Electrolytic polishing is a highly effective finishing process primarily suited for metals and alloys that can form a stable passive layer in a specific electrolyte. While stainless steel is the most common candidate, the process is also effective for aluminum, brass, carbon steels, cobalt chrome, copper and nickel alloys, titanium, and Nitinol.
The success of electrolytic polishing depends on a material's electrical conductivity and its ability to uniformly dissolve at a microscopic level. It is not a universal solution; it is a specialized electrochemical process tailored to specific metal families.
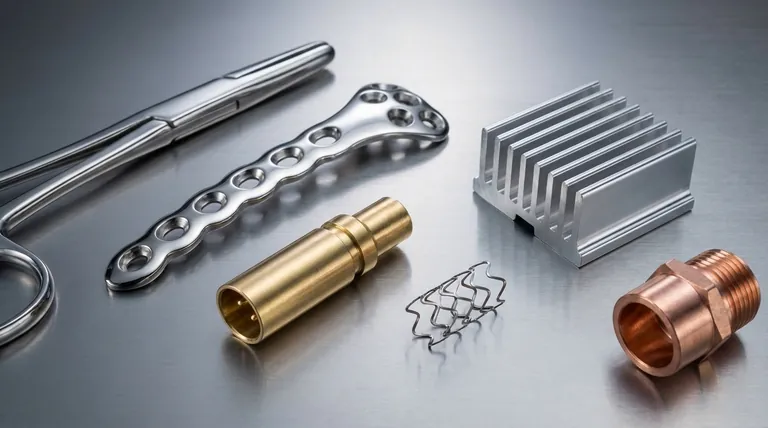

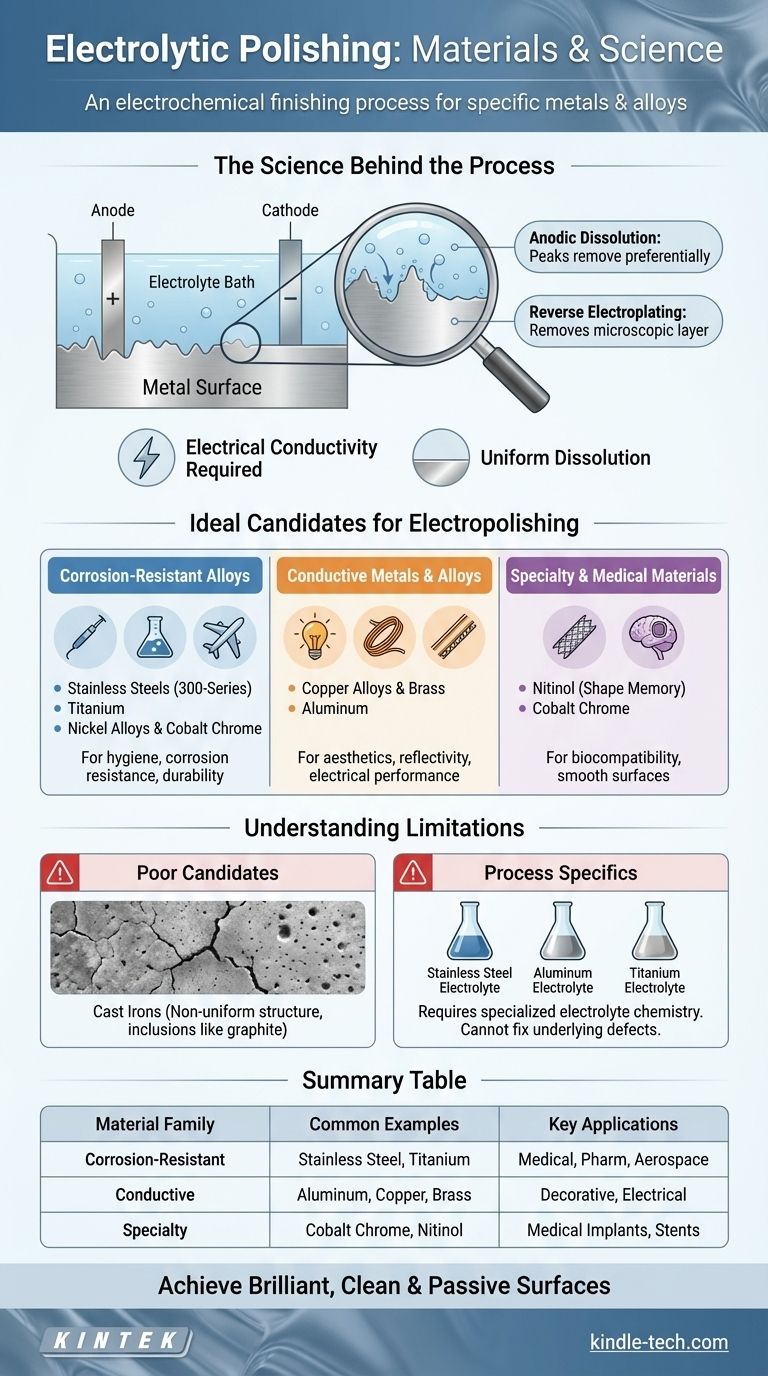
The Science Behind Material Compatibility
Electrolytic polishing is an electrochemical process, often described as the reverse of electroplating. Instead of adding a layer of material, it precisely removes a microscopic surface layer, smoothing out peaks and valleys to create a brilliant, clean, and passive surface.
