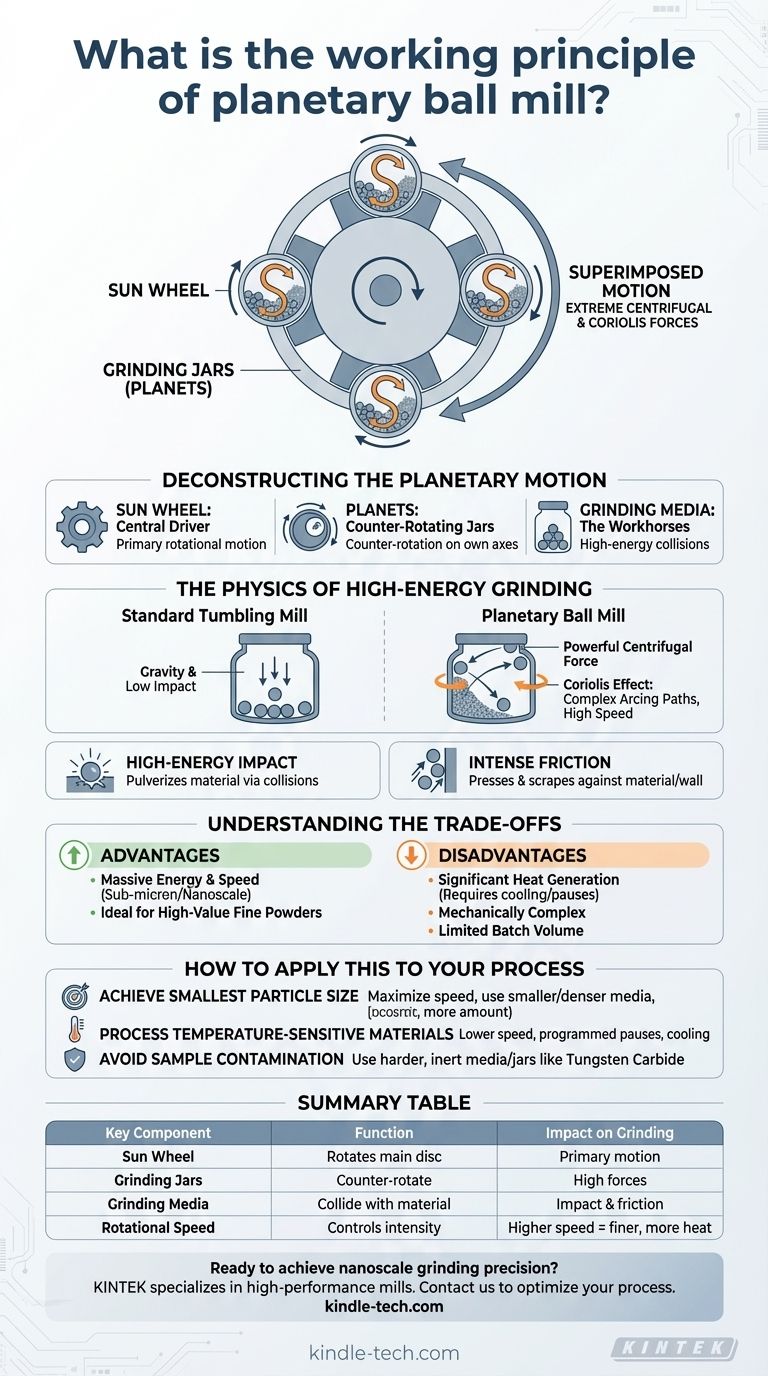
At its core, a planetary ball mill works by combining two powerful rotational movements to generate immense grinding energy. The machine consists of grinding jars, called "planets," which are mounted on a larger rotating disc, the "sun wheel." As the sun wheel turns in one direction, the grinding jars rotate on their own axes in the opposite direction, creating a unique force profile that dramatically accelerates the grinding media within.
The key to the planetary ball mill's effectiveness is its superimposed motion. This counter-rotation generates extreme centrifugal and Coriolis forces, which pulverize material far more rapidly and finely than a simple, single-axis tumbling mill ever could.
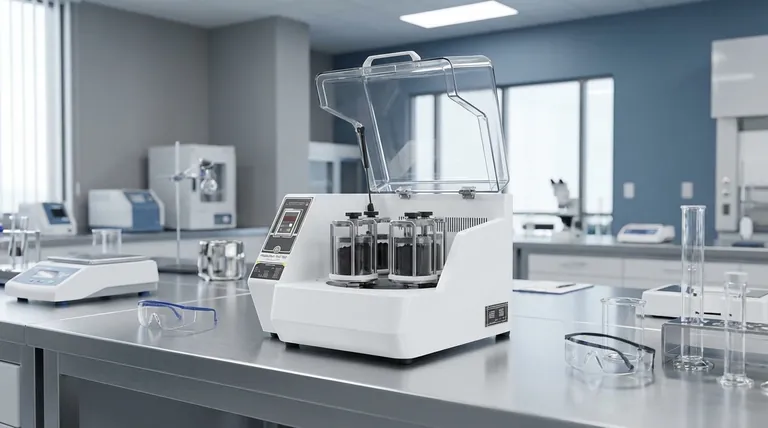

Deconstructing the Planetary Motion
To understand the working principle, we must first visualize its core components and their synchronized movement.
