Sputter coating is a vacuum deposition technique used to apply an exceptionally uniform, dense, and durable thin film of material onto a surface. This process operates on an atomic level, providing a layer of precision and control that is essential for a wide range of high-performance applications, from advanced optics and semiconductors to medical implants.
The core reason for using sputter coating is its ability to achieve superior film quality. Unlike simple spraying or dipping, sputtering uses an energized plasma to physically eject atoms from a source material, ensuring they deposit onto a substrate with unmatched consistency and adhesion.
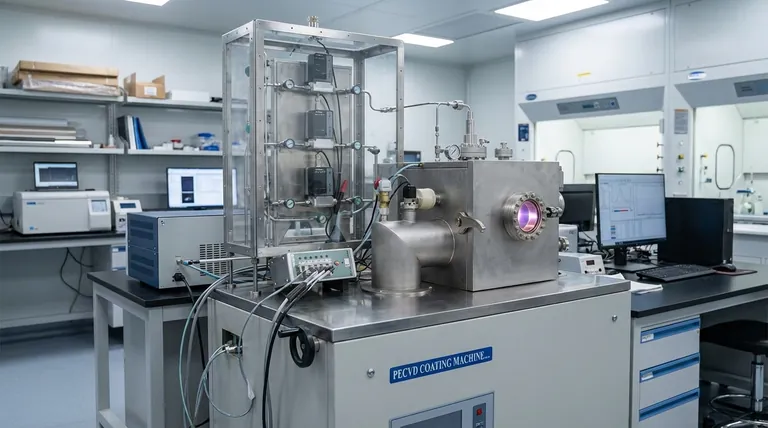

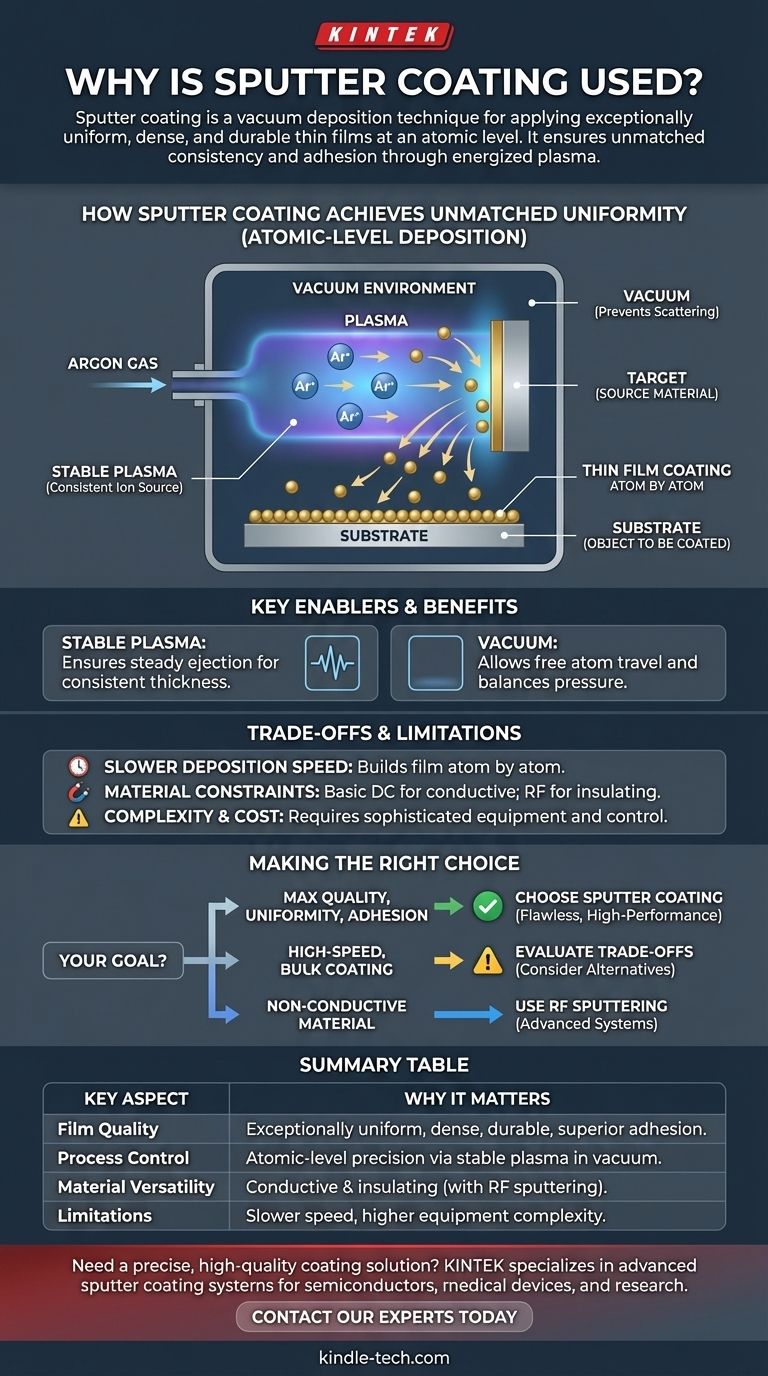
How Sputter Coating Achieves Unmatched Uniformity
The quality of a sputtered film is a direct result of its highly controlled physical process. It is not a chemical reaction but a momentum transfer, much like a microscopic game of billiards.
