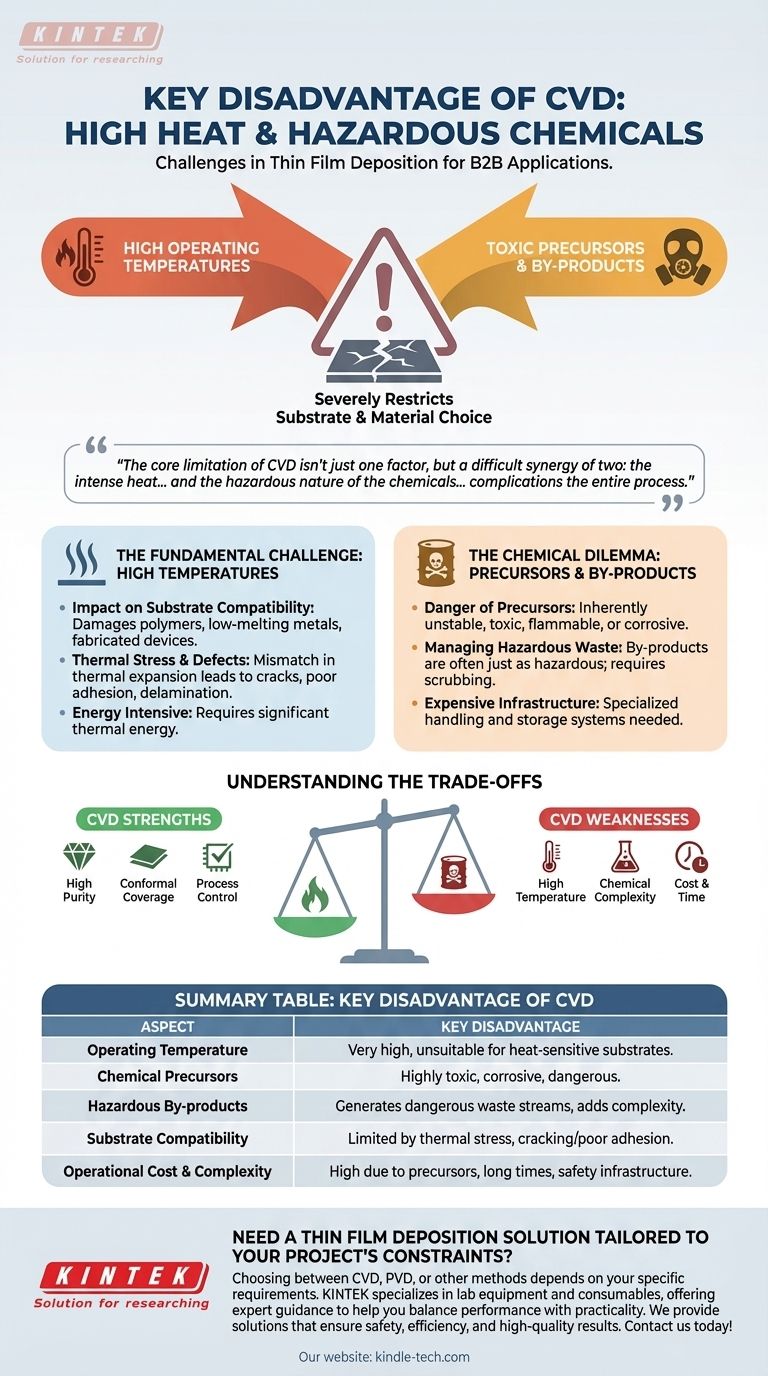
The key disadvantage of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is its requirement for high operating temperatures, often combined with the use of highly toxic, corrosive, and dangerous chemical precursors. This combination severely restricts the types of materials that can be used as substrates and introduces significant safety, environmental, and cost challenges for handling both the input chemicals and their hazardous by-products.
The core limitation of CVD isn't just one factor, but a difficult synergy of two: the intense heat required to drive the chemical reaction limits what you can coat, while the hazardous nature of the chemicals involved complicates the entire process from start to finish.

The Fundamental Challenge: High Temperatures
The "C" in CVD stands for "chemical," and these reactions typically require a great deal of thermal energy to proceed efficiently. This reliance on high heat is the source of several major drawbacks.
