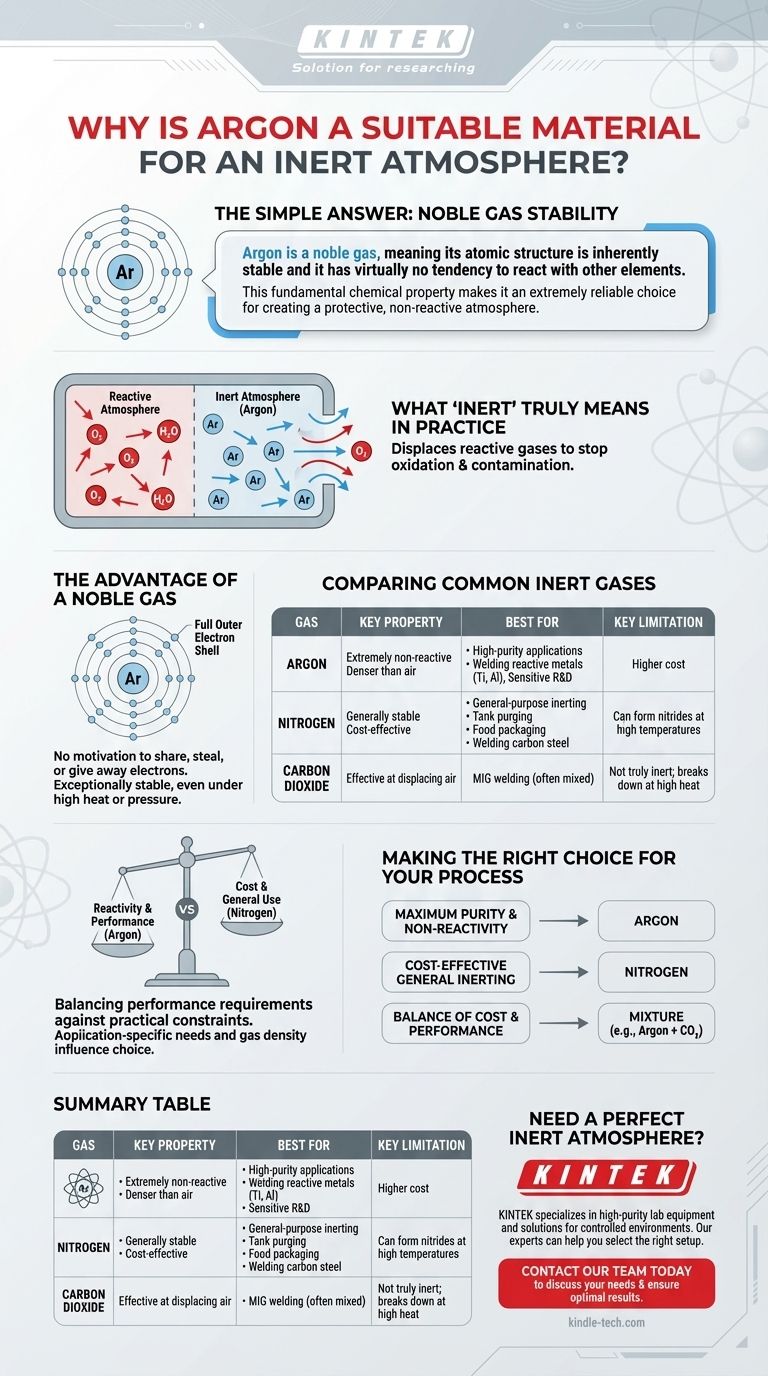
The simple answer is that argon is a noble gas, meaning its atomic structure is inherently stable and it has virtually no tendency to react with other elements. This fundamental chemical property makes it an extremely reliable choice for creating a protective, non-reactive atmosphere.
The suitability of a gas for an inert atmosphere is determined by its chemical reactivity. Argon is an ideal choice because its full outer electron shell makes it one of the least reactive elements available, ensuring it will not interfere with sensitive processes.

What "Inert" Truly Means in Practice
The core purpose of using an inert atmosphere is to prevent unwanted chemical reactions, primarily oxidation and contamination, by displacing the reactive oxygen and moisture in the ambient air.
The Principle of Reactivity
All chemical reactions are driven by the exchange or sharing of electrons between atoms. Gases that are considered "reactive," like oxygen, readily participate in these exchanges.
