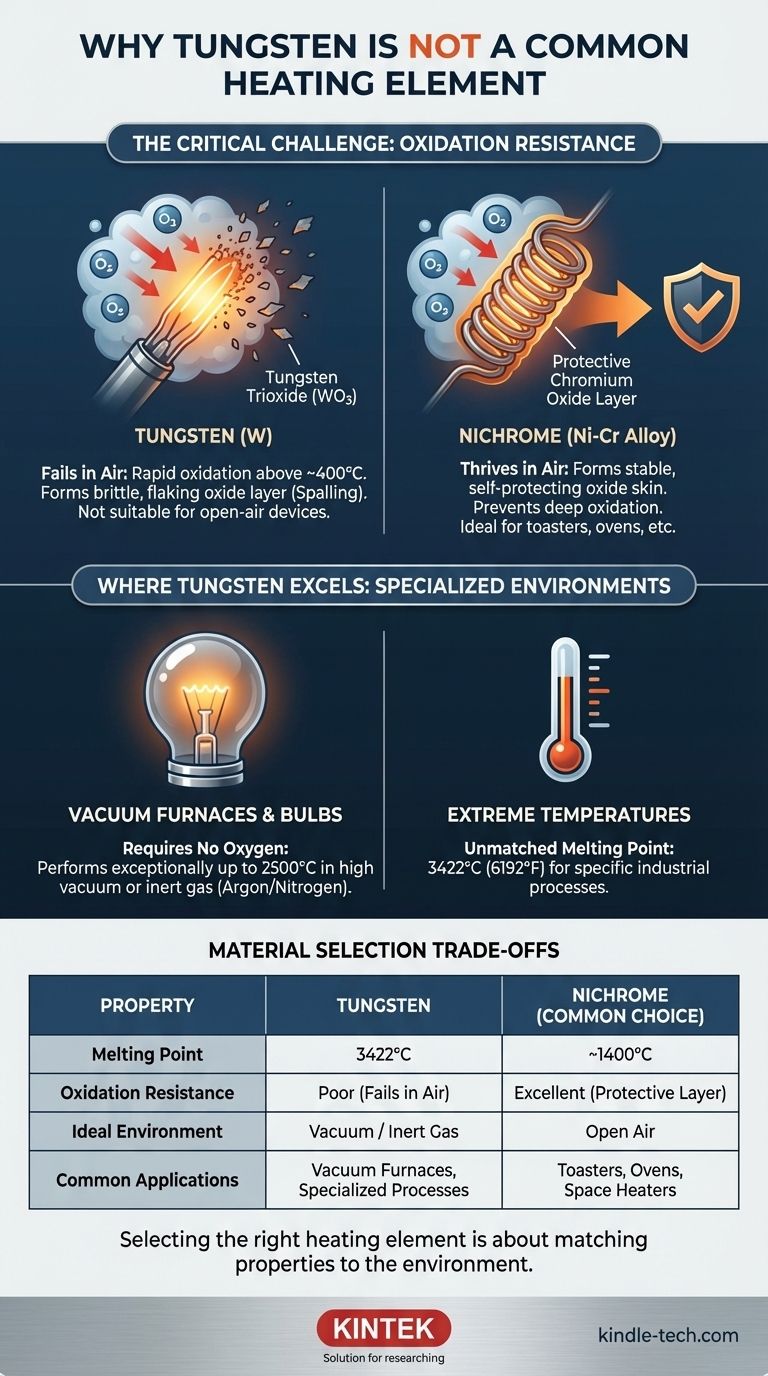
At its core, tungsten is not used for common heating elements because it reacts catastrophically with oxygen at high temperatures. While it has an exceptionally high melting point, it rapidly oxidizes and disintegrates when heated in open air, making it unsuitable for applications like toasters, ovens, or space heaters.
The ideal material for a heating element is not simply the one with the highest melting point, but the one that can best survive its specific operating environment. Tungsten is a champion in a vacuum but fails quickly in the open air where most common heating elements are needed.

The Critical Role of Oxidation Resistance
The fundamental challenge for any heating element is not just getting hot, but staying intact while hot. This is primarily a battle against oxygen.
How Common Heating Elements Work
Most heating elements you encounter daily—in a stove, toaster, or hair dryer—operate directly in the air.
