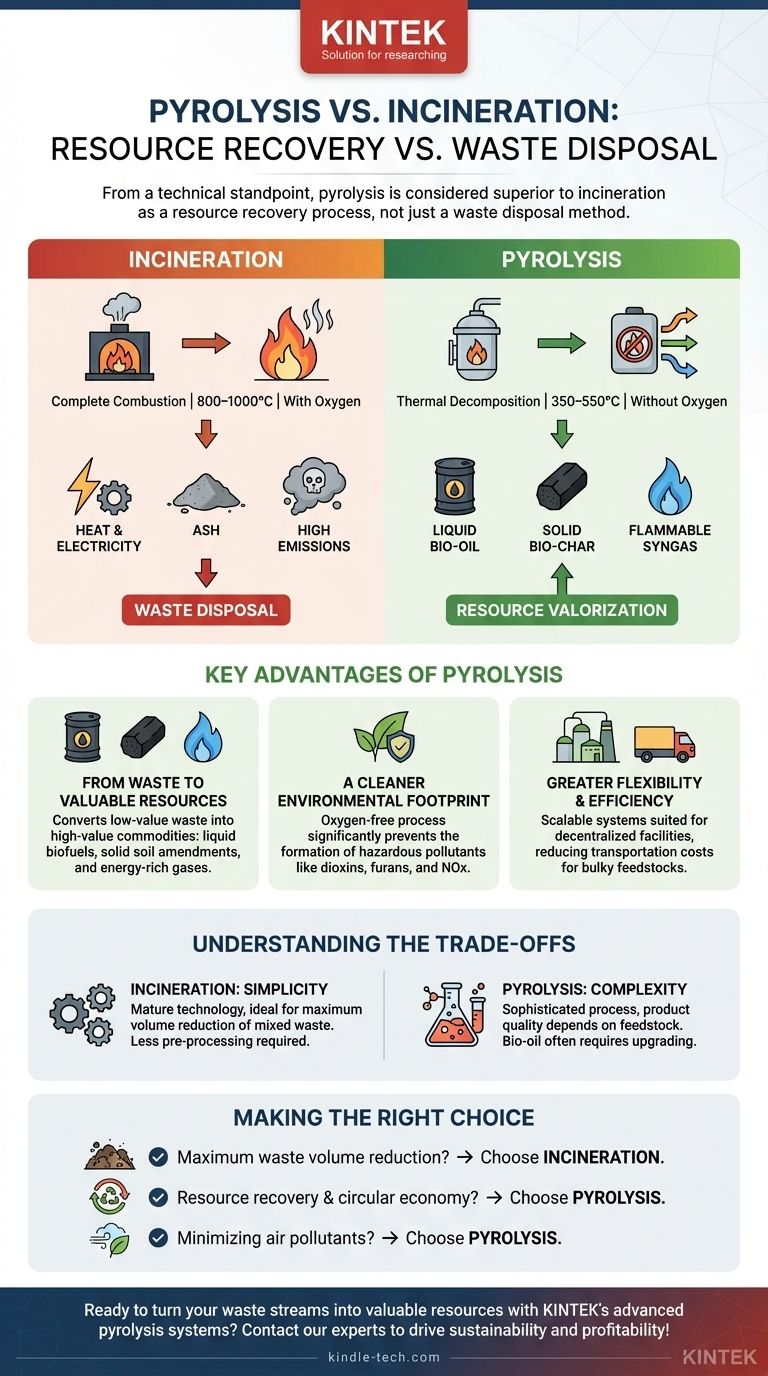
From a technical standpoint, pyrolysis is considered superior to incineration because it is a resource recovery process, not just a waste disposal method. While incineration completely combusts waste to generate heat, pyrolysis uses heat in an oxygen-free environment to break down waste into valuable new products like liquid biofuels, solid bio-char, and flammable syngas, all while producing significantly fewer harmful emissions.
Incineration is a waste disposal technology that primarily aims to reduce volume and recover energy as heat. Pyrolysis is a waste valorization technology that transforms waste into valuable, storable resources. The "better" choice depends entirely on whether the goal is simple disposal or creating new value.

The Fundamental Difference: Oxygen and Temperature
The core distinction between these two thermal processes comes down to the presence of oxygen. This single variable changes the entire chemical outcome.
How Incineration Works
Incineration is complete combustion. It involves heating waste materials to very high temperatures (800–1000°C) in the presence of a large amount of oxygen.
This process rapidly breaks all chemical bonds and releases the stored energy as heat. This heat is then used to boil water, create steam, and turn a turbine to generate electricity. The original material is destroyed.
