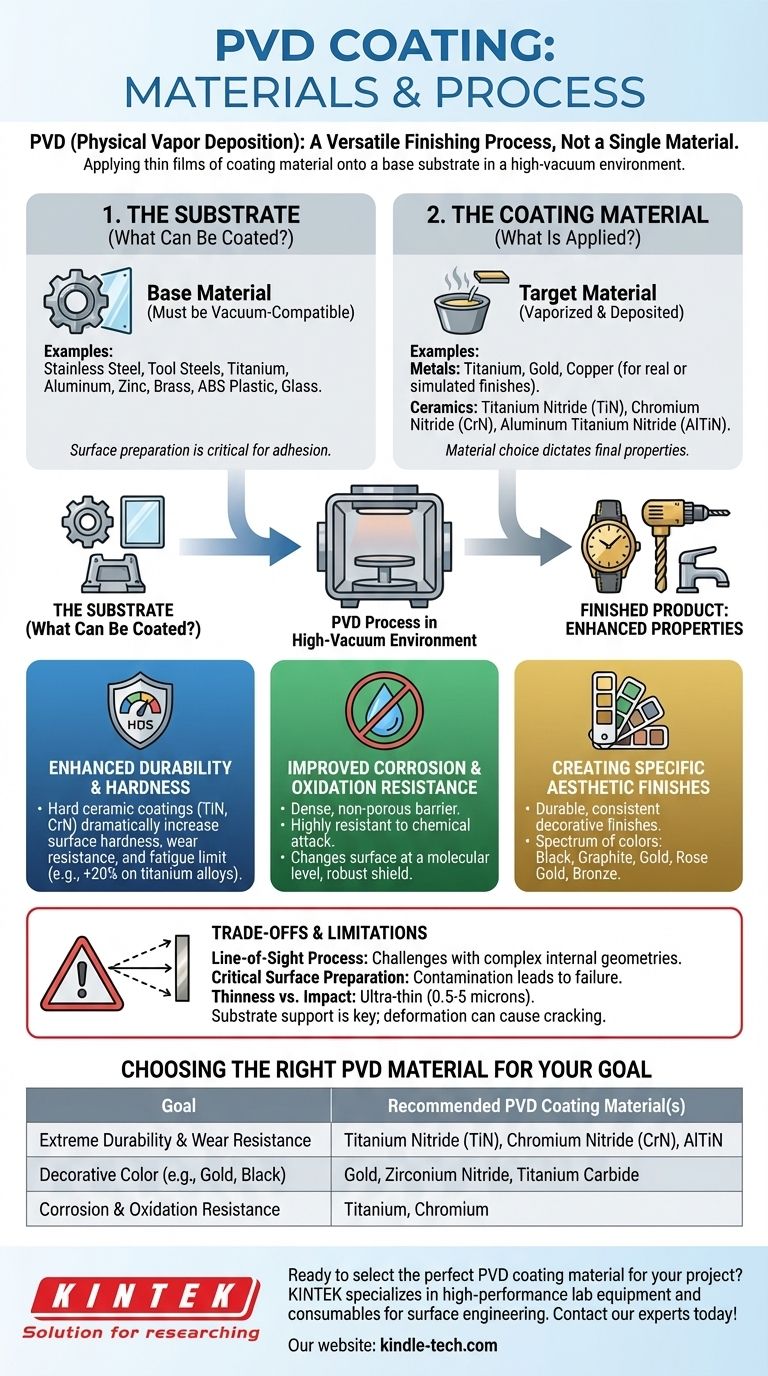
In short, PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) is a process, not a single material. It can apply a vast range of coating materials—most commonly metals and ceramics like titanium, gold, and titanium nitride—onto an equally diverse set of base materials, known as substrates, which include stainless steel, plastics, and glass. The key is that the material must be compatible with a high-vacuum environment.
The crucial insight is that PVD is a versatile finishing process that bonds a thin film of a chosen coating material onto a substrate. The final properties of the product depend entirely on the strategic combination of both the coating material and the underlying substrate.
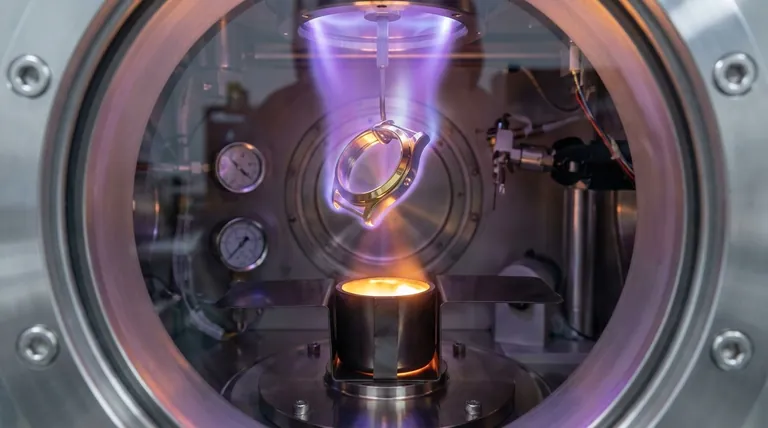
The Two Key Components: Substrate and Coating
To understand the materials used in PVD, you must distinguish between the object being coated (the substrate) and the material being applied (the coating).
