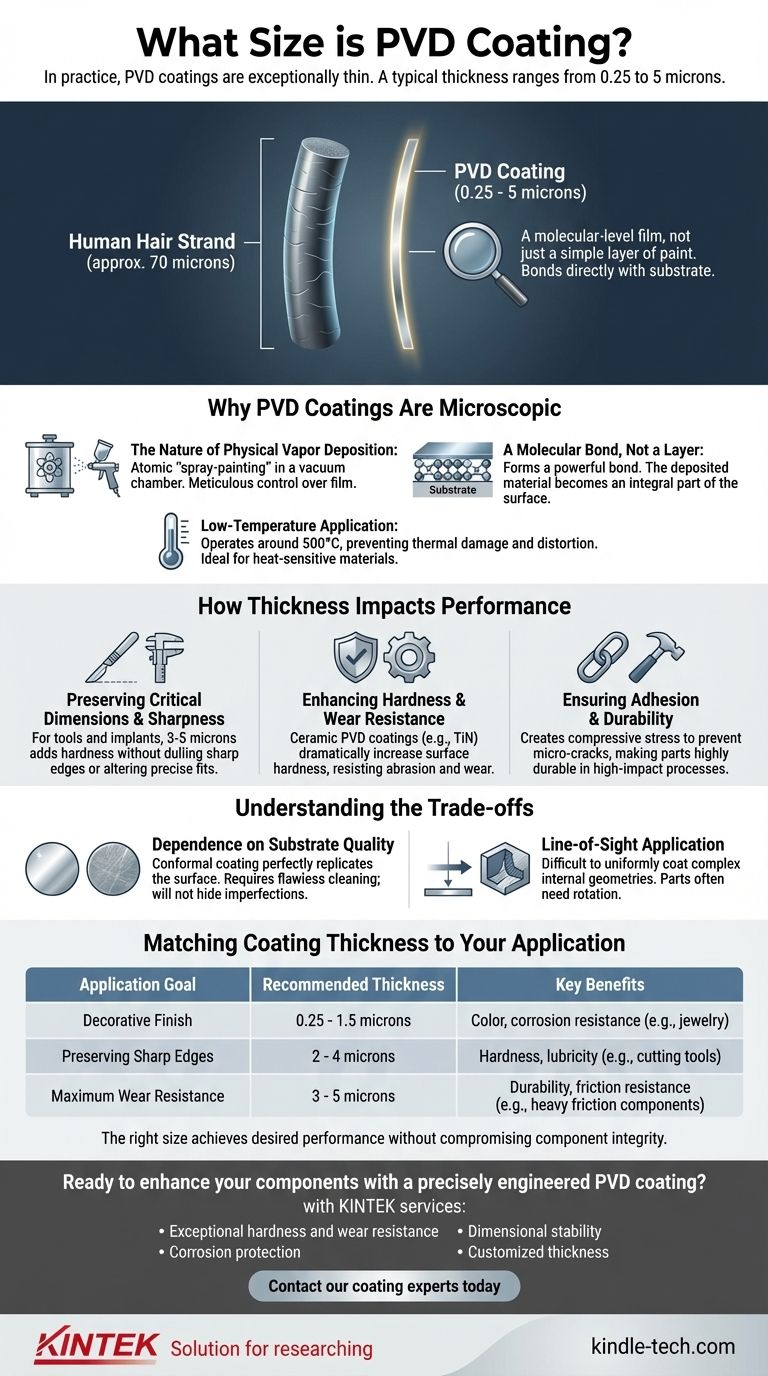
In practice, PVD coatings are exceptionally thin. A typical Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) coating has a thickness ranging from 0.25 to 5 microns (micrometers). Rather than a simple layer of paint, this is a molecular-level film that bonds directly with the substrate material, fundamentally altering its surface properties while being almost immeasurably thin.
The extremely thin nature of a PVD coating is not a limitation but its defining advantage. This microscopic layer enhances hardness, wear resistance, and aesthetics at a molecular level without compromising the underlying part's precise dimensions or sharp edges.
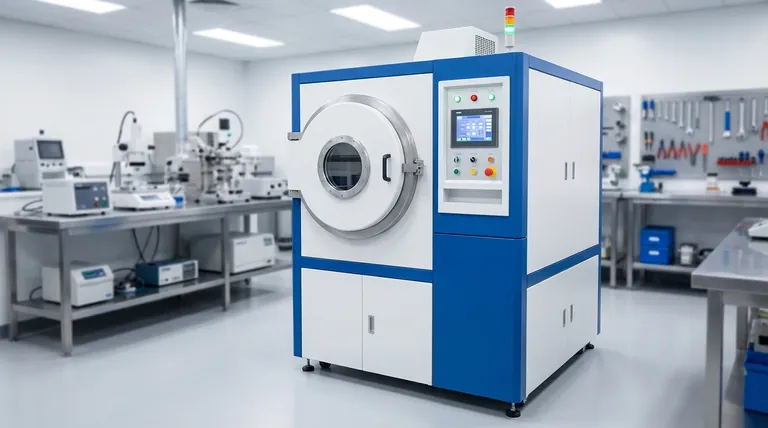

Why PVD Coatings Are Microscopic
The thinness of a PVD coating is a direct result of the highly controlled process used to create it. This is not a coating that is brushed or dipped; it's constructed atom by atom.
