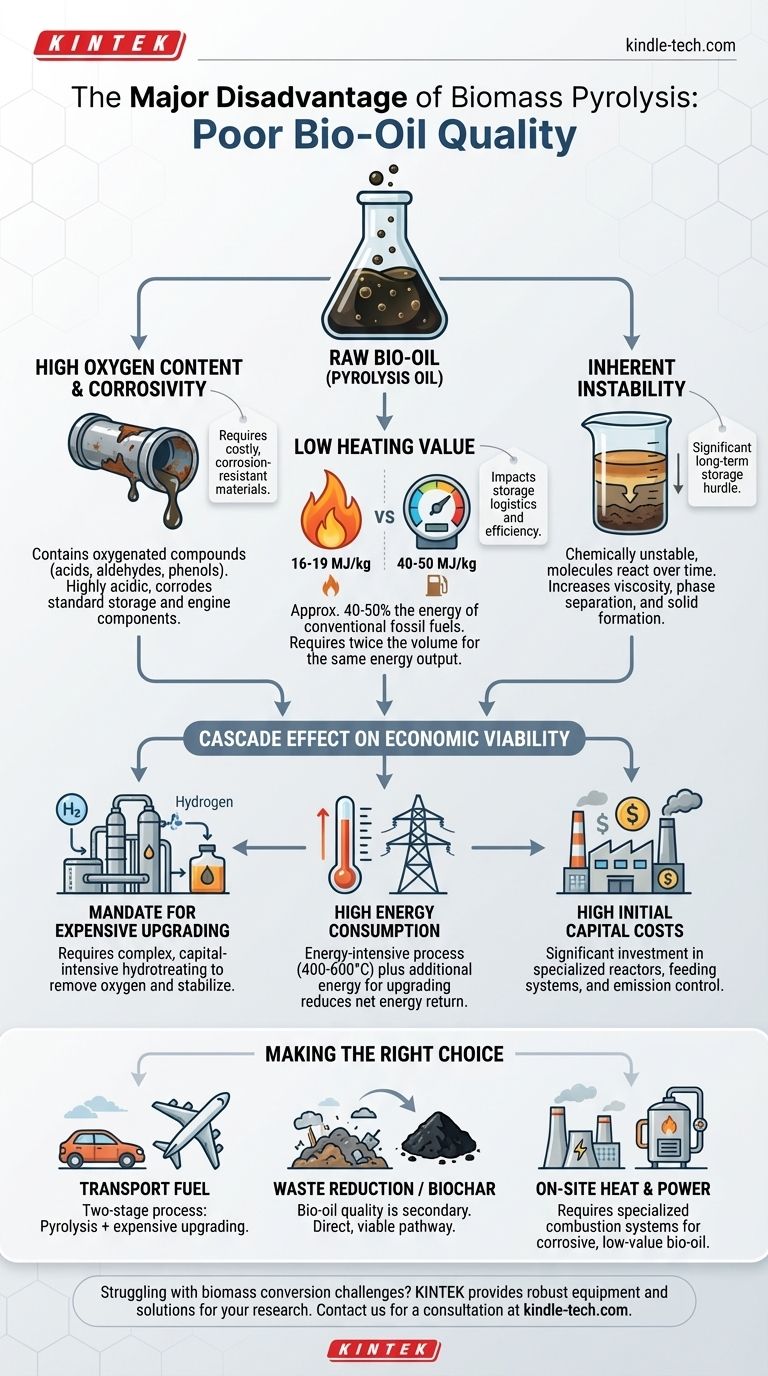
The single most important disadvantage of biomass pyrolysis is the poor quality of its primary liquid product, bio-oil. This oil is a complex, oxygen-rich mixture that is highly corrosive, unstable, and has a low heating value, preventing its direct use as a fuel without significant and costly post-processing.
While pyrolysis faces challenges like high energy use and capital costs, these are largely symptoms of a more fundamental problem: the raw bio-oil produced is not a finished product. Its poor chemical properties necessitate further expensive upgrading, which undermines the overall economic viability of the process.

The Core Problem: Unrefined Bio-Oil Quality
The central challenge of pyrolysis is not the process itself, but the nature of what it creates. The primary liquid output, known as bio-oil or pyrolysis oil, is fundamentally different from conventional crude oil and requires substantial refinement.
