- What is the function of a high-temperature furnace during burnout? Master Aluminum Foam Production with Precision
- What is the difference between liquid and gas carburizing? Precision, Safety & Environmental Impact



