Impact on Substrate Compatibility
Many CVD processes operate at temperatures that can damage or destroy heat-sensitive materials. This makes the technique unsuitable for coating polymers, certain low-melting-point metals, or fully fabricated electronic devices that cannot withstand the thermal load.
Thermal Stress and Defects
Even if a substrate can survive the high temperatures, the difference in thermal expansion between the substrate and the deposited film can be a problem. As the system cools, this mismatch can introduce stress, leading to cracks, poor adhesion, or delamination of the thin film.
The Chemical Dilemma: Precursors and By-products
CVD works by introducing reactive gases (precursors) into a chamber where they decompose and deposit a film onto a substrate. The nature of these chemicals is central to the process's limitations.
The Danger of Precursors
To be effective, CVD precursors must be volatile enough to exist as a gas and reactive enough to form the desired film. This combination often means the chemicals are inherently unstable, toxic, flammable, or corrosive, requiring specialized and expensive handling and storage systems.
Managing Hazardous Waste
The chemical reactions in a CVD process are rarely 100% efficient. This results in by-products that are often just as hazardous as the initial precursors. These waste streams must be neutralized or "scrubbed" before they can be exhausted, adding significant complexity and cost to the operation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No deposition method is perfect. The disadvantages of CVD must be weighed against its significant strengths, particularly when compared to alternative methods like Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD).
High Temperature vs. High Quality
The very heat that limits substrate choice is also what enables the growth of high-purity, highly crystalline films with excellent conformal coverage. CVD is exceptionally good at coating complex, non-flat surfaces uniformly, a task where line-of-sight PVD techniques often struggle.
Chemical Complexity vs. Process Control
While the chemicals are hazardous, they provide a high degree of control over the film's properties. By precisely adjusting gas flow, pressure, and concentration, operators can fine-tune the chemical composition and structure of the final film.
Cost and Time
CVD can be a costly process. The combination of expensive and hazardous precursors, long deposition times (sometimes many hours), and the need for complex safety and waste-handling infrastructure contributes to a higher operational cost compared to some other methods.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a deposition technique requires a clear understanding of your project's primary constraints and desired outcomes.
- If your primary focus is exceptional film purity and uniform coverage on a heat-resistant substrate: CVD is often the superior choice, as its chemical nature allows for unparalleled quality and conformality.
- If your primary focus is coating a heat-sensitive material like a polymer or a finished electronic device: A lower-temperature process like Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) or a PVD technique is almost certainly necessary.
- If your primary focus is minimizing safety risks and operational complexity: The infrastructure required to manage CVD's hazardous chemicals may make PVD or other less chemically intensive methods more practical.
Ultimately, choosing the right method involves balancing the superior film quality of CVD against its significant thermal and chemical constraints.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Disadvantage of CVD |
|---|---|
| Operating Temperature | Very high, often unsuitable for heat-sensitive substrates like polymers or finished electronics. |
| Chemical Precursors | Often highly toxic, corrosive, and dangerous, requiring specialized handling and storage. |
| Hazardous By-products | Generates dangerous waste streams that must be neutralized, adding complexity and cost. |
| Substrate Compatibility | Limited by thermal stress, which can cause cracking or poor adhesion of the thin film. |
| Operational Cost & Complexity | High due to expensive precursors, long deposition times, and complex safety infrastructure. |
Need a Thin Film Deposition Solution Tailored to Your Project's Constraints?
Choosing between CVD, PVD, or other methods depends on your specific requirements for substrate compatibility, film quality, and safety. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, offering expert guidance to help you select the perfect deposition system for your laboratory's needs.
Let our experts help you balance performance with practicality. We provide solutions that ensure safety, efficiency, and high-quality results.
Contact us today to discuss your thin film deposition challenges!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
People Also Ask
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods
- Can plasma enhanced CVD deposit metals? Why PECVD is rarely used for metal deposition
- What is the difference between plasma CVD and thermal CVD? Choose the Right Method for Your Substrate
- How do PECVD systems improve DLC coatings on implants? Superior Durability and Biocompatibility Explained



