High Oxygen Content and Corrosivity
The bio-oil contains a large number of oxygenated organic compounds, such as acids, aldehydes, and phenols. This high oxygen content, sometimes over 40%, makes the oil highly acidic and corrosive to standard pipes, tanks, and engine components.
This requires the use of expensive, corrosion-resistant materials like stainless steel for storage and transport, adding to the overall cost.
Low Heating Value
A direct consequence of the high oxygen content is a low heating value. Bio-oil typically has a heating value of around 16-19 MJ/kg, which is only 40-50% of the value of conventional fossil fuels.
This means you need roughly twice as much bio-oil to generate the same amount of energy as you would with heating oil or diesel, impacting storage logistics and combustion efficiency.
Inherent Instability
Raw bio-oil is chemically unstable. Over time, its molecules react with each other, leading to an increase in viscosity (it gets thicker) and phase separation, eventually forming gums and solids. This makes long-term storage a significant technical hurdle.
The Cascade Effect on Economic Viability
The poor quality of the bio-oil creates a domino effect that directly impacts the financial feasibility of a pyrolysis plant. The process becomes less about producing a final fuel and more about creating an intermediate that requires its own expensive industrial process.
The Mandate for Expensive Upgrading
To be used as a transportation fuel, bio-oil must undergo a process called "upgrading." This typically involves hydrotreating or hydrodeoxygenation, which uses hydrogen at high pressure and temperature to remove oxygen and stabilize the molecules.
This upgrading step is a complex and capital-intensive process that can rival the cost of the pyrolysis plant itself.
High Energy Consumption
The pyrolysis process requires heating biomass to high temperatures (typically 400-600°C) in the absence of oxygen. Achieving and maintaining these temperatures is energy-intensive.
When you add the significant energy required for the subsequent upgrading of the bio-oil, the net energy return of the entire system can become marginal.
High Initial Capital Costs
A biomass pyrolysis plant is a significant investment. It requires specialized reactors, feeding systems, and equipment to handle the solid (biochar), liquid (bio-oil), and gas products. The costs are compounded by the need for an emission cleaning line to manage air quality.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Other Challenges
While bio-oil quality is the central issue, other factors must be considered when evaluating pyrolysis as a technology.
Environmental Emissions Management
The high-temperature process can produce emissions that negatively impact air quality if not properly managed. A well-designed plant must include an extensive emission cleaning line to capture pollutants, adding to both capital and operational costs.
Feedstock and Scale Limitations
Pyrolysis is not a universal solution for all types of biomass or for all locations. The process efficiency can vary based on the feedstock's moisture content, particle size, and chemical composition.
Furthermore, the complex logistics and high capital costs often make the process less cost-effective for small-scale, decentralized applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "disadvantages" of pyrolysis are highly dependent on your ultimate objective. Understanding the role of bio-oil quality is key to determining if the technology fits your needs.
- If your primary focus is producing ready-to-use transportation fuel: Be prepared for a two-stage process; pyrolysis is just the first step, and you must budget for significant downstream upgrading costs.
- If your primary focus is waste volume reduction or creating biochar: The quality of the liquid bio-oil is a secondary concern, making pyrolysis a much more direct and viable pathway.
- If your primary focus is generating on-site heat and power: You must invest in specialized combustion systems designed to handle the corrosive nature and low heating value of raw bio-oil.
Ultimately, a clear-eyed assessment of the challenges posed by bio-oil quality is the first step in successfully leveraging pyrolysis technology.
Summary Table:
| Key Challenge | Impact |
|---|---|
| Poor Bio-Oil Quality | Highly corrosive, unstable, low heating value |
| High Upgrading Costs | Requires expensive hydrotreating to be usable |
| Economic Viability | Undermined by the need for extensive post-processing |
Struggling with the challenges of biomass conversion? KINTEK specializes in providing robust laboratory equipment and consumables to help you analyze, test, and optimize your pyrolysis processes. From reactors to analytical tools, our solutions are designed to handle demanding applications and improve your research outcomes. Let our experts help you find the right equipment for your lab's needs. Contact us today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output



















