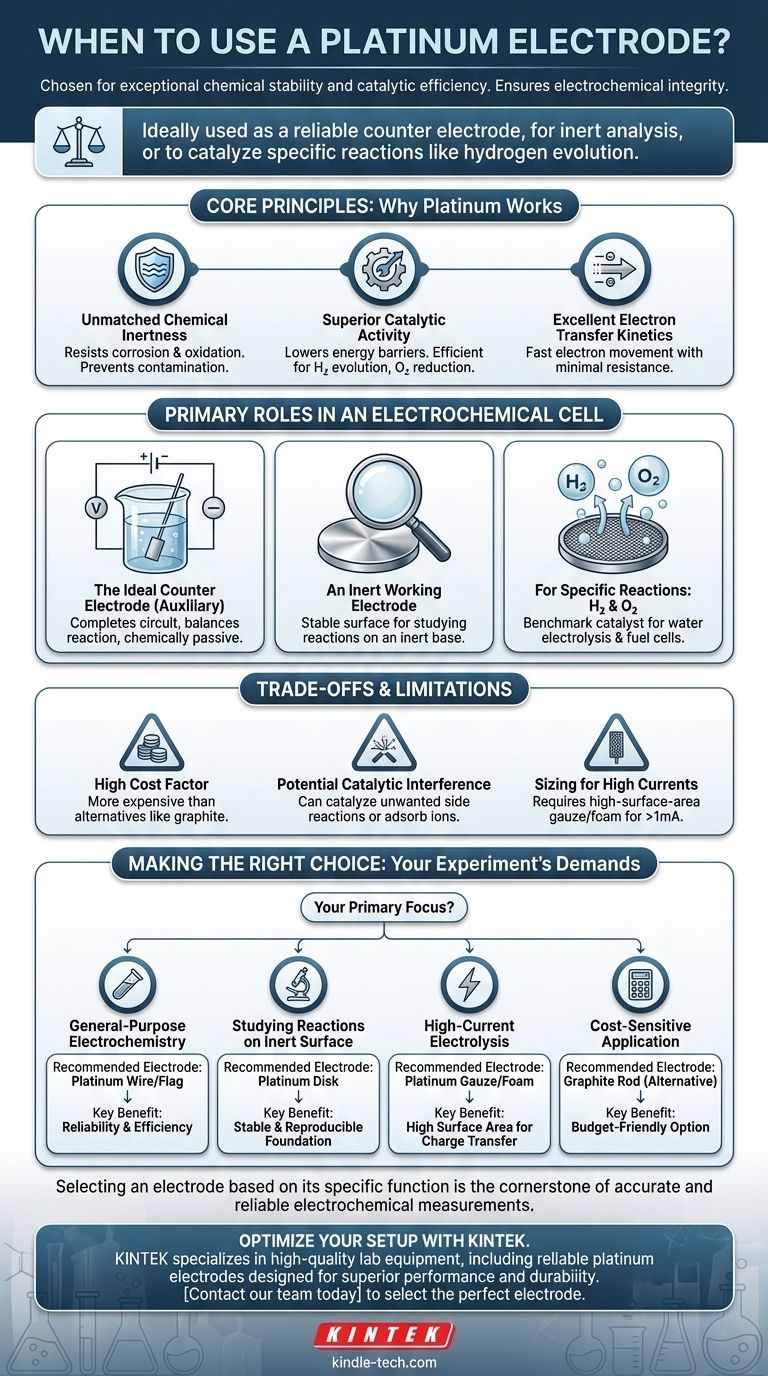
Platinum electrodes are chosen for their exceptional chemical stability and catalytic efficiency. You should use a platinum electrode when you require an inert surface for analysis, need to catalyze specific reactions like hydrogen evolution, or, most commonly, when you need a reliable counter electrode to complete an electrochemical circuit without interfering with your experiment.
The decision to use platinum is fundamentally about ensuring electrochemical integrity. It excels as a counter (or auxiliary) electrode because it can rapidly source or sink electrons to balance the reaction at your working electrode, all while remaining chemically passive in most environments.
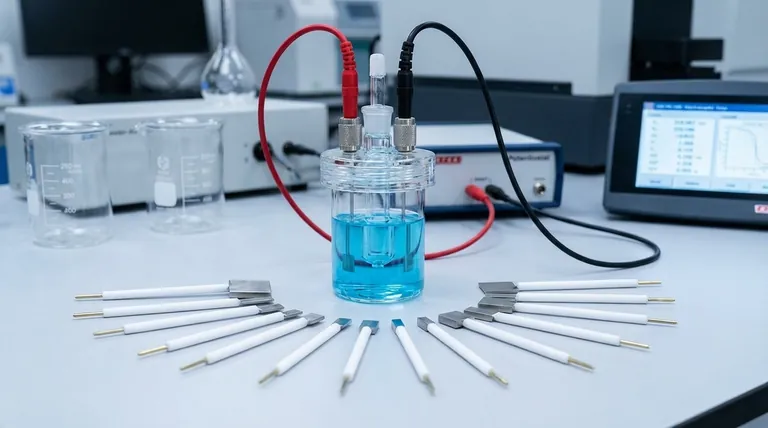

The Core Principles: Why Platinum Works
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
Platinum is a noble metal, meaning it strongly resists corrosion and oxidation in most aqueous solutions. This stability ensures the electrode itself does not dissolve or react, preventing contamination of your solution and maintaining the integrity of your experiment over time.