The Substrate: What Can Be Coated?
The substrate is the part or component that receives the coating. A wide array of materials can be used as substrates.
Common examples include stainless steel, tool steels, titanium, aluminum, zinc, and brass. Even non-metallic materials like ABS plastic and glass can be coated effectively.
The single most important requirement is that the substrate must be vacuum-compatible. This means it cannot release gases under vacuum, which would disrupt the coating process. Some materials may require special pre-treatment, like an electroplated layer of nickel-chromium, to ensure proper adhesion.
The Coating Material: What Is Applied?
The coating material, often called the "target," is what is vaporized and deposited onto the substrate. This material choice dictates the final properties of the finish.
Metals are frequently used, such as titanium, gold, and copper. For instance, a "gold PVD" finish can be achieved using real 18k or 24k gold, or it can simulate the color using less expensive materials like brass.
Ceramics are also extremely common, particularly for durability. Titanium Nitride (TiN) is a classic example, known for its gold color and exceptional hardness. Other popular ceramics include Chromium Nitride (CrN) and Aluminum Titanium Nitride (AlTiN).
How Material Choice Defines the Outcome
The primary goal of PVD is to impart the desirable properties of the coating material onto the surface of the substrate.
Achieving Enhanced Durability and Hardness
Hard ceramic coatings are a primary application of PVD. They dramatically increase the surface hardness and wear resistance of a part.
For example, applying a Titanium Nitride (TiN) coating to a titanium alloy part can increase its fatigue limit by over 20%. This makes it invaluable for high-performance tools, medical implants, and aerospace components.
Improving Corrosion and Oxidation Resistance
PVD creates a dense, non-porous barrier on the substrate's surface, making it highly resistant to corrosion, oxidation, and chemical attack.
Because the coating changes the surface on a molecular level, it provides a much more robust shield than traditional painting or plating, which can chip or flake away.
Creating Specific Aesthetic Finishes
PVD is widely used for creating durable and consistent decorative finishes. A variety of metals and compounds can be used to produce a spectrum of colors, from black and graphite to gold, rose gold, and bronze.
This is commonly seen on watches, faucets, and architectural hardware, where a finish must be both attractive and able to withstand daily handling.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, PVD is not without its constraints. Understanding these is critical for successful implementation.
Line-of-Sight Application
PVD is a "line-of-sight" process, meaning the vaporized coating material travels in a straight line to the substrate. This can make it challenging to achieve a uniform coating on parts with complex internal geometries or deep, narrow holes.
The Critical Role of Surface Preparation
The success of a PVD coating is highly dependent on the cleanliness and preparation of the substrate. Any surface contamination—such as oils, oxides, or dust—will prevent proper adhesion and lead to coating failure.
Thinness vs. Impact Resistance
PVD coatings are extremely thin, typically between 0.5 and 5 microns. While incredibly hard, the coating relies on the support of the substrate beneath it. A significant impact that dents or deforms the softer substrate can cause the hard coating to crack or fail.
Choosing the Right PVD Material for Your Goal
Your choice of coating material should be driven directly by your primary objective for the product.
- If your primary focus is extreme durability and wear resistance: Opt for hard ceramic coatings like Titanium Nitride (TiN), Chromium Nitride (CrN), or Aluminum Titanium Nitride (AlTiN).
- If your primary focus is a specific decorative color: Choose from a range of metals and compounds known for their aesthetic properties, such as gold, zirconium nitride (for a brass color), or titanium carbide (for a black finish).
- If your primary focus is corrosion resistance in a harsh environment: Use stable and non-reactive materials like titanium or chromium as the base for your coating.
Ultimately, selecting a PVD material is an engineering decision that balances performance, aesthetics, and cost to achieve your specific design intent.
Summary Table:
| Goal | Recommended PVD Coating Material(s) |
|---|---|
| Extreme Durability & Wear Resistance | Titanium Nitride (TiN), Chromium Nitride (CrN), Aluminum Titanium Nitride (AlTiN) |
| Decorative Color (e.g., Gold, Black) | Gold, Zirconium Nitride, Titanium Carbide |
| Corrosion & Oxidation Resistance | Titanium, Chromium |
Ready to select the perfect PVD coating material for your project? KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables for surface engineering. Our expertise ensures you achieve the precise durability, corrosion resistance, or aesthetic finish your products demand. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific substrate and coating goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Containers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Culture Dish and Evaporation Dish
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
People Also Ask
- What factors affect evaporation and condensation? Master the Science of Water's Phase Changes
- What are the 5 factors that affect the rate of evaporation? Master the Process for Your Lab
- What temperature does evaporation occur? Unlock the Secrets to Controlling the Rate of Evaporation
- What is the delta 20 rule of evaporation? Master Safe and Effective Spraying
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy



















