For processing materials described as "heavy," such as high-viscosity pastes and stiff slurries, a Colloid Mill is the preferred equipment. This type of mill excels at the smooth grinding and emulsification of semi-solid and liquid materials, which is likely what is meant by the term "weight grinding."
The term "weight grinding" is not standard, but it strongly implies the processing of dense, viscous materials rather than dry powders. The critical distinction is not the material's weight, but its state (liquid/paste vs. dry solid), which dictates whether you need high shear or high impact.
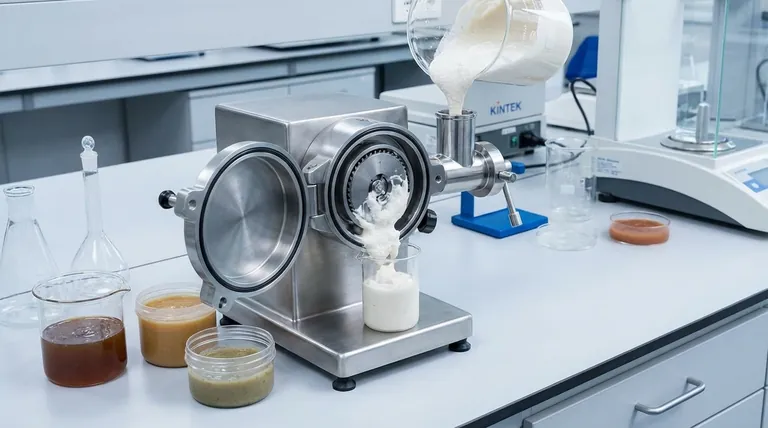

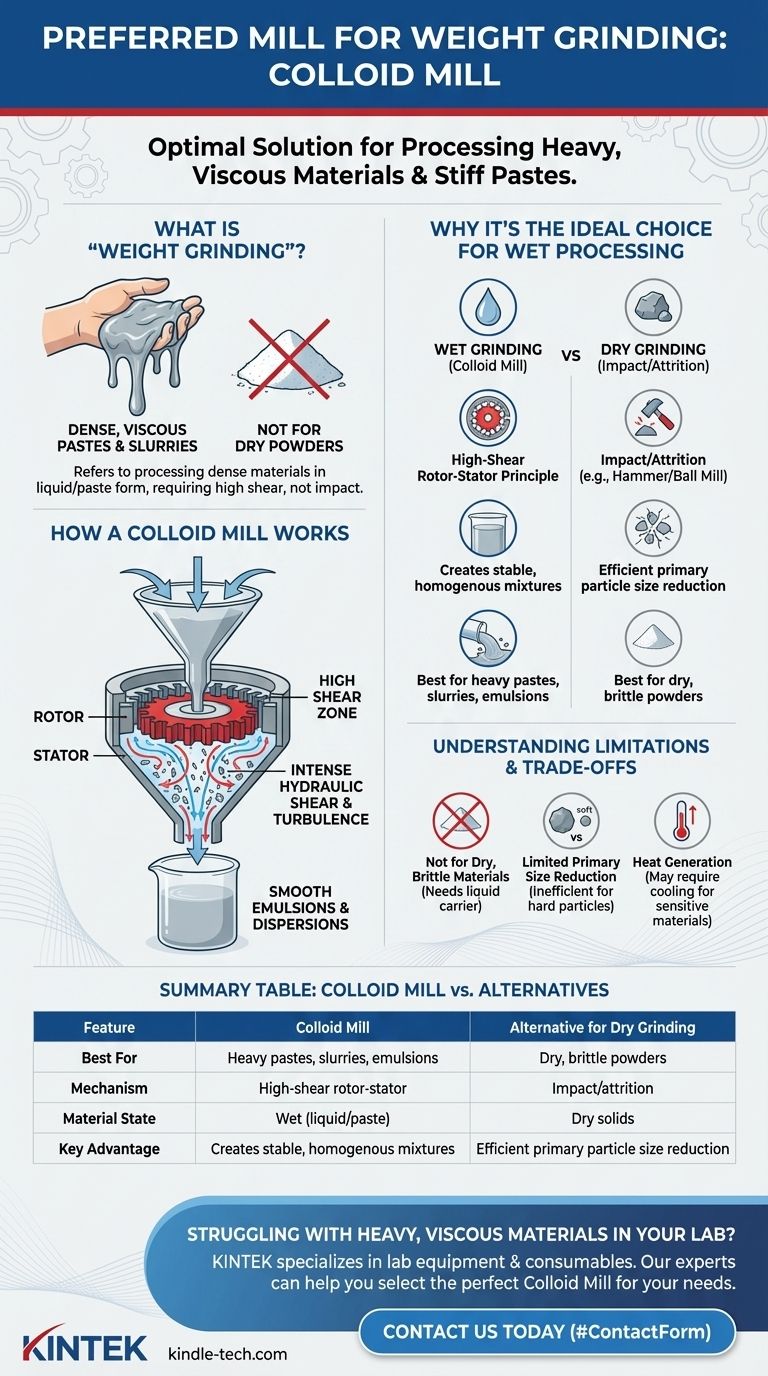
What is a Colloid Mill and How Does It Work?
A colloid mill does not grind in the traditional sense of crushing dry, brittle materials. Instead, it specializes in processing substances that are already in a liquid or paste-like form to create a stable, homogenous mixture.
