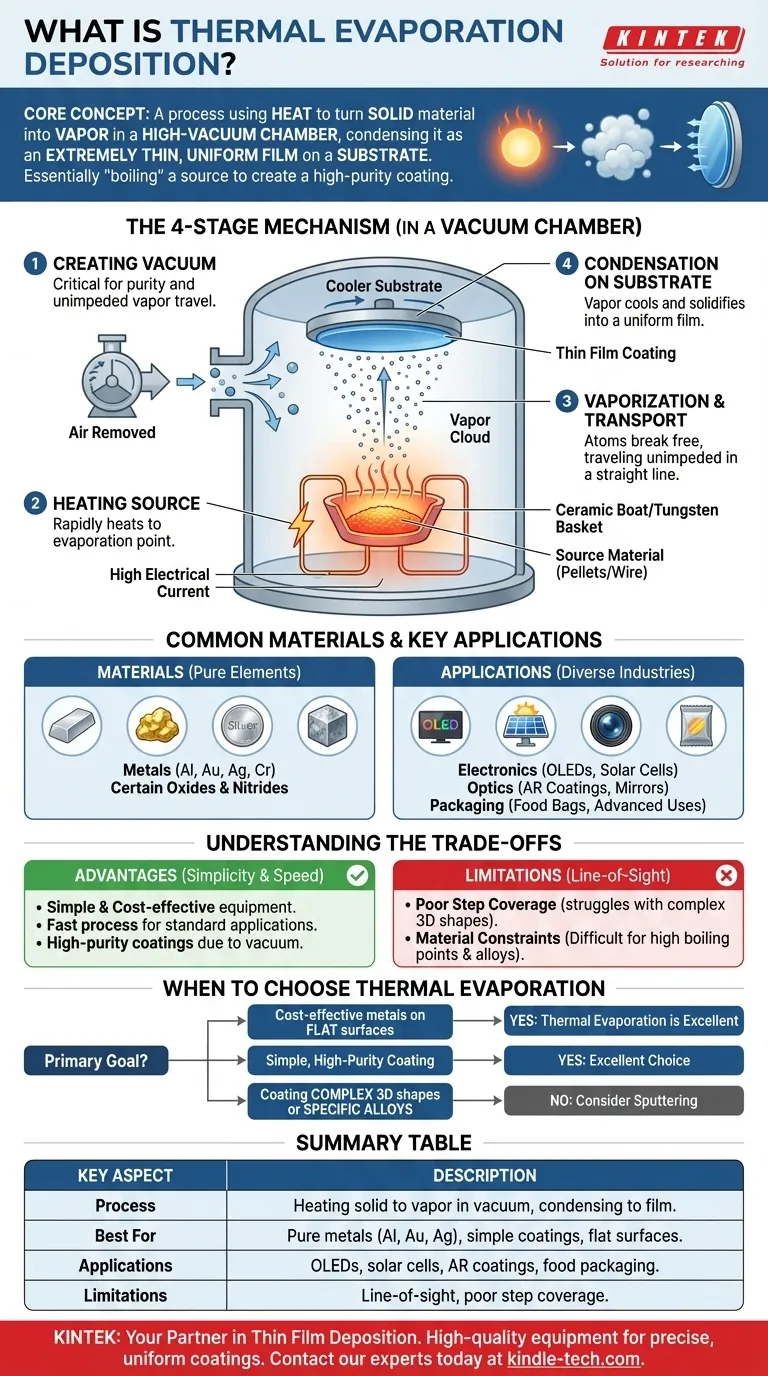
At its core, thermal evaporation deposition is a process that uses heat to turn a solid material into a vapor within a high-vacuum chamber. This vapor then travels and condenses onto a cooler target surface, known as a substrate, forming an extremely thin, uniform film. It is one of the most fundamental methods of physical vapor deposition (PVD).
The central concept is remarkably straightforward: you are essentially "boiling" a source material in a vacuum and allowing its vapor to solidify as a high-purity coating on a target object. This simplicity makes it a versatile and widely-used technique for creating thin films.
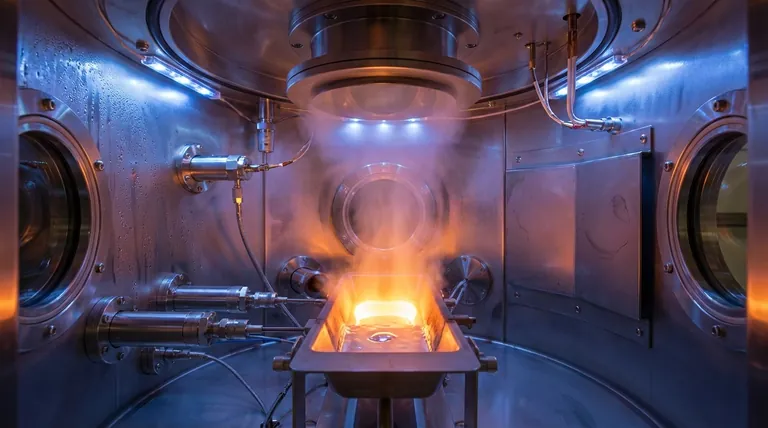

The Core Mechanism: From Solid to Thin Film
Understanding the thermal evaporation process involves breaking it down into four distinct stages that occur within a controlled vacuum chamber.
