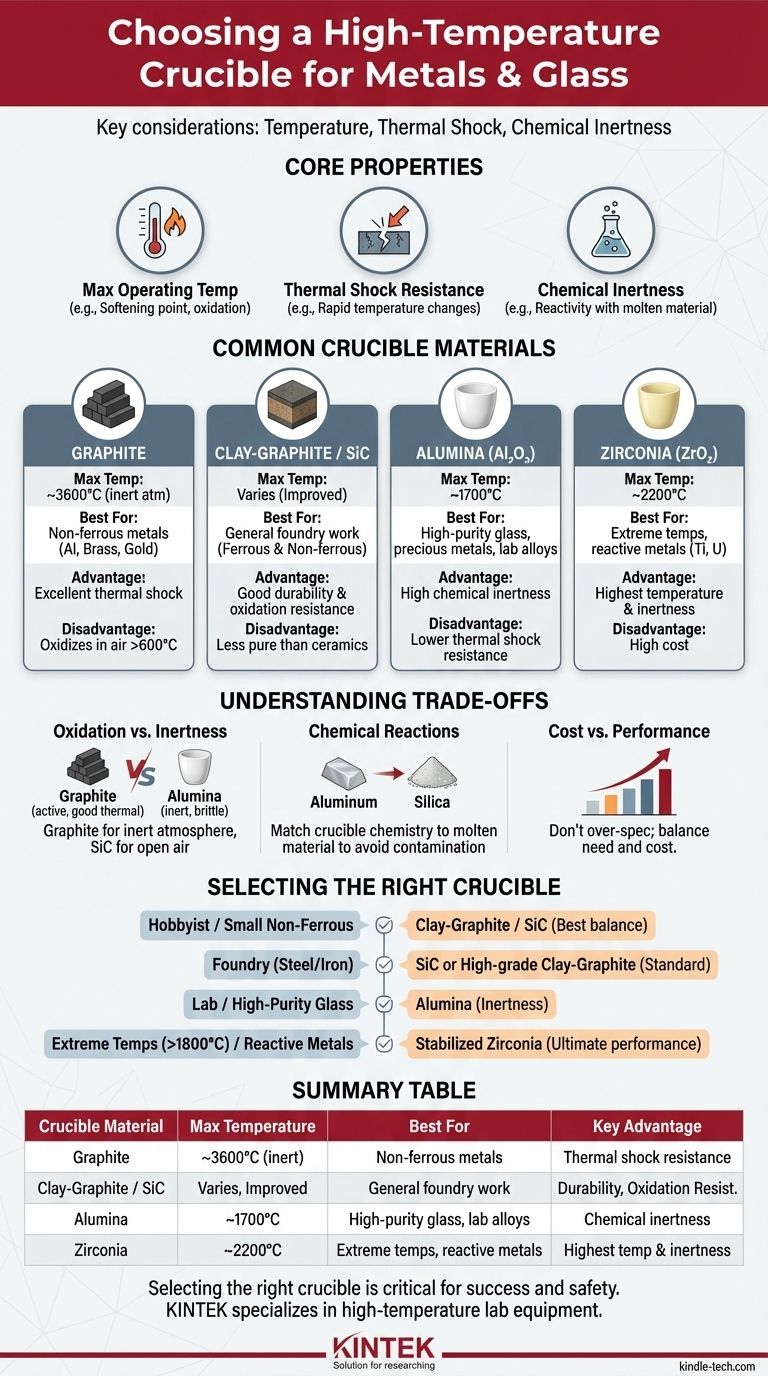
For high-temperature applications involving metals and glass, the most common and versatile choices are graphite, clay-graphite, and ceramic crucibles such as those made from alumina or zirconia. The ideal choice depends entirely on the maximum temperature you need to reach and the specific chemical composition of the material you are melting.
The selection of a crucible is not just about withstanding heat. It is a critical decision balancing thermal performance, chemical compatibility with your molten material, and cost to prevent both catastrophic failure and contamination of your final product.

The Core Properties of a Crucible
Before choosing a material, you must understand the key properties that define a crucible's performance. The "best" crucible performs well across all three of these metrics for your specific task.
Maximum Operating Temperature
This is the most obvious factor. Every material has a temperature at which it begins to soften, melt, or degrade. Exceeding this limit will destroy the crucible and your furnace.
Graphite, for example, sublimes at extremely high temperatures (~3600°C), but it begins to oxidize (burn away) in the presence of oxygen at temperatures as low as 600°C.
Thermal Shock Resistance
This is the ability to withstand rapid changes in temperature without cracking. A material with poor thermal shock resistance can shatter if heated or cooled too quickly.
Graphite and silicon carbide have excellent thermal shock resistance, making them very durable for foundry work. Pure ceramics, like alumina, are often more brittle and require more careful heating and cooling cycles.
Chemical Inertness
A crucible must act as a neutral container. It should not react with, dissolve into, or otherwise contaminate the molten metal or glass it holds.
This is often the most overlooked property. For example, melting a highly reactive metal in the wrong type of ceramic can leach elements from the crucible into the melt, ruining the purity of your alloy.
