At its core, thermal evaporation is a process for creating exceptionally thin films of material. It works by heating a source material inside a vacuum chamber until it vaporizes. These vaporized atoms then travel through the vacuum and condense onto a cooler surface, known as a substrate, forming a uniform, thin coating.
Thermal evaporation is a foundational thin-film deposition technique that leverages a simple physical principle: heating a material in a high vacuum causes it to turn into a vapor, which then coats a target object. The process's effectiveness is entirely dependent on the vacuum, which ensures the vaporized atoms have a clear, unimpeded path to the substrate.
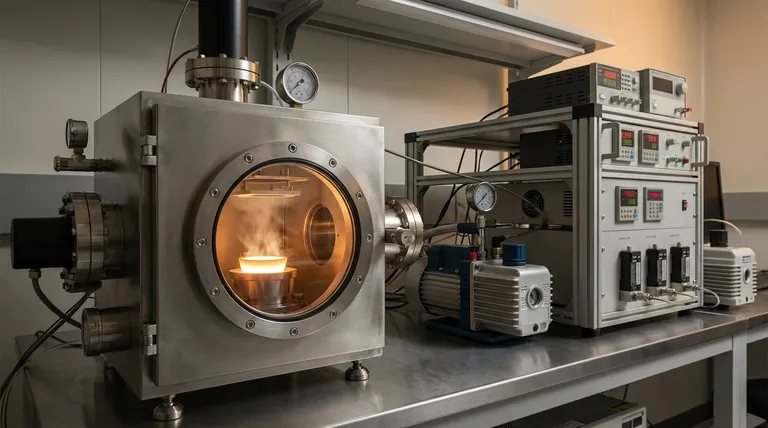

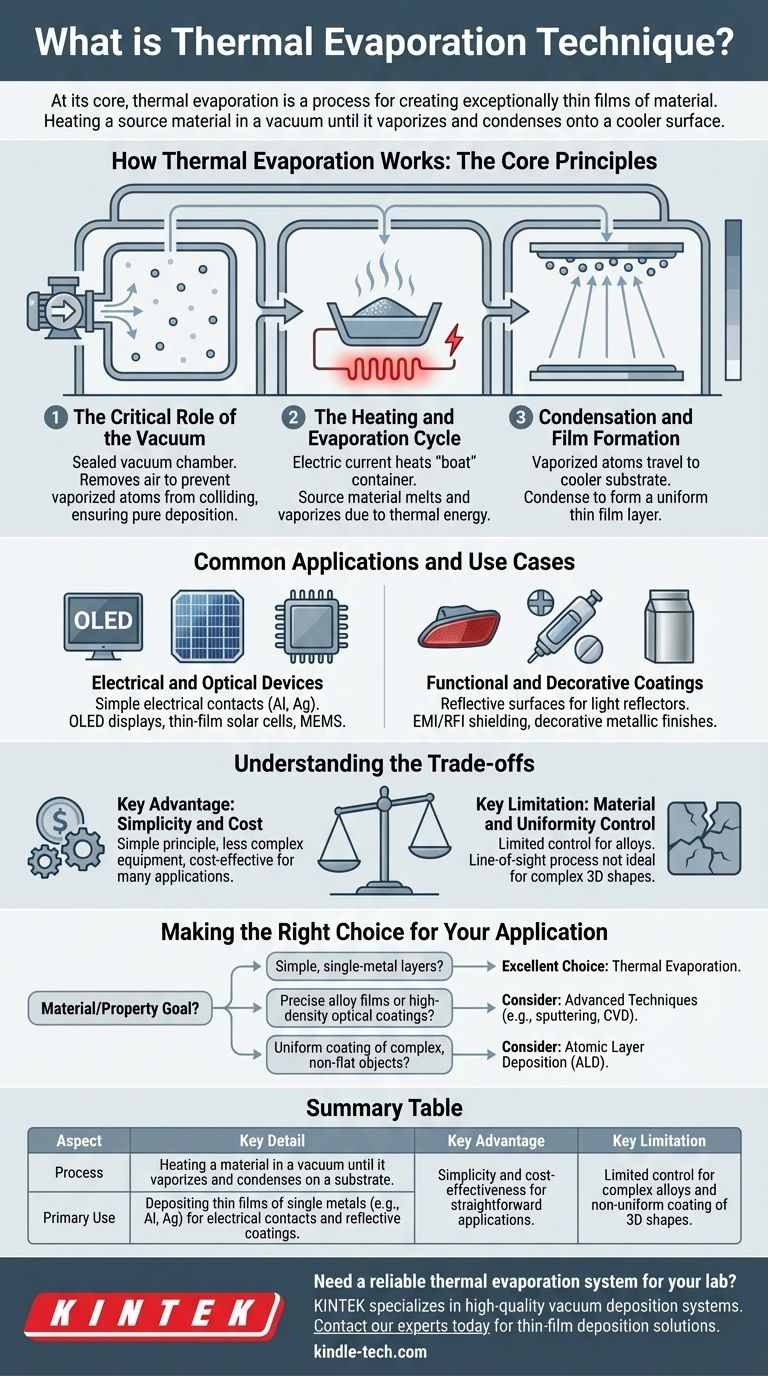
How Thermal Evaporation Works: The Core Principles
Thermal evaporation, also known as resistive evaporation, is a straightforward line-of-sight deposition process. Its success relies on controlling two key environmental factors: heat and pressure.