Your measurements remain focused on the reaction you intend to study, not on unintended side reactions from a degrading electrode.
Superior Catalytic Activity
While inert, platinum is not entirely passive. It is an excellent catalyst for many important electrochemical reactions. This means it lowers the energy barrier required for these reactions to occur, making them happen more efficiently and at lower potentials.
Its surface actively facilitates processes like the splitting of water or the reduction of oxygen.
Excellent Electron Transfer Kinetics
A key function of an electrode is to move electrons between the solid electrode and species in the solution. Platinum exhibits very fast electron transfer kinetics, meaning it can give or take electrons with minimal resistance.
This efficiency is critical for the counter electrode, whose job is to perfectly mirror the current flowing at the working electrode without becoming a bottleneck for the entire system.
Primary Roles in an Electrochemical Cell
The Ideal Counter Electrode
In a standard three-electrode setup, the counter electrode (or auxiliary electrode) serves one purpose: to complete the electrical circuit. It passes whatever current is needed to balance the reaction occurring at the working electrode.
Platinum is the default choice here because its inertness and fast kinetics ensure it can perform this balancing act without influencing the sensitive potential measurements being taken at the working electrode.
An Inert Working Electrode
While less common, a platinum disk or wire can also be used as the working electrode—the primary surface where the reaction of interest is studied.
This is done when the goal is to investigate a reaction on a well-defined, catalytically active, and reproducible inert surface. The oxidation of small organic molecules, for example, is often studied on platinum working electrodes.
For Specific Reactions: H₂ and O₂
Platinum is the benchmark catalyst for both the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) and the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR). These are fundamental processes in water electrolysis and fuel cells.
When your goal is to generate hydrogen or reduce oxygen efficiently, a platinum electrode is often the most effective choice, serving as the catalytic surface itself.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
The High Cost Factor
The most significant drawback of platinum is its cost. As a precious metal, it is far more expensive than alternatives like graphite or stainless steel. This can make it prohibitive for large-scale industrial applications or budget-constrained labs.
Potential for Catalytic Interference
Platinum's catalytic nature can be a double-edged sword. In some experiments, it may catalyze unwanted side reactions involving the solvent or other species in the electrolyte.
It can also adsorb ions or molecules from the solution onto its surface, which can passivate the electrode or interfere with sensitive measurements.
Sizing for High Currents
For experiments involving high currents (typically >1 mA), a small platinum wire may not have enough surface area to handle the electron transfer demands. In these cases, the reaction can become limited by the counter electrode.
To prevent this, a high-surface-area platinum gauze or metal foam electrode must be used to provide adequate charge transfer capacity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Experiment
Your choice of electrode must be driven by its specific role in your setup and the demands of your experiment.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose electrochemistry: Use a platinum wire or flag as your default counter electrode for its reliability and efficiency.
- If your primary focus is studying a reaction on an inert surface: A platinum disk can serve as an excellent working electrode, providing a stable and reproducible foundation.
- If your primary focus is high-current electrolysis: Select a high-surface-area platinum gauze or foam electrode to ensure it can handle the required charge transfer.
- If your primary focus is a cost-sensitive application: Consider a graphite rod as a less expensive alternative for the counter electrode, accepting a potential drop in performance.
Selecting an electrode based on its specific function is the cornerstone of accurate and reliable electrochemical measurements.
Summary Table:
| Scenario | Recommended Electrode Type | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| General-purpose electrochemistry (Counter Electrode) | Platinum wire or flag | Reliability and efficiency |
| Studying reactions on an inert surface (Working Electrode) | Platinum disk | Stable and reproducible foundation |
| High-current electrolysis | Platinum gauze or foam | High surface area for charge transfer |
| Cost-sensitive applications | Graphite rod | Budget-friendly alternative |
Optimize your electrochemical setup with KINTEK's precision lab equipment.
Choosing the right electrode is critical for the integrity of your research. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including reliable platinum electrodes designed for superior performance and durability. Our products ensure your experiments are not compromised by equipment limitations, providing the chemical stability and catalytic efficiency your work demands.
Let our experts help you select the perfect electrode for your specific application. Contact our team today to discuss your laboratory needs and discover how KINTEK can support your research goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Platinum Auxiliary Electrode for Laboratory Use
- Metal Disc Electrode Electrochemical Electrode
- Reference Electrode Calomel Silver Chloride Mercury Sulfate for Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- Roles of Platinum Counter vs Ag/AgCl Reference Electrodes in 3-Electrode Systems
- What is a common application for the platinum mesh electrode in electrochemistry? Achieve Accurate & Stable Results
- How should the PTFE electrode stand and its components be cleaned after use? A Step-by-Step Guide to Prevent Contamination
- How can the cleanliness of a pre-treated glassy carbon sheet be verified? Ensure Accurate Electrochemical Results
- What precautions should be taken when using metal disk electrodes? Ensure Accuracy and Longevity
- What are the primary advantages of using an Ir-Ta metal oxide coating? Maximize Durability & Oxidation Efficiency
- Why must platinum paste electrodes be fired at 1100°C? Unlock High Conductivity and Mechanical Stability
- What are the proper procedures for post-treatment and storage of an electrode holder after an experiment? Ensure Accuracy and Longevity



















