Current Status of Electrocatalytic CO₂ Reduction Research
Challenges in Industrial Application
The research on electrocatalytic CO₂ reduction has shown significant advancements, yet it continues to grapple with several critical challenges. One of the primary issues is low product selectivity, where the catalysts often yield a mixture of products rather than a single desired compound. This lack of specificity can lead to inefficient resource utilization and increased downstream separation costs.
Another persistent problem is the low local current density, which directly impacts the overall efficiency of the process. High current densities are crucial for industrial scalability, but current systems often fall short, limiting their applicability in large-scale operations.
The high overpotential required for the reaction to proceed is also a major concern. This overpotential not only increases energy consumption but also accelerates the degradation of the catalysts and the electrolytic cell components, further complicating the process.
Moreover, the unclear reaction mechanisms pose a significant barrier to optimization. Without a thorough understanding of the underlying processes, it becomes challenging to design and develop more efficient catalysts and electrolyzers. This lack of clarity hampers the ability to predict and control the reaction pathways, thereby affecting the reproducibility and reliability of the results.
In addition to these technical hurdles, the reaction devices themselves require substantial improvements in terms of durability and stability. The current systems often fail to maintain consistent performance over extended periods, necessitating frequent maintenance and replacement, which adds to the operational costs and complexity.
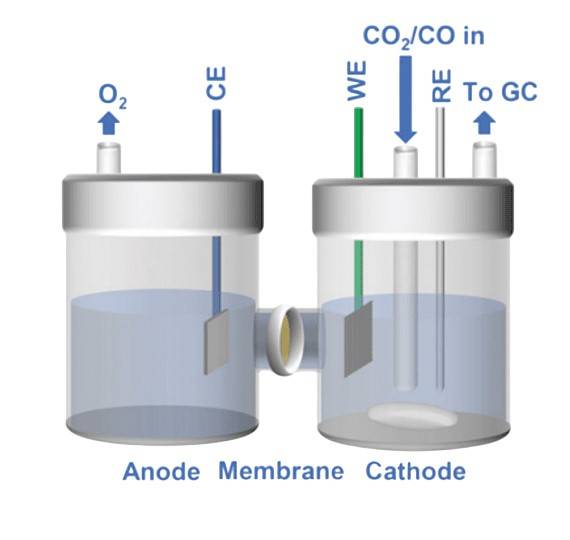
To address these challenges, future research must focus on enhancing the selectivity and current density of the catalysts, reducing the overpotential, and elucidating the reaction mechanisms. Simultaneously, advancements in the design and materials used for the electrolyzers are essential to improve their durability and stability, making electrocatalytic CO₂ reduction a viable option for industrial applications.
Types of Electrolytic Cells for CO₂ Reduction
H-Type Electrolyzer
The H-Type Electrolyzer is a distinct configuration in electrocatalytic CO₂ reduction, characterized by its unique compartmentalization. This setup comprises a cathode chamber, an anode chamber, and a critical component—the ion-exchange membrane. The electrolyte of choice for this system is a 0.5 M KHCO₃ solution, which plays a pivotal role in facilitating the electrochemical reactions necessary for CO₂ reduction.
However, despite its structural simplicity and straightforward operational mechanics, the H-Type Electrolyzer faces notable challenges. One of the primary issues is its relatively low mass transfer efficiency, which significantly hampers the overall reaction rate. This inefficiency is further compounded by the generally low current densities observed in these systems, typically falling below 100 mA/cm². These limitations underscore the need for advancements in both the electrolyte composition and the overall design to enhance the performance and viability of H-Type Electrolyzers in industrial applications.
Flow-Through Electrolyzer
The flow-through electrolyzer employs a porous hydrophobic gas diffusion layer combined with a 1 M KOH electrolyte, which allows it to achieve significantly higher current densities compared to other types of electrolytic cells. Specifically, it can operate at current densities exceeding 500 mA/cm², making it a promising candidate for industrial applications where high efficiency is paramount.
However, this design is not without its challenges. One of the primary issues is the stability of the system, which can be compromised under prolonged operation or under certain environmental conditions. Additionally, there is a risk of electrolyte overflow, which can lead to operational inefficiencies and potential safety hazards. These stability concerns and the risk of overflow necessitate further research and development to enhance the durability and reliability of flow-through electrolyzers.

Membrane Electrode Electrolyzer
The Membrane Electrode Electrolyzer (MEE) stands out by maintaining high mass transfer efficiency without the need for an electrolyte in the cathode chamber. This design significantly reduces the system impedance, thereby enhancing the overall reaction rate. The absence of an electrolyte in the cathode chamber minimizes the risk of electrolyte-related issues, such as ionic contamination and increased ohmic losses, which are common in other types of electrolyzers.
However, the MEE is not without its challenges. One of the primary issues it faces is the blocking of the gas diffusion layer, which can hinder the efficient transfer of reactant gases to the catalytic sites. This blockage often results from the accumulation of reaction intermediates or by-products, leading to a decline in performance over time. Additionally, the ion exchange membranes used in MEEs have a limited lifetime, which can be a critical factor in the long-term viability of this technology. The membranes are susceptible to degradation under continuous operation, particularly under high current densities and harsh chemical environments.
To address these challenges, ongoing research is focused on developing advanced gas diffusion layers and more durable ion exchange membranes. These improvements aim to enhance the longevity and efficiency of the MEE, making it a more viable option for industrial applications of electrocatalytic CO₂ reduction.
PLS-MECF Series Double Chamber Alkaline Electrolyzer
The PLS-MECF Series Double Chamber Alkaline Electrolyzer represents a groundbreaking innovation in reactor design, which is pivotal for advancing the field of electrocatalytic CO₂ reduction. This new design addresses several key challenges inherent in traditional electrolytic cells, such as low mass transfer efficiency, high overpotential, and instability issues. By incorporating a double chamber configuration, the PLS-MECF series enhances the separation of the cathode and anode chambers, thereby optimizing the flow of reactants and products.
One of the most significant advancements in this design is the integration of advanced catalysts, which play a critical role in improving the reaction rate and selectivity of CO₂ reduction products. The catalyst development, in conjunction with the reactor design, aims to achieve higher local current densities and lower overpotentials, making the process more efficient and scalable for industrial applications.
Moreover, the PLS-MECF series is designed to enhance the durability and stability of the electrolyzer, which are crucial for long-term operation. This is achieved through the use of robust materials and innovative structural designs that minimize issues such as electrolyte overflow and the blocking of gas diffusion layers. As a result, the PLS-MECF series offers a promising solution for overcoming the limitations of existing electrolytic cells, paving the way for more effective and sustainable CO₂ reduction technologies.
Related Products
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell Gas Diffusion Liquid Flow Reaction Cell
- H Type Electrolytic Cell Triple Electrochemical Cell
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Five-Port
- Flat Corrosion Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
Related Articles
- Overcoming Challenges with H-Type Electrolytic Cell Operation
- Applications of H-Type Electrolytic Cell in Metal Extraction
- Advanced Electrolytic Cell Techniques for Cutting-Edge Lab Research
- Electrochemical Cells: Generating Electricity and Driving Reactions
- The Vessel of Truth: Why the Container Matters More Than the Chemistry
















