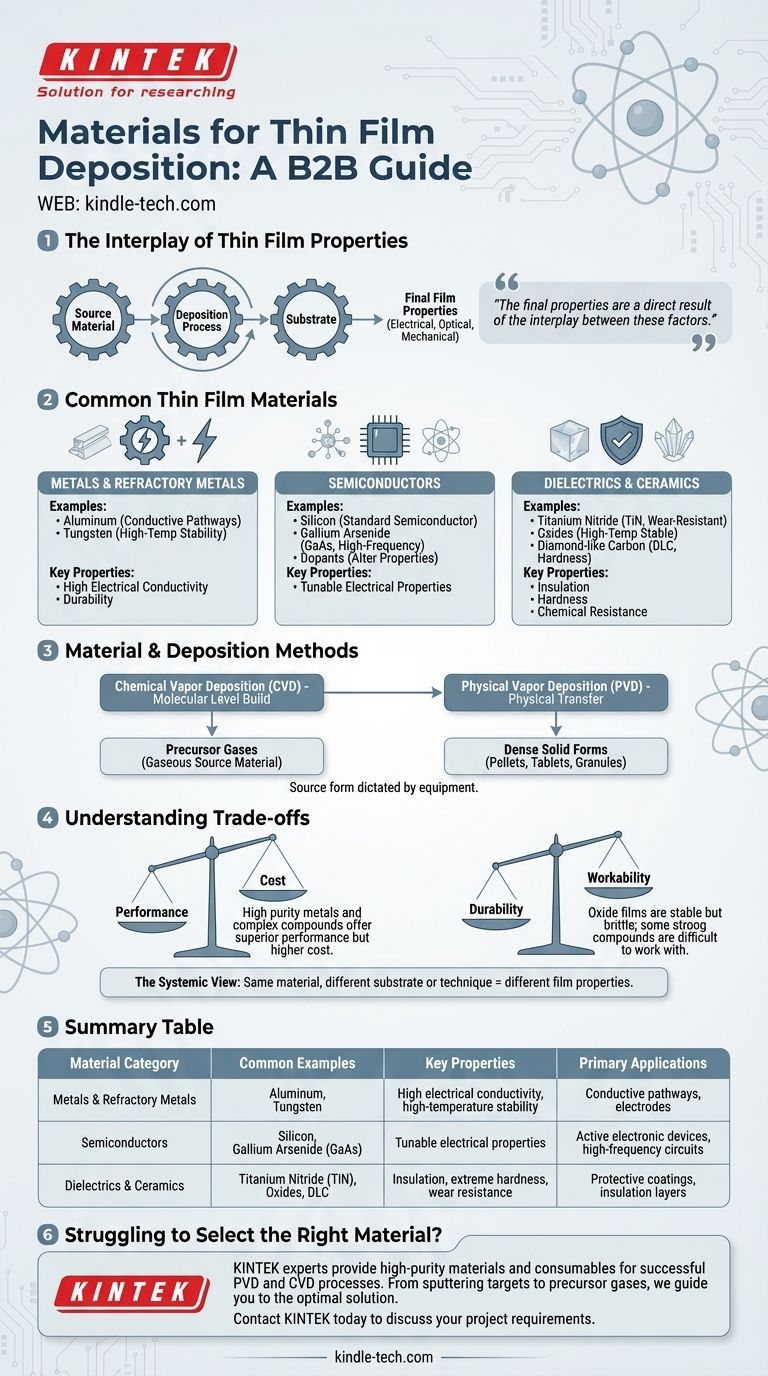
The materials used in thin film deposition are incredibly diverse, ranging from pure metals like aluminum to complex compound semiconductors like gallium arsenide (GaAs). The most common categories include metals, dielectrics, ceramics, and various forms of silicon. These materials are chosen for the specific electrical, optical, or mechanical properties they impart to a surface.
The choice of a thin film material is never made in isolation. The final properties of the film are a direct result of the interplay between the source material, the deposition process used to apply it, and the substrate it is applied to.

A Closer Look at Common Thin Film Materials
The material selected is the foundation of the thin film's function, whether it's for creating a semiconductor circuit, a wear-resistant coating, or an anti-reflective lens.
