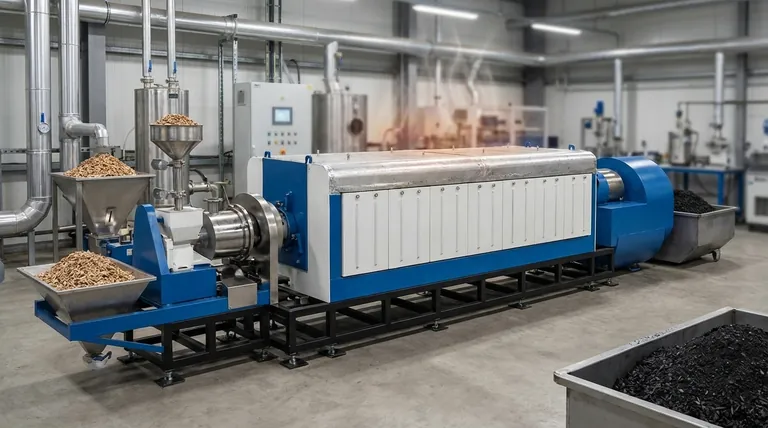
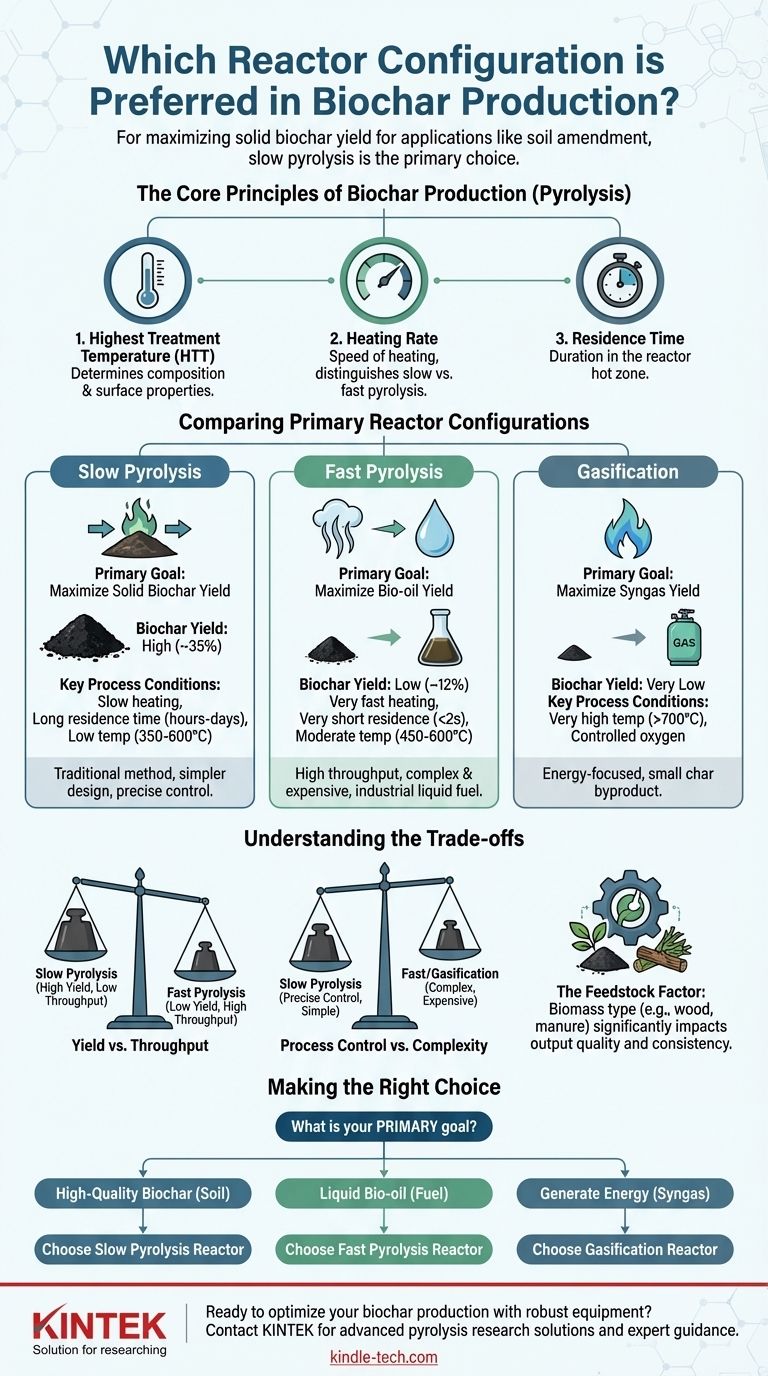
For producing biochar intended for applications like soil amendment, slow pyrolysis is the most established and widely preferred reactor configuration. This method is favored because its long residence times and lower temperatures are specifically optimized to maximize the yield of the solid biochar product, rather than liquid or gas co-products.