Common Crucible Materials for High-Temperature Work
Your choice will almost certainly be one of the materials below. Each serves a different purpose based on its unique balance of properties.
Graphite Crucibles
Primarily used for melting non-ferrous metals like aluminum, brass, and gold. They offer superb thermal conductivity and excellent thermal shock resistance.
Their main weakness is oxidation. When used in an electric furnace or an oxygen-rich flame, the graphite will literally burn away over time, limiting the crucible's life.
Clay-Graphite and Silicon Carbide (SiC) Crucibles
These are composite materials that improve upon pure graphite. Adding clay or silicon carbide to the graphite mix creates a harder, stronger crucible with significantly better resistance to oxidation.
These are the workhorses of most small foundries and hobbyist metal casters due to their durability, versatility, and reasonable cost. They are suitable for both ferrous and non-ferrous metals.
Alumina (Al₂O₃) Crucibles
Alumina is a high-purity ceramic capable of withstanding very high temperatures (up to ~1700°C). It is highly resistant to chemical attack from many molten metals and slags.
It is a standard choice for melting high-purity glass, precious metals, and superalloys in laboratory or specialized industrial settings. Its primary drawback is lower thermal shock resistance compared to graphite.
Zirconia (ZrO₂) Crucibles
For the most extreme applications, Zirconia is the answer. It has an even higher melting point than alumina (up to ~2200°C) and is exceptionally inert, even against highly reactive materials like titanium or uranium.
Stabilized Zirconia is the material of choice for aerospace alloys and research applications where purity is paramount and temperatures are extreme. This performance comes at a significantly higher cost.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a crucible involves balancing performance against risk and cost. Understanding these trade-offs is critical to avoid failed experiments and wasted material.
The Risk of Oxidation vs. Inertness
Graphite offers fantastic thermal properties but is "active" in an oxygen environment. A ceramic like Alumina is far more inert but can't handle the same thermal abuse.
If you are using an open-air furnace, a silicon carbide composite is a better choice than pure graphite. If you are in a vacuum or inert atmosphere, graphite's performance is unmatched.
Chemical Reactions and Contamination
Never melt aluminum in a silica-based (glass or sand) crucible. The molten aluminum is highly reactive and will strip oxygen from the silica (silicon dioxide), contaminating your aluminum with silicon and destroying the crucible.
This is a perfect example of why chemical inertness is so important. You must match the crucible material to the chemistry of what you are melting. Alumina and Zirconia are go-to choices for preventing such reactions.
Cost vs. Performance
The relationship is direct and steep. A small clay-graphite crucible might cost tens of dollars. A similarly sized Alumina crucible could be several hundred, and a Zirconia crucible could be many times that.
Do not over-spec your crucible. Using a Zirconia crucible to melt aluminum is unnecessary and financially unwise. Conversely, using a cheap crucible for a high-purity alloy will ruin your expensive material.
Selecting the Right Crucible for Your Application
Use your primary goal to guide your decision.
- If your primary focus is hobbyist or small-scale non-ferrous metal casting (aluminum, brass): A clay-graphite or silicon carbide crucible offers the best balance of cost, durability, and performance.
- If your primary focus is melting steel or iron in a foundry: A silicon carbide or specialized high-grade clay-graphite crucible is the standard choice.
- If your primary focus is high-purity glass or laboratory-grade alloys: An alumina crucible provides the necessary temperature resistance and chemical inertness.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperatures (>1800°C) or highly reactive metals: A stabilized zirconia crucible is the technically correct, albeit expensive, solution.
Choosing the right crucible is the first step toward a successful high-temperature process.
Summary Table:
| Crucible Material | Max Temperature | Best For | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Graphite | ~3600°C (inert atm) | Non-ferrous metals (Al, brass, gold) | Excellent thermal shock resistance |
| Clay-Graphite / SiC | Varies, improved over graphite | General foundry work, ferrous & non-ferrous metals | Good durability & oxidation resistance |
| Alumina (Al₂O₃) | Up to ~1700°C | High-purity glass, precious metals, lab alloys | High chemical inertness |
| Zirconia (ZrO₂) | Up to ~2200°C | Extreme temps, reactive metals (Ti, U) | Highest temperature & inertness |
Selecting the right crucible is critical for your lab's success and safety. KINTEK specializes in high-temperature lab equipment and consumables, including a full range of crucibles for metals and glass. Our experts can help you choose the perfect crucible material for your specific application, ensuring optimal performance, purity, and value. Contact our technical team today for a personalized recommendation and to explore our reliable, high-performance crucible solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- High Purity Pure Graphite Crucible for Evaporation
People Also Ask
- Why use high-purity alumina crucibles for RPPO calcination? Ensure Stoichiometric Purity at 1150°C
- What temperature is an Al2O3 crucible? Key Factors for High-Temperature Success Up to 1700°C
- What are the benefits of using an alumina crucible with a lid for TiB2 nanopowder heat treatment? Ensure High Purity
- What temperature can alumina crucible withstand? A Guide to High-Temperature Stability and Safety
- What is the purpose of using an alumina crucible with a lid for g-C3N4 synthesis? Optimize Your Nanosheet Production



