Why Metal Conductivity is Essential
The process requires the part to be an anode (the positive electrode) in an electrochemical cell. An electrical current must pass through the part and into the chemical electrolyte.
Therefore, the fundamental requirement for any candidate material is electrical conductivity. Non-conductive materials like plastics or ceramics cannot be electropolished.
The Role of Anodic Dissolution
When current is applied, the metal surface begins to dissolve into the electrolyte. This dissolution happens faster on microscopic high points ("peaks") than in low points ("valleys").
This preferential removal of peaks is what creates the signature smooth, mirror-like finish. The material must be able to dissolve uniformly without creating pits or intergranular attack, which is heavily dependent on its metallurgical structure.
Alloy Composition is Critical
Not all grades of a metal are equally suited for electropolishing. For instance, 300-series stainless steels (like 304 and 316) are ideal because their high chromium and nickel content promotes a stable, passive film.
In contrast, some 400-series stainless steels can be more challenging due to a different crystalline structure and lower nickel content. The success of the process is directly tied to the specific alloy and its homogeneity.
Key Material Families for Electropolishing
Different metals require different electrolyte chemistries and operating parameters, but several families are consistently good candidates.
Corrosion-Resistant Alloys
This is the largest group of electropolished materials.
- Stainless Steels: Used for hygiene, corrosion resistance, and deburring in medical, pharmaceutical, and food processing industries.
- Titanium: Valued in aerospace and medical implants for its high strength-to-weight ratio and superior biocompatibility.
- Nickel Alloys & Cobalt Chrome: Used in high-temperature, high-stress environments like jet engines and for medical implants due to their extreme durability and corrosion resistance.
Conductive Metals and Alloys
This group is often polished for aesthetic appeal, reflectivity, or to improve electrical performance.
- Copper Alloys & Brass: Electropolishing removes surface oxides and impurities, improving electrical conductivity and providing a bright, decorative finish.
- Aluminum: Used to create a highly reflective, mirror-like surface for lighting components and decorative trim.
Specialty and Medical Materials
- Nitinol: A nickel-titanium "shape memory" alloy used for medical devices like stents. Electropolishing is critical for creating a smooth, clean, and biocompatible surface free of micro-cracks.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Electropolishing is a powerful tool, but it is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Materials That Are Poor Candidates
Materials that lack a uniform, single-phase structure do not polish well. Cast irons, for example, contain inclusions like graphite flakes that dissolve at different rates than the surrounding iron matrix, resulting in a pitted, uneven surface.
Process-Specific Electrolytes
A material's compatibility is tied to the availability of a suitable electrolyte. The chemistry used for stainless steel is entirely different from what is required for aluminum or titanium. A mismatch will result in pitting, etching, or no polishing at all.
The Myth of "Fixing" Poor-Quality Material
Electropolishing enhances the surface of a quality material; it cannot fix underlying metallurgical defects. Issues like porosity, large non-metallic inclusions, or seams in the base metal will often be exposed and even exaggerated by the process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your material and finishing process based on the final performance you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is hygiene and corrosion resistance: Austenitic stainless steels (304, 316L) and titanium are the industry standard for electropolishing.
- If your primary focus is biocompatibility: Titanium, cobalt chrome, and Nitinol are superior choices, as electropolishing removes contaminants and creates a highly passive surface.
- If your primary focus is aesthetics or reflectivity: Aluminum and copper alloys like brass provide excellent results when processed with the correct electrolytes.
Ultimately, the suitability of a material for electropolishing depends on its chemical composition, metallurgical uniformity, and your end-use application.
Summary Table:
| Material Family | Common Examples | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion-Resistant Alloys | Stainless Steel (304, 316), Titanium | Medical, Pharmaceutical, Aerospace |
| Conductive Metals & Alloys | Aluminum, Copper, Brass | Decorative, Electrical, Lighting |
| Specialty & Medical Materials | Cobalt Chrome, Nitinol | Medical Implants, Stents |
Need the perfect surface finish for your metal components?
Electropolishing is a specialized process that requires the right equipment and expertise. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for precise electrochemical processes. Whether you're working with stainless steel, titanium, or specialized alloys, our solutions help you achieve brilliant, clean, and passive surfaces every time.
Enhance your lab's capabilities—contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- Lab Plastic PVC Calender Stretch Film Casting Machine for Film Testing
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- How should the thin-layer spectroelectrochemical cell be handled to ensure its longevity? Expert Maintenance Tips
- Are there any chemical substances that should be avoided with an all-PTFE electrolytic cell? Know the Critical Limits for Your Lab
- What is the technical significance of the aging process in an electrolytic cell? Refine Your Nanotube Structures
- What are the primary functions of a high-performance electrolytic cell in the eCO2R process? Optimize Your Lab Results
- How should an all-PTFE electrolytic cell be stored after use? Expert Maintenance Tips for Long-Lasting Performance
- What role do molten salt electrolyzers play in ammonia synthesis? Powering the Lithium-Mediated Cycle
- What is the electro deposition method? A Guide to Superior, Uniform Coatings
- How does a two-electrode DC system influence coating quality? Achieve Dense Trivalent Chromium on 304L Stainless Steel



