How Pyrolysis Works
Pyrolysis is thermal decomposition. It involves heating organic materials to lower temperatures (350–550°C) in a sealed, oxygen-free environment.
Without oxygen, the material cannot burn. Instead, the heat breaks down the complex organic polymers into smaller, more valuable molecules. This is less like burning and more like "cooking" the waste to separate it into its useful components: a liquid bio-oil, a solid bio-char, and a gaseous syngas.
Key Advantages of Pyrolysis
The oxygen-free nature of pyrolysis creates several distinct advantages over traditional incineration, shifting the focus from waste destruction to resource creation.
From Waste to Valuable Resources
The primary benefit of pyrolysis is its ability to convert low-value waste into high-value commodities. Incineration produces ash and heat; pyrolysis produces a portfolio of useful products.
- Bio-oil: This liquid can be refined into transportation fuels, chemicals, or used directly for heat and power generation. It is easily stored and transported, unlike raw biomass.
- Bio-char: This stable, carbon-rich solid is a valuable soil amendment that improves water retention and agricultural fertility. It also serves as a method of long-term carbon sequestration.
- Syngas: This mixture of flammable gases (primarily hydrogen and carbon monoxide) is captured and can be used on-site to provide energy for the pyrolysis process itself, making it highly energy-efficient.
A Cleaner Environmental Footprint
The absence of oxygen fundamentally changes the emissions profile. Incineration, by its nature, produces oxides.
Because there is no oxygen in the pyrolysis reactor, the formation of hazardous pollutants like dioxins, furans, and nitrogen oxides (NOx) is largely prevented. Incinerators require complex and expensive flue gas scrubbing systems to remove these toxins, whereas pyrolysis avoids creating them in the first place.
Greater Flexibility and Efficiency
Pyrolysis systems can be deployed effectively at various scales. They are well-suited for smaller, decentralized facilities located closer to the source of waste, such as farms or remote communities.
This reduces transportation costs for bulky feedstocks like biomass and agricultural waste. By converting this waste into energy-dense bio-oil on-site, it becomes much cheaper to transport the resulting energy.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While pyrolysis has clear advantages in resource recovery, it is not a universally perfect solution. Objectivity requires acknowledging where incineration still holds a place.
The Simplicity of Incineration
Incineration is a mature, well-understood technology. Its primary goal is simple: maximum waste volume reduction. For mixed, unsorted municipal solid waste, it is a robust and direct disposal method that requires less pre-processing than pyrolysis often does.
The Complexity of Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is a more sophisticated chemical process. The quality of the end products, particularly the bio-oil, is highly dependent on the feedstock composition and process parameters.
Furthermore, bio-oil is not a "drop-in" replacement for petroleum diesel. It is acidic and unstable, and it typically requires additional industrial upgrading (refining) before it can be used in standard engines.
Economic Viability
The business case for incineration is straightforward: you are paid to dispose of waste (tipping fees) and you sell electricity. The economics of pyrolysis are more complex, as they depend on creating stable markets for its outputs—bio-oil, bio-char, and syngas—whose values can fluctuate.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting between pyrolysis and incineration is a strategic decision that hinges on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum waste volume reduction with established technology: Incineration is a direct and proven method, especially for heterogeneous municipal solid waste where sorting is impractical.
- If your primary focus is resource recovery and supporting a circular economy: Pyrolysis is the superior choice, capable of transforming specific organic waste streams into valuable fuels, chemicals, and soil amendments.
- If your primary focus is minimizing air pollutants like dioxins and oxides: Pyrolysis offers a significant advantage due to its oxygen-free process, which inherently avoids the creation of many combustion-related toxins.
Ultimately, selecting the right technology requires a clear-eyed assessment of whether you are trying to simply dispose of waste or strategically create new value from it.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Incineration | Pyrolysis |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Complete combustion with oxygen | Thermal decomposition without oxygen |
| Primary Goal | Waste volume reduction & heat recovery | Resource recovery & valorization |
| Key Products | Heat, electricity, ash | Bio-oil, bio-char, syngas |
| Emissions | Produces dioxins, furans, NOx (requires scrubbing) | Significantly fewer harmful pollutants |
| Temperature | 800–1000°C | 350–550°C |
Ready to turn your waste streams into valuable resources? KINTEK specializes in advanced pyrolysis systems and lab equipment designed for efficient resource recovery. Whether you're processing biomass, plastics, or agricultural waste, our solutions help you produce bio-oil, bio-char, and syngas while minimizing emissions. Contact our experts today to explore how pyrolysis can drive sustainability and profitability for your laboratory or facility!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What temperature is tube annealing? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges for Optimal Results
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- How do you clean a tubular furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan



