Metals and Refractory Metals
These materials are primarily used for their high electrical conductivity and durability.
Common examples include aluminum, which is a staple in microelectronics for creating conductive pathways. Refractory metals like tungsten are also used for their high-temperature stability.
Semiconductors
Semiconductors form the basis of virtually all modern electronics.
Silicon is the most widely used semiconductor material. Other critical materials include germanium, compound semiconductors like gallium arsenide (GaAs) for high-frequency applications, and various dopants introduced via ion implantation to alter electrical properties.
Dielectrics and Ceramics
These materials are valued for their insulating properties, hardness, and chemical resistance.
Nitrides, such as Titanium Nitride (TiN), provide extremely hard and wear-resistant coatings. Oxides are durable and can withstand high temperatures, while materials like diamond-like carbon (DLC) offer exceptional hardness and low friction.
The Critical Link: Materials and Deposition Methods
A material is only useful if it can be effectively applied. The physical form of the source material is often dictated by the deposition equipment it will be used in.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
CVD builds films from the molecular level using chemical reactions.
This process relies on precursor gases that react and decompose on the substrate surface, meaning the source material must be in a gaseous state or easily vaporized.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)
PVD involves physically transferring material from a source to a substrate, typically through evaporation or sputtering.
For these methods, the source material is often synthesized into a dense solid form, such as pellets, tablets, or granules, which can be heated or bombarded to release atoms.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a material always involves balancing competing factors. There is no single "best" material, only the most appropriate one for a specific goal and budget.
Performance vs. Cost
Highly pure metals and complex compounds offer superior performance but can be significantly more expensive and difficult to process.
The strength and durability of a metallic film, for example, must be weighed against its material and processing cost.
Durability vs. Workability
Some of the most durable materials present significant processing challenges.
Oxide films are exceptionally stable at high temperatures but can be brittle. Similarly, certain strong compound materials can be difficult to work with, requiring specialized equipment.
The Systemic View
It is critical to remember that the final film properties are not solely determined by the source material.
The same material deposited on a different substrate or using a different deposition technique can yield films with vastly different characteristics, including adhesion, stress, and density.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final material selection must be driven by the primary function of the thin film.
- If your primary focus is electrical conductivity: Metals like aluminum or refractory metals like tungsten are the standard choices for interconnects and electrodes.
- If your primary focus is hardness and wear resistance: Ceramics like Titanium Nitride (TiN) or coatings like diamond-like carbon (DLC) are ideal.
- If your primary focus is creating active electronic devices: Silicon, compound semiconductors (GaAs), or specific dopants delivered via ion implantation are necessary.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature stability or insulation: Oxides and other dielectric materials are the most suitable candidates.
Ultimately, successful thin film engineering depends on understanding that the material is just the starting point of a complex, interconnected system.
Summary Table:
| Material Category | Common Examples | Key Properties | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metals & Refractory Metals | Aluminum, Tungsten | High electrical conductivity, high-temperature stability | Conductive pathways, electrodes |
| Semiconductors | Silicon, Gallium Arsenide (GaAs) | Tunable electrical properties | Active electronic devices, high-frequency circuits |
| Dielectrics & Ceramics | Titanium Nitride (TiN), Oxides, DLC | Insulation, extreme hardness, wear resistance | Protective coatings, insulation layers |
Struggling to select the right thin film material for your specific application? The experts at KINTEK are here to help. We specialize in providing the high-purity materials and consumables—from sputtering targets and evaporation pellets to precursor gases—that your lab needs for successful PVD and CVD processes. Let our deep application knowledge guide you to the optimal solution for conductivity, hardness, or thermal stability.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project requirements and discover how our materials can enhance your thin film performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Containers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Hollow Etching Flower Basket ITO FTO Developing Glue Removal
People Also Ask
- How long does it take for THC to evaporate? The Real Science Behind Potency Loss
- How does a molybdenum evaporation source function in H2S for MoS2 synthesis? Master Reactive Film Deposition
- What factors affect evaporation and condensation? Master the Science of Water's Phase Changes
- What temperature does evaporation occur? Unlock the Secrets to Controlling the Rate of Evaporation
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs



