The Sun Wheel: The Central Driver
The sun wheel is the large, primary turntable on which the entire system is built. Its rotation provides the first layer of motion, carrying the grinding jars around a central axis.
The Planets: Counter-Rotating Grinding Jars
Mounted eccentrically on the sun wheel are one or more grinding jars. As the sun wheel rotates, a gearing system forces these jars to rotate on their own axes in the opposite direction. This counter-rotation is the defining feature of the "planetary" design.
The Grinding Media: The Workhorses
Inside each jar are the grinding media—typically hard ceramic or steel balls—along with the sample material to be ground. These balls are the instruments that perform the grinding through high-energy collisions.
The Physics of High-Energy Grinding
The planetary design is not arbitrary; it is engineered to exploit specific physical forces to maximize grinding efficiency. This is what separates it from simpler grinding methods.
Beyond Simple Tumbling
In a standard tumbling ball mill, the rotation simply lifts the balls and allows them to fall with gravity, creating impacts. A planetary mill's rotation creates a powerful centrifugal force that pins the balls and material to the far wall of the jar with many times the force of gravity.
The Secret Ingredient: The Coriolis Effect
Because the balls are moving within a rotating jar that is itself revolving on the sun wheel, they are subjected to a powerful Coriolis effect. This force causes the balls to travel in complex, arcing paths, scraping along the jar wall and then detaching and flying across the jar's interior at high speed.
Combining Impact and Friction
This process results in two distinct grinding mechanisms happening simultaneously. High-energy impact occurs when balls fly across the jar and smash into the material. Intense friction occurs as the balls are pressed and scraped against the material and the jar wall by the immense forces.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the planetary ball mill is not the universal solution for every grinding task. Understanding its advantages and disadvantages is crucial for proper application.
Energy and Speed: The Planetary Advantage
The primary advantage is the massive increase in grinding energy and speed. Planetary mills can achieve particle sizes down to the sub-micron or even nanometer scale, which is often impossible with standard mills.
Heat Generation: A Critical Consideration
The intense friction and impact energy inevitably generate significant heat. This can be a major issue for temperature-sensitive materials, potentially leading to sample degradation or unwanted phase changes. Many processes require cooling or programmed grinding pauses.
Complexity and Throughput
Planetary mills are mechanically more complex than standard tumbling mills. While they are ideal for laboratory-scale research and producing high-value fine powders, their jar size limits batch volume. For large-scale industrial grinding of less-demanding materials, a simpler, high-capacity tumbling mill is often more economical.
How to Apply This to Your Grinding Process
Your choice of parameters directly controls the forces inside the jar. By understanding the principles, you can tailor the process to your specific material and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is achieving the smallest possible particle size: Maximize the rotational speed and use smaller, denser grinding media to increase the frequency and energy of collisions.
- If your primary focus is processing temperature-sensitive materials: Use lower speeds, introduce programmed pauses to allow for cooling, or use specialized water-cooled grinding jars.
- If your primary focus is avoiding sample contamination: Ensure your grinding jars and media are made of a material harder and more inert than your sample (e.g., tungsten carbide, silicon nitride, or zirconia).
By mastering these variables, you can harness the complex forces of a planetary ball mill to achieve precise and repeatable results.
Summary Table:
| Key Component | Function | Impact on Grinding |
|---|---|---|
| Sun Wheel | Rotates the main disc, carrying grinding jars | Provides the primary rotational motion |
| Grinding Jars (Planets) | Counter-rotate on their own axes | Creates high centrifugal and Coriolis forces |
| Grinding Media | Balls inside jars that collide with material | Performs pulverization through impact and friction |
| Rotational Speed | Controls the intensity of motion | Higher speed = finer particles, but more heat |
Ready to achieve nanoscale grinding precision in your lab? KINTEK specializes in high-performance planetary ball mills and lab equipment tailored for material science and research. Our experts can help you select the right mill and parameters to optimize your process for maximum efficiency and minimal contamination. Contact us today to discuss your specific grinding needs and discover the KINTEK advantage!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type Milling Machine
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- Laboratory Horizontal Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a planetary ball mill in Li2S cathode prep? Master Nano-Scale Material Synthesis
- What is the primary function of a planetary ball mill in preparing LLZO? Achieve High-Purity Solid-State Electrolytes
- What critical role does high-energy ball milling equipment play in the fabrication of Al6061/B4C composites?
- What role does a planetary ball mill play in the synthesis of LZTC solid-state electrolytes? Enhancing Ionic Conductivity
- What is the difference between a mixer mill and a planetary mill? Power vs. Versatility for Your Lab
- What role does a centrifugal ball mill play in the activation of magnesium-based alloy waste for hydrogen production?
- How does speed of ball affect size reduction in working of ball mill? Optimize for Maximum Efficiency
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of ball milling method? A Guide to the Trade-Offs



