The Rotor-Stator Principle
The core of a colloid mill is a high-speed rotor that spins with very fine clearance (often fractions of a millimeter) relative to a stationary part called the stator. Both the rotor and stator are typically cone-shaped and feature a pattern of grooves or teeth.
Generating High Shear, Not Impact
As the material is fed into the gap between the rotor and stator, it is subjected to intense hydraulic shear, turbulence, and mechanical tearing forces. This force is fundamentally different from the impact force used in a hammer mill or the attrition in a ball mill.
The Result: Emulsions and Dispersions
The purpose of this intense shear is to break down droplets and de-agglomerate particles suspended within a liquid. This action creates extremely fine and stable emulsions (like oil in water) or dispersions (like solids in a liquid), resulting in a smooth, uniform final product.
Why "Weight" Points to Wet Processing
The choice of mill depends entirely on whether your material is wet or dry. The reference to "stiff paste and heavier viscosity" materials clearly points toward a wet process.
Interpreting "Heavy" Materials
In an industrial processing context, a "heavy" material often refers to its consistency, not just its density. A thick, viscous slurry or paste feels heavy and is difficult to pump and mix, fitting the description perfectly.
Dry Grinding vs. Wet Grinding
Dry grinding is used for hard, brittle solids like minerals, grains, or chemicals. It uses impact, compression, and attrition to shatter particles. Equipment like ball mills, hammer mills, and jet mills are common here.
Wet grinding involves reducing particle size or creating a mixture within a liquid medium. The liquid cushions the particles, and the primary force is often shear. Colloid mills and bead mills are designed specifically for this purpose.
Understanding the Trade-offs: When NOT to Use a Colloid Mill
While excellent for its specific purpose, a colloid mill is the wrong tool for many other applications. Understanding its limitations is key to making a sound investment.
Not for Dry, Brittle Materials
A colloid mill is completely ineffective for grinding dry powders or hard, crystalline solids. It requires a liquid carrier to function. Attempting to feed it dry material will result in no grinding and potential damage to the machine.
Limited Primary Particle Reduction
While a colloid mill excels at breaking up soft agglomerates and droplets, it is not efficient at significant size reduction of hard primary particles. For example, if you need to grind hard pigment crystals suspended in a liquid from 50 microns down to 5 microns, a bead mill would be far more effective.
Heat Generation
The immense shear energy applied by a colloid mill is largely converted into heat. This can be problematic for heat-sensitive materials, such as certain pharmaceuticals or food products, and may require a jacketed, cooled unit.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct equipment, you must first define your material and your desired final product.
- If your primary focus is creating a stable emulsion or dispersion (e.g., mayonnaise, lotions, sauces, inks): A colloid mill is your ideal choice due to its high-shear homogenizing action.
- If your primary focus is grinding dry, brittle powders to a smaller size (e.g., minerals, sugar, grains): You should investigate dry grinding equipment like a hammer mill, pin mill, or ball mill.
- If your primary focus is aggressively reducing the size of hard particles within a liquid (e.g., pigments, ceramics): A bead mill, which uses grinding media to impart high energy, is likely the more suitable technology.
Ultimately, selecting the right mill comes down to matching the machine's mechanical action to your material's properties and processing objective.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Colloid Mill | Alternative for Dry Grinding |
|---|---|---|
| Best For | Heavy pastes, slurries, emulsions | Dry, brittle powders (e.g., minerals, grains) |
| Mechanism | High-shear rotor-stator principle | Impact/attrition (e.g., hammer mill, ball mill) |
| Material State | Wet (liquid/paste) | Dry solids |
| Key Advantage | Creates stable, homogenous mixtures | Efficient primary particle size reduction |
Struggling to process heavy, viscous materials in your lab? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select the perfect Colloid Mill for your high-viscosity pastes and slurries, ensuring smooth grinding and emulsification. Contact us today (#ContactForm) to enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve superior results with the right equipment!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory High Throughput Tissue Grinding Mill Grinder
- Laboratory Hybrid Tissue Grinding Mill
- Laboratory Disc Cup Vibratory Mill for Sample Grinding
- Laboratory Jar Ball Mill with Alumina Zirconia Grinding Jar and Balls
- Liquid Nitrogen Cryogenic Grinder Mill Cryomill with Screw Feeder
People Also Ask
- What is sample grinding? Achieve Accurate Analysis with Proper Sample Preparation
- What are the factors that affect grindability? Master Your Bead Mill for Optimal Particle Size
- What is the role of a laboratory-scale ball mill in the pretreatment of microalgae biomass? Boost Cell Wall Disruption
- What is the role of an agate mortar and pestle in preparing sulfur and iron oxide mixtures? Ensure Purity in Research
- How does ball milling assist in the modification of materials for biomass binders? Optimize Your Dry Electrode Performance
- Why is an intermediate grinding step necessary for solid-state synthesis? Achieving Phase Purity in Niobates
- How does a probe-type ultrasonic homogenizer facilitate C3N4 exfoliation? Enhance Surface Area for Photocatalysis
- What is the significance of using an automatic grinding and polishing machine for Boron Carbide? Achieve Mirror Finishes



















