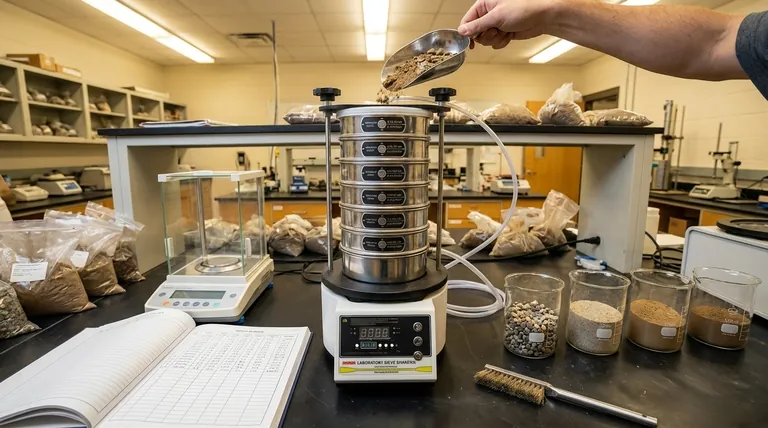
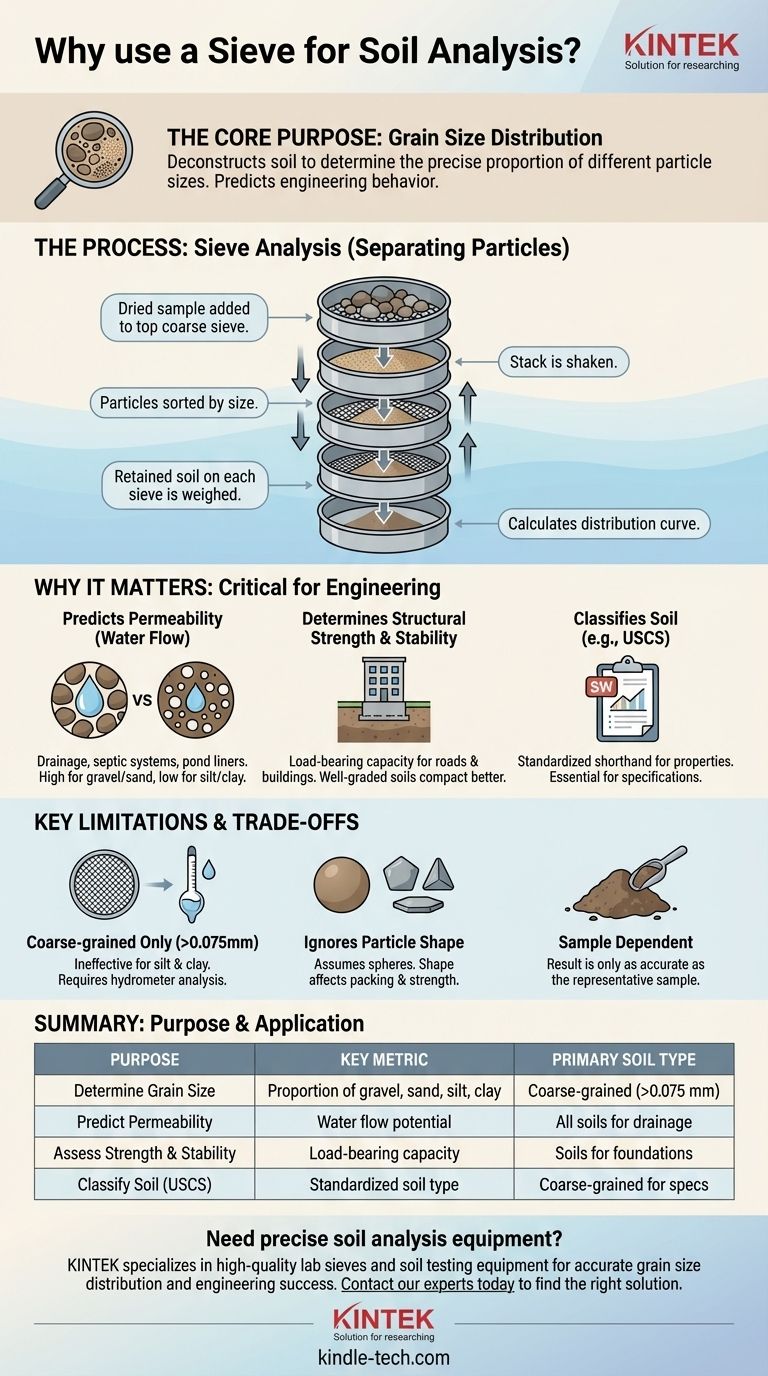
In soil analysis, a sieve is used for one primary purpose: to perform a sieve analysis. This is the foundational technique for determining the grain size distribution of a soil sample, which means figuring out the precise proportion of different sized particles like gravel and sand.
Using a sieve is not about cleaning the soil; it's about deconstructing it. By separating particles by size, you uncover the soil's fundamental physical makeup, which allows you to predict its engineering behavior—specifically its strength, stability, and ability to manage water.