Creating the Vacuum Environment
The entire process must take place in a high-vacuum environment. This is critical because it removes air and other gas molecules that could otherwise react with the hot vapor or block its path to the substrate.
This ensures the deposited film is pure and that the evaporated particles travel in a straight line directly to their target.
Heating the Source Material
The source material, often in the form of pellets or wire, is placed in a heat-resistant container, typically a ceramic "boat" or a tungsten "basket." A high electrical current is passed through this container, causing it to heat up rapidly.
This intense heat is transferred to the source material, raising its temperature until it reaches its melting and subsequent evaporation point.
Vaporization and Transport
As the source material heats up, its atoms gain enough thermal energy to break free from the surface and enter a gaseous state. This cloud of vapor expands throughout the vacuum chamber.
Because there are very few gas molecules to collide with, the vaporized atoms travel unimpeded in a direct line-of-sight path from the source to the substrate.
Condensation on the Substrate
The substrate (the object to be coated) is positioned above the source. Being much cooler than the vapor, it acts as a condensation surface.
When the vapor atoms strike the substrate, they rapidly lose their energy, cool down, and solidify, growing into a thin, uniform film. The substrate is often rotated to ensure the coating is applied evenly across its entire surface.
Common Materials and Key Applications
The versatility of thermal evaporation allows for a wide range of materials to be deposited, serving countless industries.
Materials Suitable for Deposition
This technique is most effective for depositing pure atomic elements, particularly metals with relatively low boiling points like aluminum, gold, silver, and chromium.
It can also be used for certain non-metals and molecular compounds, including some oxides and nitrides, making it useful for a variety of functional coatings.
Electronics and Optics
In electronics, thermal evaporation is essential for creating the thin, electrically conductive metallic layers required for OLED displays, solar cells, and thin-film transistors.
For optics, it's used to apply anti-reflective coatings on lenses, create reflective layers for mirrors, and add UV-protection films.
Packaging and Advanced Uses
The shiny metallic layer inside many food packages (like chip bags) is often an ultra-thin film of aluminum deposited onto a polymer using this method.
More advanced applications include reflective coatings for NASA spacesuits, heat-shielding layers on firefighter uniforms, and anti-static enclosures in aircraft.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, thermal evaporation is not the right choice for every application. Its strengths in simplicity and cost-effectiveness are balanced by specific limitations.
The Advantage of Simplicity and Speed
Compared to other deposition methods, thermal evaporation is relatively simple, fast, and cost-effective. The equipment is less complex, making it a go-to method for many standard thin-film applications.
Limitation: Line-of-Sight Deposition
Because the vapor travels in a straight line, the process struggles to evenly coat complex, three-dimensional shapes with intricate features or undercuts. This is known as poor step coverage.
Limitation: Material Constraints
The technique is not ideal for materials with extremely high boiling points, as they are difficult to vaporize with simple resistive heating. It is also challenging to deposit precise alloys, as the different elements in the source material may evaporate at different rates.
When to Choose Thermal Evaporation
Your decision to use thermal evaporation should be based on your material, substrate shape, and final goal.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective metal layers for electronics or optics: Thermal evaporation is an excellent choice for depositing pure metals like aluminum or gold onto relatively flat surfaces.
- If your primary focus is a simple, high-purity coating: This method provides excellent purity because the vacuum environment minimizes contamination during deposition.
- If your primary focus is coating complex 3D shapes or specific alloys: You should consider alternative methods like sputtering, which offers better step coverage and more precise control over alloy composition.
Ultimately, thermal evaporation remains a foundational and indispensable tool in modern materials science and engineering for its ability to efficiently create high-quality thin films.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Heating solid materials in vacuum to create vapor that condenses into thin films |
| Best For | Pure metals (Al, Au, Ag), simple coatings, flat surfaces |
| Applications | OLED displays, solar cells, anti-reflective coatings, food packaging |
| Limitations | Line-of-sight deposition, poor step coverage for complex shapes |
Need reliable thermal evaporation equipment for your lab? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for thin film deposition. Our thermal evaporation systems deliver precise, uniform coatings for your research and production needs. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can enhance your deposition processes with equipment tailored to your specific requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Conductive Boron Nitride Crucible BN Crucible
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the evaporation technique for nanoparticles? A Guide to High-Purity Synthesis
- What does an e-beam do? A Versatile Tool for Welding, Sterilization, and Microfabrication
- What materials are used in evaporation techniques? A Guide to Thin-Film Deposition Materials
- What precautions should be taken during evaporation process? Ensure High-Quality Film Deposition
- What is the thermal evaporation method? A Guide to Simple, Cost-Effective Thin-Film Deposition
- What is the purpose of an evaporator? The Key Component That Creates Cooling
- How is a thin film prepared by thermal evaporation? Master the Vacuum Deposition Process
- What is the principle of thermal evaporation method? A Simple Guide to Thin Film Deposition



