They function by passing an electric current through a material with high electrical resistance, generating heat. The key is that this material must be able to withstand repeated cycles of heating and cooling in an oxygen-rich environment without breaking down.
Tungsten's Reaction with Air
Tungsten has a remarkable melting point of 3422°C (6192°F), but its weakness is oxidation. When heated above approximately 400°C (750°F) in the presence of air, it begins to form tungsten trioxide.
This oxide layer is brittle, non-protective, and flakes off easily. This process, known as spalling, rapidly eats away at the tungsten element until it fails completely.
The Nichrome Alternative: A Self-Protecting Alloy
This is why alloys like Nichrome (a blend of nickel and chromium) dominate the market for common heating elements.
When Nichrome is heated, it also oxidizes. However, it forms a thin, stable, and highly adherent outer layer of chromium oxide. This passive layer acts as a protective skin, preventing oxygen from reaching the metal underneath and allowing the element to have a long and reliable service life in open air.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Where Tungsten Is Used
Tungsten's properties make it an exceptional heating element, but only when its critical weakness—oxidation—is managed. This means it is reserved for specialized, controlled environments.
The Need for a Vacuum or Inert Gas
To use tungsten effectively as a heating element, it must be shielded from oxygen. This is achieved by placing it inside a vacuum or enclosing it in an inert gas like argon or nitrogen.
As your reference material notes, tungsten performs exceptionally well at extreme temperatures (up to 2500°C) in a high vacuum, an environment where an alloy like Nichrome would fail.
High-Temperature Industrial Furnaces
The primary industrial use for tungsten heating elements is in vacuum furnaces. These are used for processes like sintering, annealing, and brazing materials that require extremely high temperatures without atmospheric contamination.
Incandescent Light Bulbs
The most classic example was the filament in an incandescent light bulb. The tungsten filament was heated to the point of glowing inside a sealed glass bulb filled with an inert gas. This protected the filament from oxidation, allowing it to function for hundreds or thousands of hours.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a heating element material is a direct trade-off between the required temperature and the operating environment.
- If your primary focus is reliability in open air for consumer or standard industrial applications: A self-protecting alloy like Nichrome is the definitive choice due to its superior oxidation resistance.
- If your primary focus is reaching extreme temperatures above 1200°C in a controlled environment: Tungsten is an excellent choice, provided you can create a vacuum or use an inert gas atmosphere to protect it.
Ultimately, material selection is about precisely matching a material's properties to the demands of its environment.
Summary Table:
| Property | Tungsten | Nichrome (Common Choice) |
|---|---|---|
| Melting Point | 3422°C (6192°F) | ~1400°C (2552°F) |
| Oxidation Resistance | Poor (fails above 400°C in air) | Excellent (forms protective chromium oxide layer) |
| Ideal Environment | Vacuum or inert gas (e.g., argon) | Open air |
| Common Applications | Vacuum furnaces, specialized high-temperature processes | Toasters, ovens, space heaters, industrial heaters |
Need a reliable heating solution for your lab? Selecting the right heating element is critical for performance and safety. At KINTEK, we specialize in lab equipment and consumables, offering expert guidance to match your specific temperature and environmental requirements. Whether you need standard heating elements for open-air applications or specialized solutions for controlled atmospheres, we have the expertise to help. Contact our experts today to optimize your lab's heating systems!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Thermally Evaporated Tungsten Wire for High Temperature Applications
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
People Also Ask
- Why are tungsten-rhenium (W/Re) thermocouples selected for monitoring the combustion synthesis of ferroalloys? - Up to 2400°C
- What should heating element be made of? A Guide to High-Temp, Durable Materials
- How does the placement of K-type or R-type thermocouples affect temperature control? Ensure Precise Pyrolysis Results
- What is the life expectancy of a heating element? Maximize Lifespan with Proper Care
- What is the design and application of PTC surface heaters? Optimize Direct Contact Heating for Laboratory Precision
- What are the factors on which heat produced in a heating element depends? Master Joule's Law for Precise Control
- How does the heating element work? Mastering Heat Transfer for Your Lab Equipment
- How does an armored K-type thermocouple ensure the repeatability of experimental results? Achieve Precision in Nitriding



