The choice of a reactor is not about finding a single "best" design, but about aligning the production process with your primary goal. Slow pyrolysis is preferred for maximizing the solid biochar yield, while other methods like fast pyrolysis are designed to maximize the liquid bio-oil yield.

The Core Principles of Biochar Production
To understand why a specific reactor is chosen, we must first look at the fundamental variables that control the outcome of the process. The production technique is known as pyrolysis, which involves heating biomass in a low-oxygen environment.
The Three Key Control Levers
Three main parameters dictate the final output of any pyrolysis reactor.
- Highest Treatment Temperature (HTT): This determines the chemical composition and surface properties of the final biochar. Higher temperatures generally create more porous but lower-yield char.
- Heating Rate: This is the speed at which the biomass is heated to the target temperature. It is the primary factor that distinguishes slow from fast pyrolysis.
- Residence Time: This is the duration the biomass and its vapors spend inside the hot zone of the reactor.
Comparing the Primary Reactor Configurations
The interplay of these three levers leads to distinct processes, each favoring a different primary output.
Slow Pyrolysis: Maximizing Solid Biochar Yield
This is the traditional and most common method for making biochar for agricultural and environmental uses.
The process conditions are defined by a slow heating rate and a long residence time (hours to days) at relatively low temperatures (350-600°C). This slow "cooking" process breaks down the biomass in a way that maximizes the conversion to solid carbon, resulting in the highest possible biochar yields (around 35% by weight).
Fast Pyrolysis: Prioritizing Bio-oil
This method is designed to produce liquid fuels, not solid char.
It uses a very fast heating rate and a very short vapor residence time (less than 2 seconds) at moderate temperatures (450-600°C). These conditions rapidly break down the biomass into vapors that are quickly cooled and condensed into a liquid known as bio-oil, with biochar being a co-product in much smaller quantities (around 12%).
Gasification: An Energy-Focused Process
Gasification's main goal is to create a combustible fuel gas called syngas.
This process uses very high temperatures (>700°C) and a small, controlled amount of oxygen. The primary output is syngas, with biochar being a relatively small byproduct.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a reactor configuration involves balancing competing priorities. The challenges in production often stem from not aligning the process with the desired outcome.
Yield vs. Throughput
Slow pyrolysis provides the highest yield of solid biochar but has a very low throughput, often operating in batches that take many hours.
Fast pyrolysis offers a much lower biochar yield but has an extremely high throughput, making it suitable for continuous industrial processing where bio-oil is the target product.
Process Control vs. Complexity
Slow pyrolysis reactors are generally simpler in design, allowing for precise control over the final biochar properties. This is critical for creating a consistent product for soil application.
Fast pyrolysis and gasification systems are significantly more complex and expensive to build and operate, reflecting their focus on high-throughput fuel production.
The Feedstock Factor
No matter the reactor, the type of biomass used is a critical variable. Feedstock like dense wood will produce a different biochar than leafy crop residue or manure under the exact same process conditions. Consistency in feedstock is essential for a consistent biochar product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your selection must be driven by the product you value most.
- If your primary focus is producing high-quality biochar for soil amendment: A slow pyrolysis reactor is the correct choice due to its high solid yield and controllable output.
- If your primary focus is producing liquid bio-oil as a primary product: A fast pyrolysis reactor is the necessary configuration to maximize liquid yield.
- If your primary focus is generating energy from biomass with biochar as a byproduct: Gasification is the most suitable process to maximize syngas production.
Ultimately, aligning your reactor configuration with your primary output goal is the key to successful and efficient production.
Summary Table:
| Reactor Type | Primary Goal | Biochar Yield | Key Process Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Slow Pyrolysis | Maximize Biochar | High (~35%) | Slow heating, long residence time, low temp (350-600°C) |
| Fast Pyrolysis | Maximize Bio-oil | Low (~12%) | Very fast heating, short vapor residence, moderate temp (450-600°C) |
| Gasification | Maximize Syngas | Very Low | High temp (>700°C), controlled oxygen |
Ready to produce high-quality biochar for soil amendment?
Choosing the right reactor configuration is critical for maximizing your yield and achieving consistent results. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing robust and reliable laboratory equipment for pyrolysis research and development.
Our expertise can help you:
- Optimize your process for the highest biochar yield.
- Select the right equipment for your specific feedstock and goals.
- Ensure precise control over temperature and residence time for a superior product.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can advance your biochar production. Get in touch via our contact form and let's talk about your project needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time



