An "inert" gas is one that resists this process. By flooding a chamber or workspace with an inert gas, you physically push out the reactive gases, effectively stopping reactions like rust or combustion from ever starting.
The Advantage of a Noble Gas
The noble gases—including helium, neon, and argon—are in a special class of elements. Their defining characteristic is a full outer shell of electrons.
Because this shell is already complete, argon has no chemical motivation to share, steal, or give away electrons. This makes it exceptionally stable and non-reactive, even under conditions like high heat or pressure where other gases might break down.
Comparing Common Inert Gases
While argon is highly effective, it isn't the only option. The choice often depends on the specific requirements and budget of the application.
Argon: The High-Purity Standard
Argon's extreme non-reactivity makes it the go-to choice for highly sensitive applications. It is significantly denser than air, allowing it to form a stable, protective "blanket" over a work area, which is particularly useful in processes like TIG welding.
Nitrogen: The Cost-Effective Workhorse
Nitrogen (N₂) is the most common gas in our atmosphere and is much less expensive to produce than argon. It is also quite stable due to the strong triple bond holding its two atoms together.
However, this bond can be broken under extreme heat. In certain high-temperature applications, such as welding titanium or stainless steel, nitrogen can react with the metal to form undesirable nitrides, compromising the material's integrity.
Carbon Dioxide: A Different Kind of Shield
Carbon dioxide (CO₂) is sometimes used, especially in MIG welding. It is not truly inert and can break down into oxygen and carbon monoxide at high temperatures. While it effectively displaces air, its reactive potential makes it unsuitable for processes requiring true chemical inertness.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right gas involves balancing performance requirements against practical constraints. The most "inert" gas is not always the most logical choice.
Reactivity vs. Cost
This is the central trade-off. Argon provides superior chemical protection but comes at a higher price point. Nitrogen offers excellent general-purpose inerting for a fraction of the cost.
Application-Specific Needs
For welding reactive metals like titanium, magnesium, or aluminum, argon's non-reactivity is non-negotiable. For general-purpose purging of tanks or welding common carbon steel, the cost savings of nitrogen often outweigh the minimal risk of reaction.
Gas Density and Behavior
Argon's high density makes it excellent for shielding open-air work, as it settles and displaces oxygen effectively. Nitrogen, being slightly lighter than air, diffuses more quickly and is better suited for filling enclosed containers or systems from the top down.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your final decision should be based on the sensitivity of your materials and the goals of your process.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity and non-reactivity: Argon is the definitive choice for sensitive electronics manufacturing, scientific research, and welding reactive metals.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for general inerting: Nitrogen is the industry standard for purging tanks, food packaging, and welding non-reactive metals.
- If your primary focus is a balance of cost and performance in welding: A mixture of argon and another gas (like CO₂) is often used to optimize arc stability and weld quality while managing costs.
Ultimately, choosing the right inert gas is about matching the chemical stability of the gas to the precise sensitivity of your application.
Summary Table:
| Gas | Key Property | Best For | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Argon | Extremely non-reactive (noble gas), denser than air | High-purity applications, welding reactive metals (Ti, Al), sensitive R&D | Higher cost compared to nitrogen |
| Nitrogen | Generally stable, cost-effective | General-purpose inerting, tank purging, food packaging, welding carbon steel | Can form nitrides with some metals at high temperatures |
| Carbon Dioxide | Effective at displacing air | MIG welding (often mixed with argon) | Not truly inert; breaks down at high heat |
Need to create a perfect inert atmosphere for your process?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-purity lab equipment and consumables, including solutions for creating controlled environments. Whether your application in welding, manufacturing, or research requires the ultimate purity of argon or the cost-effectiveness of nitrogen, our experts can help you select the right setup for your specific materials and goals.
Contact our team today to discuss your inert atmosphere needs and ensure optimal results for your sensitive processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is meant by inert atmosphere? A Guide to Preventing Oxidation & Ensuring Safety
- How do you make an inert atmosphere? Master Safe, Pure Processes with Inerting
- What gases are used in inert atmospheres? Choose the Right Gas for Non-Reactive Environments
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes
- How we can develop inert atmosphere for a chemical reaction? Master Precise Atmospheric Control for Your Lab



















