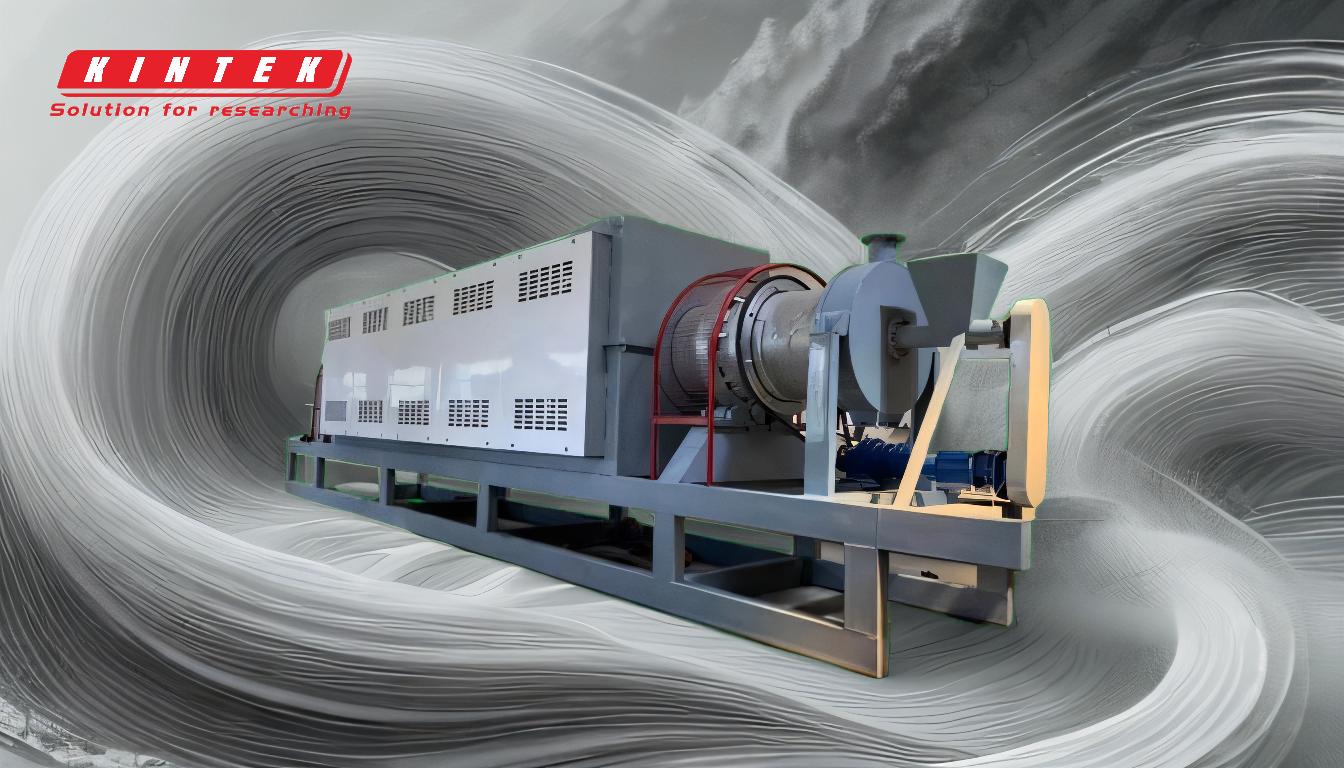
Tire pyrolysis oil is a synthetic fuel derived from the thermal decomposition of waste tires in the absence of oxygen, a process known as pyrolysis. This oil is a valuable by-product of the tire pyrolysis process, which also yields carbon black, steel wire, and non-condensable gases. Tire pyrolysis oil is characterized by its low viscosity and high calorific value, making it suitable for direct use as fuel in industrial applications such as cement, glass, ceramic, power, and steel factories. It can also be further processed into non-standard diesel or fuel oil. The production process involves heating waste tires in a reactor at high temperatures (around 500°C) for several hours, followed by condensation and separation of the resulting gases and liquids. The oil has diverse applications, including use as a heating fuel, for power generation, and as an additive in various industrial products.
Key Points Explained:
-
Definition and Production Process:
- Tire pyrolysis oil is a by-product of the pyrolysis process, where waste tires are thermally decomposed in the absence of oxygen.
- The process involves heating whole or shredded tires in a reactor at temperatures around 500°C (900°F) for 3-5 hours.
- During pyrolysis, the rubber's main chain breaks down into smaller molecules, which then polymerize into various hydrocarbons.
- The resulting gases are condensed to separate the pyrolysis oil from non-condensable gases, which are cleaned and stored for further use.
-
Characteristics of Tire Pyrolysis Oil:
- The oil has low viscosity and a high calorific value, making it an efficient fuel source.
- It contains a high oxygen content, distinguishing it from conventional petroleum products.
- The composition of the oil can vary depending on the pyrolysis method, temperature, and other conditions.
-
Applications of Tire Pyrolysis Oil:
- Industrial Fuel: It is used as a fuel in cement, glass, ceramic, power, and steel factories due to its high energy content.
- Power Generation: The oil can be used to generate electricity using generators.
- Fuel Reprocessing: It can be distilled into non-standard diesel or fuel oil for broader industrial use.
- Heating: It serves as a direct fuel source for boilers and furnaces.
- Additives: The oil can be used as an additive in the production of plastics and other industrial products.
-
End Products of Tire Pyrolysis:
- Fuel Oil: The primary product, used for various industrial and energy applications.
- Carbon Black: A solid residue used in the production of tires, inks, and other rubber products.
- Steel Wire: Recovered from the tires and recycled for use in manufacturing.
- Non-Condensable Gas: Cleaned and used as a fuel source within the pyrolysis plant or for other energy needs.
-
Environmental and Economic Benefits:
- Waste Reduction: Tire pyrolysis helps in recycling waste tires, reducing landfill use and environmental pollution.
- Energy Recovery: The process converts waste into valuable energy resources, contributing to energy sustainability.
- Cost-Effective: The production of tire pyrolysis oil and other by-products offers a cost-effective solution for waste management and energy generation.
-
Challenges and Considerations:
- Quality Variability: The composition of tire pyrolysis oil can vary, requiring careful processing to ensure consistent quality.
- Emissions: The pyrolysis process must be carefully controlled to minimize harmful emissions, particularly sulfur compounds.
- Market Demand: The economic viability of tire pyrolysis depends on the demand for its by-products, particularly in industrial sectors.
In summary, tire pyrolysis oil is a versatile and valuable product derived from the pyrolysis of waste tires. Its production not only addresses the issue of tire waste but also provides a sustainable source of fuel and other industrial materials. The process and its by-products offer significant environmental and economic benefits, making tire pyrolysis an important technology in the context of waste management and energy recovery.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Synthetic fuel from thermal decomposition of waste tires in the absence of oxygen. |
| Production Process | Heating tires at ~500°C for 3-5 hours, followed by condensation and separation. |
| Characteristics | Low viscosity, high calorific value, and high oxygen content. |
| Applications | Industrial fuel, power generation, heating, additives, and fuel reprocessing. |
| End Products | Fuel oil, carbon black, steel wire, and non-condensable gas. |
| Environmental Benefits | Reduces waste, recovers energy, and offers cost-effective waste management. |
| Challenges | Quality variability, emissions control, and market demand considerations. |
Interested in tire pyrolysis oil for your industrial needs? Contact us today to learn more!