The Critical Role of the Vacuum
The entire process takes place within a sealed vacuum chamber. A high-power vacuum pump removes air and other gas molecules.
This high vacuum is essential because it prevents the vaporized source atoms from colliding with other particles on their way to the substrate, ensuring a pure and direct deposition.
The Heating and Evaporation Cycle
The material to be deposited, known as the source material, is placed in a container often called a "boat" or "crucible." This boat is typically made from a metal with a very high melting point.
An electric current is passed through this boat. Due to electrical resistance, the boat heats up rapidly, transferring this thermal energy to the source material.
Condensation and Film Formation
As the source material reaches its evaporation point, it transforms into a vapor. These vaporized atoms travel in a straight line from the source to the cooler substrate, which is typically positioned above it.
Upon contact with the substrate, the atoms lose their energy, condense back into a solid state, and build up layer by layer to form a thin film.
Common Applications and Use Cases
The simplicity and versatility of thermal evaporation make it a widely used technique across numerous industries for both functional and decorative purposes.
Electrical and Optical Devices
This method is a go-to for creating simple electrical contacts by depositing single metals like aluminum or silver.
It is also a key manufacturing step for more complex devices like OLED displays, thin-film solar cells, and microelectromechanical systems (MEMS).
Functional and Decorative Coatings
Thermal evaporation is used to create highly reflective surfaces for automotive light reflectors and medical or aerospace components.
It is also used for applying EMI/RFI shielding to electronic housings and creating the metallic finish on decorative items like cosmetic packaging.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, thermal evaporation is not the solution for every thin-film challenge. Understanding its inherent limitations is key to using it effectively.
Key Advantage: Simplicity and Cost
The underlying principle is simple, which means the equipment is often less complex and more cost-effective than other deposition technologies like sputtering or chemical vapor deposition. This makes it highly accessible for research and many industrial applications.
Key Limitation: Material and Uniformity Control
The process offers limited control for depositing complex materials like alloys, as different elements may evaporate at different rates. Furthermore, because it is a line-of-sight technique, it is not ideal for uniformly coating complex, three-dimensional shapes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct deposition technique depends entirely on the material you are using and the properties you need in the final film.
- If your primary focus is depositing simple, single-metal layers for contacts or reflectors: Thermal evaporation is an excellent, reliable, and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is creating precise alloy films or high-density optical coatings: You may need to evaluate more advanced techniques that offer greater control over stoichiometry and film structure.
- If your primary focus is coating a complex, non-flat object uniformly: The line-of-sight nature of thermal evaporation is a significant drawback, and a method like atomic layer deposition (ALD) may be required.
By understanding its fundamental principles and trade-offs, you can confidently determine when thermal evaporation is the optimal tool for your engineering or research goals.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Process | Heating a material in a vacuum until it vaporizes and condenses on a substrate. |
| Primary Use | Depositing thin films of single metals (e.g., Al, Ag) for electrical contacts and reflective coatings. |
| Key Advantage | Simplicity and cost-effectiveness for straightforward applications. |
| Key Limitation | Limited control for complex alloys and non-uniform coating of 3D shapes. |
Need a reliable thermal evaporation system for your lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including vacuum deposition systems. Whether you're creating electrical contacts, optical coatings, or conducting materials research, our thermal evaporation tools offer the simplicity and cost-effectiveness you need.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory's thin-film deposition requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- What are the process capabilities of ICPCVD systems? Achieve Low-Damage Film Deposition at Ultra-Low Temperatures
- How do PECVD systems improve DLC coatings on implants? Superior Durability and Biocompatibility Explained
- What is the difference between PECVD and APCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application
- Why does a PECVD vacuum system require both a rotary vane and turbo pump? Ensure High-Purity Coatings
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application



















