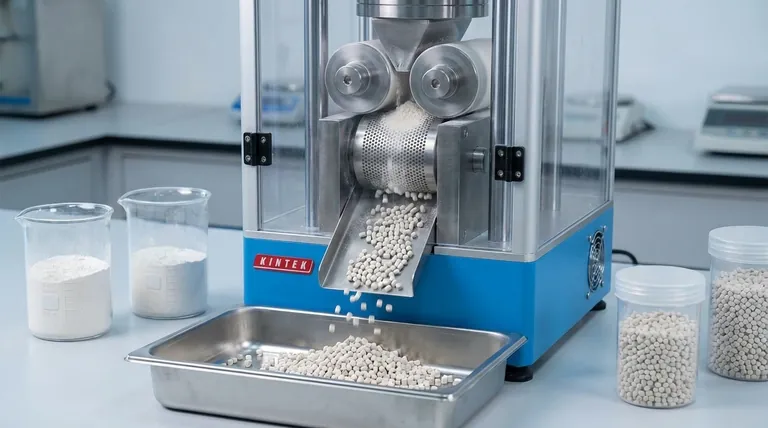
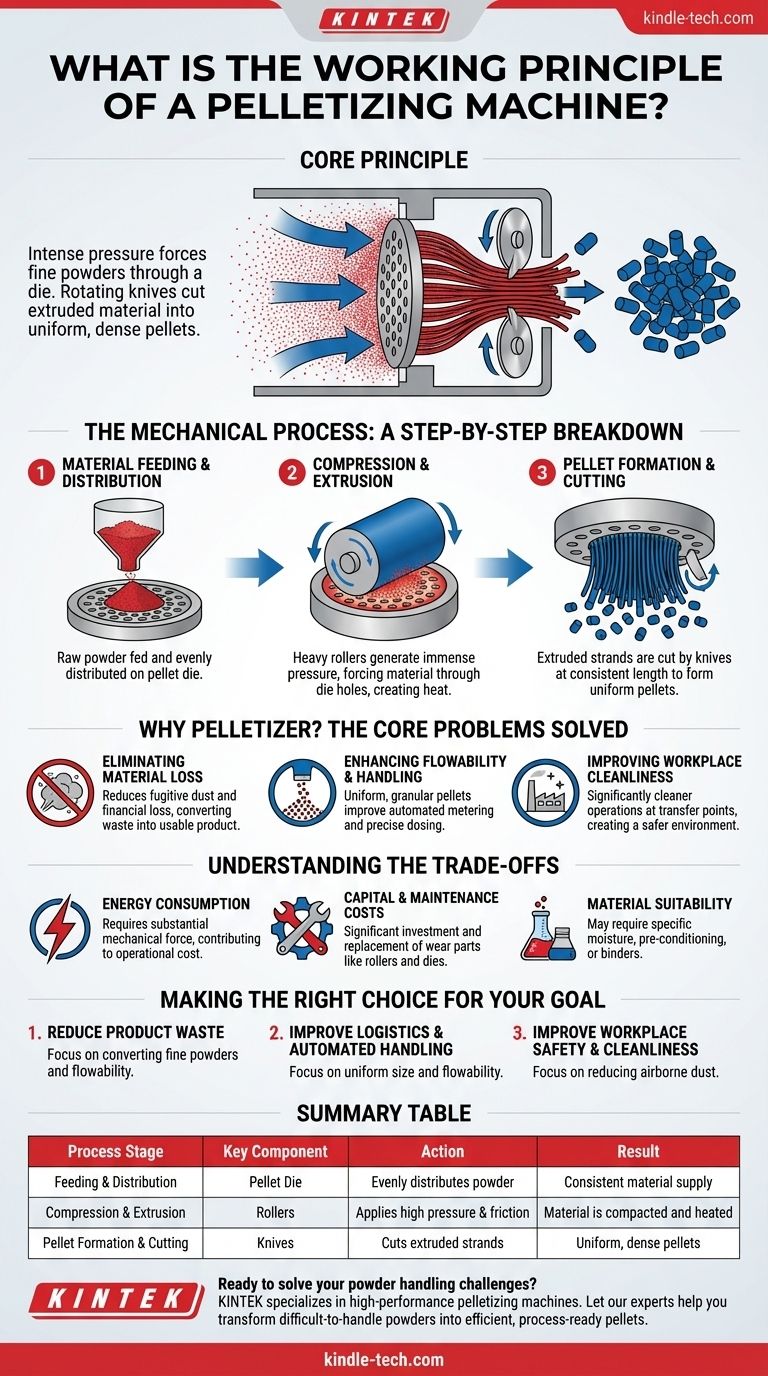
At its core, a pelletizing machine works by using intense mechanical pressure to force fine, powdery materials through the holes of a perforated metal plate, known as a die. As the material is extruded through these holes, rotating knives cut it into small, dense, uniform granules called pellets.