The Core Principle: Atomic-Level Deposition
Sputtering begins by placing a substrate (the object to be coated) and a target (the source material for the coating) inside a vacuum chamber.
An inert gas, typically Argon, is introduced into the chamber.
A strong electric field is applied, which strips electrons from the Argon atoms, creating a plasma—a glowing, ionized gas consisting of positive ions and free electrons.
These positively charged Argon ions are accelerated with great force into the negatively charged target, striking its surface and physically knocking off, or "sputtering," individual atoms. These ejected atoms then travel through the vacuum and deposit onto the substrate, building the coating one atom at a time.
The Role of Stable Plasma
The stable plasma created during the process is the engine of sputter coating. It provides a consistent and controllable source of high-energy ions.
This stability ensures that atoms are ejected from the target at a steady rate and from all over its surface, which is the key to achieving a highly uniform and consistent film thickness across the entire substrate.
Why a Vacuum is Non-Negotiable
The process must occur in a vacuum for two critical reasons. First, it ensures the ejected target atoms can travel freely to the substrate without colliding with air molecules, which would scatter them and ruin the film's uniformity.
Second, the vacuum pressure must be perfectly balanced. If it's too low, there won't be enough Argon atoms to sustain the plasma. If it's too high, the ejected atoms will collide too frequently with gas ions, preventing them from reaching the substrate efficiently.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, sputter coating is not the ideal solution for every scenario. Understanding its limitations is crucial for making an informed decision.
Deposition Speed
The fundamental nature of sputtering—building a film atom by atom—means it can be a relatively slow process compared to other coating methods like thermal evaporation.
Simple DC diode sputtering, the original method, suffers from a particularly low deposition rate. While modern techniques have improved this, speed remains a key consideration.
Material and Substrate Constraints
The most basic form of sputtering (DC sputtering) works well for conductive target materials like noble metals (gold, platinum) but cannot sputter insulating materials.
Specialized techniques, such as RF (Radio Frequency) sputtering, are required to deposit non-conductive materials, adding complexity to the equipment and process.
Process Complexity and Cost
Sputter coating requires sophisticated equipment to create and maintain the vacuum and generate the plasma.
This complexity, combined with the need for precise control over gas pressure and power, makes it a more intricate and often more expensive process than simpler coating alternatives.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting sputter coating depends entirely on balancing the need for quality against constraints like speed, cost, and material type.
- If your primary focus is maximum coating uniformity, density, and adhesion: Sputter coating is the superior choice for creating flawless, high-performance thin films for demanding applications.
- If your primary focus is high-speed, bulk coating on simple shapes: You may need to evaluate the trade-off between sputtering's quality and its slower deposition rates.
- If your primary focus is coating a non-conductive or insulating material: Basic DC sputtering is not an option; you must explore more advanced sputtering systems designed for these materials.
Ultimately, sputter coating is chosen when the precision and quality of the final film are more critical than any other factor.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Why It Matters for Sputter Coating |
|---|---|
| Film Quality | Creates exceptionally uniform, dense, and durable thin films with superior adhesion |
| Process Control | Uses stable plasma in a vacuum for atomic-level precision and consistency |
| Material Versatility | Capable of coating conductive and insulating materials (with RF sputtering) |
| Limitations | Slower deposition speed and higher equipment complexity compared to simpler methods |
Need a precise, high-quality coating solution for your laboratory applications? KINTEK specializes in advanced sputter coating systems and lab equipment designed to deliver the uniform, durable thin films required for semiconductors, medical devices, and research. Our expertise ensures you get the right equipment for your specific material and performance needs. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can enhance your coating processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- How do PECVD systems improve DLC coatings on implants? Superior Durability and Biocompatibility Explained
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- Can plasma enhanced CVD deposit metals? Why PECVD is rarely used for metal deposition
- Why does a PECVD vacuum system require both a rotary vane and turbo pump? Ensure High-Purity Coatings
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods



