The Nature of Physical Vapor Deposition
PVD is a vacuum deposition method where a solid material is vaporized in a vacuum chamber and deposited onto a target substrate. Think of it as a form of atomic "spray-painting."
The process allows for meticulous control over the final film. Key technologies like pulsed bias systems and multiple arc targets ensure the coating is applied uniformly with powerful adhesion.
A Molecular Bond, Not a Layer
Unlike traditional plating, PVD forms a powerful molecular bond with the substrate. The deposited material becomes an integral part of the component's surface.
This is why an incredibly thin layer can provide such a dramatic increase in durability—it isn't just sitting on top; it's fused with the material underneath.
Low-Temperature Application
PVD processes operate at relatively low temperatures (around 500°C). This prevents the thermal damage, warping, or distortion that can occur with higher-temperature coating methods like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
This makes PVD ideal for coating heat-sensitive materials or finished parts with tight dimensional tolerances.
How Thickness Impacts Performance
The specified thickness of a PVD coating is not arbitrary. It is engineered to balance durability with the functional requirements of the part.
Preserving Critical Dimensions and Sharpness
For components like cutting tools, injection molds, or medical implants, even a tiny change in dimension can render the part useless.
A PVD coating, typically between 3 to 5 microns thick for tools, adds immense hardness and lubricity without dulling a sharp cutting edge or altering precise fits.
Enhancing Hardness and Wear Resistance
Even at just a few microns thick, a ceramic PVD coating (like Titanium Nitride, or TiN) dramatically increases the surface hardness of the underlying metal.
This creates a surface that is highly resistant to abrasion, friction, and wear. For some alloys, it can even increase the fatigue limit and overall endurance of the part.
Ensuring Adhesion and Durability
The PVD process creates compressive stress within the coating layer as it cools. This internal stress helps prevent the formation and spread of micro-cracks.
This quality makes PVD-coated parts exceptionally durable in high-impact or interrupted processes, such as milling.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, PVD is not a universal solution. Its characteristics create specific limitations that are critical to understand.
Dependence on Substrate Quality
PVD coatings are conformal, meaning they perfectly replicate the surface they are applied to. They are not a filler and will not hide scratches, tool marks, or other imperfections.
For a high-quality finish, the substrate must be polished and flawlessly clean before entering the vacuum chamber.
Line-of-Sight Application
The PVD process generally works on a line-of-sight basis. The vaporized material travels in a straight line from the source to the substrate.
This makes it difficult to uniformly coat complex internal geometries or deeply recessed areas. Parts often need to be rotated on complex fixtures to ensure even coverage.
Matching Coating Thickness to Your Application
The ideal thickness depends entirely on your primary goal for the component.
- If your primary focus is a decorative finish: A thinner coating (0.25 to 1.5 microns) is often sufficient for achieving a specific color, like black or blue, and providing corrosion resistance on items like jewelry or architectural hardware.
- If your primary focus is preserving sharp edges: A thin to medium coating (2 to 4 microns) is ideal for cutting tools, blades, and molds to gain hardness and lubricity without dulling the critical edge.
- If your primary focus is maximum wear resistance: A thicker coating (3 to 5 microns) is best for components subjected to heavy friction or harsh environments, where a slight dimensional addition is acceptable.
Ultimately, the 'right' size for a PVD coating is the one that achieves your desired performance without compromising the integrity of the component.
Summary Table:
| Application Goal | Recommended Coating Thickness | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Decorative Finish | 0.25 - 1.5 microns | Color, corrosion resistance |
| Preserving Sharp Edges | 2 - 4 microns | Hardness, lubricity |
| Maximum Wear Resistance | 3 - 5 microns | Durability, friction resistance |
Ready to enhance your components with a precisely engineered PVD coating?
At KINTEK, we specialize in applying high-performance PVD coatings to laboratory equipment, tools, and precision components. Our coatings deliver:
- Exceptional hardness and wear resistance for longer service life
- Corrosion protection to withstand harsh environments
- Dimensional stability to preserve critical tolerances
- Customized thickness tailored to your specific application needs
Whether you're coating cutting tools, medical instruments, or specialized lab consumables, our PVD solutions can significantly improve performance and durability.
Contact our coating experts today to discuss how we can optimize your components with our advanced PVD coating services.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