The fundamental purpose of pelletizing is not just to change a material's shape, but to transform its physical properties. It converts dusty, difficult-to-handle powders into dense, flowable pellets, drastically reducing waste and improving operational efficiency.

The Mechanical Process: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
To understand how this transformation occurs, it's best to look at the process as a sequence of distinct mechanical actions inside the pelletizing chamber.
Material Feeding and Distribution
First, the raw feedstock—typically a fine powder or ground material—is fed into the pelletizing chamber. Inside, it is evenly distributed across the surface of the pellet die, ensuring a consistent supply for the compression stage.
Compression and Extrusion
This is the heart of the process. A set of heavy rollers rotates over the surface of the die. This action generates immense pressure, forcing the feedstock into and through the small holes of the die. The combination of pressure and friction heats the material, which can help bind the particles together.
Pellet Formation and Cutting
As the compacted material is pushed out the other side of the die holes, it emerges as long, dense strands. A set of precisely adjusted knives then cuts these strands at a consistent length, resulting in the final, uniform pellets.
Why Pelletize? The Core Problems Solved
Understanding the mechanics is only half the story. The true value of pelletizing lies in the operational problems it solves, which is why it is used across industries from minerals to specialty chemicals.
Eliminating Material Loss
Fine powders are prone to becoming airborne dust. This fugitive material represents a direct financial loss and can create significant housekeeping challenges. By converting powder into dense pellets, the process dramatically reduces dust, ensuring more of your raw material becomes a usable final product.
Enhancing Flowability and Handling
Powders are notoriously difficult to handle; they can clump, bridge in hoppers, and are challenging to measure accurately. Pellets, with their uniform, granular shape, are inherently more flowable. This allows for precise, automated metering and dosing, which is critical for many industrial processes.
Improving Workplace Cleanliness
The reduction in fugitive dust has a direct impact on the facility's environment. Operations that use pellets instead of powders are significantly cleaner, especially at material drop and transfer points, leading to a more efficient and pleasant workspace.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly beneficial, pelletizing is a significant industrial process with inherent considerations. Objectivity requires acknowledging them.
Energy Consumption
The mechanical force required to compress and extrude material is substantial. Pelletizing machinery can be a significant consumer of energy, which factors into the overall operational cost.
Capital and Maintenance Costs
These are robust, heavy-duty machines that represent a significant capital investment. Key components like the rollers and dies are wear parts that require regular maintenance and eventual replacement, adding to the ongoing cost of operation.
Material Suitability
Not all materials can be pelletized easily in their raw state. Some may require specific moisture content, pre-conditioning, or the addition of a binding agent to form a stable pellet.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding to integrate pelletizing depends entirely on the problem you need to solve.
- If your primary focus is reducing product waste: Pelletizing is highly effective at converting fine powders that would otherwise be lost as dust into a valuable, usable product.
- If your primary focus is improving logistics and automated handling: The uniform size and high flowability of pellets are ideal for precise dosing, metering, and conveying systems.
- If your primary focus is workplace safety and cleanliness: The significant reduction in airborne dust makes pelletizing a key strategy for creating a cleaner, safer operational environment.
Ultimately, pelletizing is a process that transforms a raw material liability into a process-ready asset.
Summary Table:
| Process Stage | Key Component | Action | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| Feeding & Distribution | Pellet Die | Evenly distributes powder | Consistent material supply |
| Compression & Extrusion | Rollers | Applies high pressure & friction | Material is compacted and heated |
| Pellet Formation & Cutting | Knives | Cuts extruded strands | Uniform, dense pellets |
Ready to solve your powder handling challenges? KINTEK specializes in high-performance pelletizing machines and lab equipment designed to reduce waste, improve flowability, and create a cleaner workspace. Let our experts help you transform difficult-to-handle powders into efficient, process-ready pellets. Contact us today to discuss your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press Machine for Lab Use
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
- Ring Press Mold for Lab Applications
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a laboratory hydraulic press in sulfide solid-state electrolyte pellet formation? Maximize Density
- Why is a hydraulic pellet press used for FTIR? Transform Nanofillers into Clear Data
- How do laboratory hydraulic presses facilitate biomass pelletization? Optimize Biofuel Density and Prevent Slagging
- Why is a laboratory hydraulic press used for MOF-CGC pellets? Maximize Density and Encapsulation Quality
- Why is a laboratory hydraulic press essential for Ca3Co4O9 pelletizing? Optimize Pre-Sintering Mass Transport



