What Sieve Analysis Actually Measures
A sieve analysis is a straightforward, mechanical process that yields critical data about a soil's composition. It's the first step in understanding how that soil will behave under real-world conditions.
Separating Particles by Size
The process involves passing a dried soil sample through a stack of nested sieves. Each sieve in the stack has a screen with progressively smaller openings, from coarse on top to fine at the bottom.
As the stack is shaken, soil particles are sorted by size. The largest particles are retained on the top sieves, while the smallest pass through to the lower ones.
Quantifying the Grain Size Distribution
After shaking, the soil retained on each sieve is weighed. This data is used to calculate the percentage of the total sample that falls within specific size ranges.
The result is a grain size distribution curve. This graph is the universal language for describing the makeup of coarse-grained soil to other engineers and geologists.
The Limit of Sieving
Sieve analysis is highly effective for coarse-grained soils—namely sand and gravel. These are particles with a diameter greater than 0.075 mm.
For finer particles like silt and clay, the physical process of sieving becomes impractical. Another method, such as a hydrometer analysis, is required to determine the grain size distribution of these fine-grained soils.
Why Grain Size Distribution is Critical
Knowing the proportion of sand, gravel, and finer particles is essential because it directly dictates the soil's most important physical properties. This data moves you from guesswork to predictable engineering.
Predicting Water Flow (Permeability)
Soils dominated by large, coarse particles (like gravel and clean sand) have large voids between them. This results in high permeability, meaning water flows through them easily. This is ideal for drainage applications.
Conversely, soils with a high percentage of fine particles have small voids, leading to low permeability. They retain water, making them suitable for applications like pond liners or core material for dams.
Determining Structural Strength and Stability
The load-bearing capacity of a soil is heavily influenced by its grain size. Coarse-grained soils generally have higher shear strength and are better at supporting structural loads from buildings, roads, and embankments.
The distribution also determines how well the soil can be compacted. A "well-graded" soil, with a good mix of particle sizes, can be compacted to a dense, stable state with few voids.
Classifying the Soil for Engineering Use
Sieve analysis is a mandatory step for classifying coarse-grained soils according to standards like the Unified Soil Classification System (USCS).
This classification provides a standardized shorthand for a soil's properties. An engineer who sees a soil classified as "SW" (well-graded sand) instantly knows its general strength, drainage, and compaction characteristics without needing to see the raw data.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While fundamental, sieve analysis is not a complete picture of a soil's properties. Its value depends on understanding its limitations.
The 0.075 mm Cutoff
The most significant limitation is that sieving is only for coarse-grained soils. If a sample contains a significant amount of silt or clay, a sieve analysis alone will be incomplete and potentially misleading. A hydrometer test is necessary for the finer fraction.
Particle Shape is Ignored
Sieve analysis inherently treats particles as if they are spheres. In reality, particles can be angular, rounded, or flat. Particle shape affects how they pack together and can influence strength and permeability in ways that a simple size analysis won't capture.
The Result is Only as Good as the Sample
The analysis is performed on a relatively small amount of soil. If that sample is not truly representative of the overall soil conditions at the site, the results, no matter how precise, will be useless for making accurate design decisions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your reason for performing a sieve analysis is directly tied to the problem you need to solve with the soil.
- If your primary focus is foundation design or road construction: You are using sieve analysis to determine the soil's load-bearing capacity, stability, and suitability as a compacted fill material.
- If your primary focus is drainage, septic systems, or environmental remediation: You are using it to assess how quickly water and other liquids will move through the soil (permeability).
- If your primary focus is general site characterization: You are using it as a fundamental first step to classify the soil, creating a baseline for all future geotechnical and engineering decisions.
Ultimately, using a sieve on a soil sample is how you transform a raw, unknown material into a predictable engineering component.
Summary Table:
| Purpose of Sieve Analysis | Key Metric Measured | Primary Soil Type Analyzed |
|---|---|---|
| Determine Grain Size Distribution | Proportion of gravel, sand, silt, clay | Coarse-grained soils (particles > 0.075 mm) |
| Predict Soil Permeability | Water flow potential | All soils for drainage design |
| Assess Structural Strength & Stability | Load-bearing capacity | Soils for foundations & construction |
| Classify Soil (e.g., USCS) | Standardized soil type | Coarse-grained soils for engineering specs |
Need precise soil analysis equipment for your geotechnical projects? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab sieves and soil testing equipment to help you accurately determine grain size distribution, predict soil behavior, and ensure the success of your engineering designs. Contact our experts today to find the right sieving solution for your laboratory's needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
People Also Ask
- Why is a laboratory electromagnetic vibratory sieve shaker used? Optimize Walnut Shell Chemical Pretreatment
- Why use a vibratory sieve shaker for PET powder? Achieve Precise Particle Size Control for Chemical Research
- What function does a sieving system perform during HPS powder pretreatment? Ensure Uniform Particle Size Distribution
- What are the disadvantages of sieve machine? Key Limitations in Particle Size Analysis
- How do high-precision sieving systems benefit zeolite preparation? Maximize Adsorption for Wastewater Treatment



















