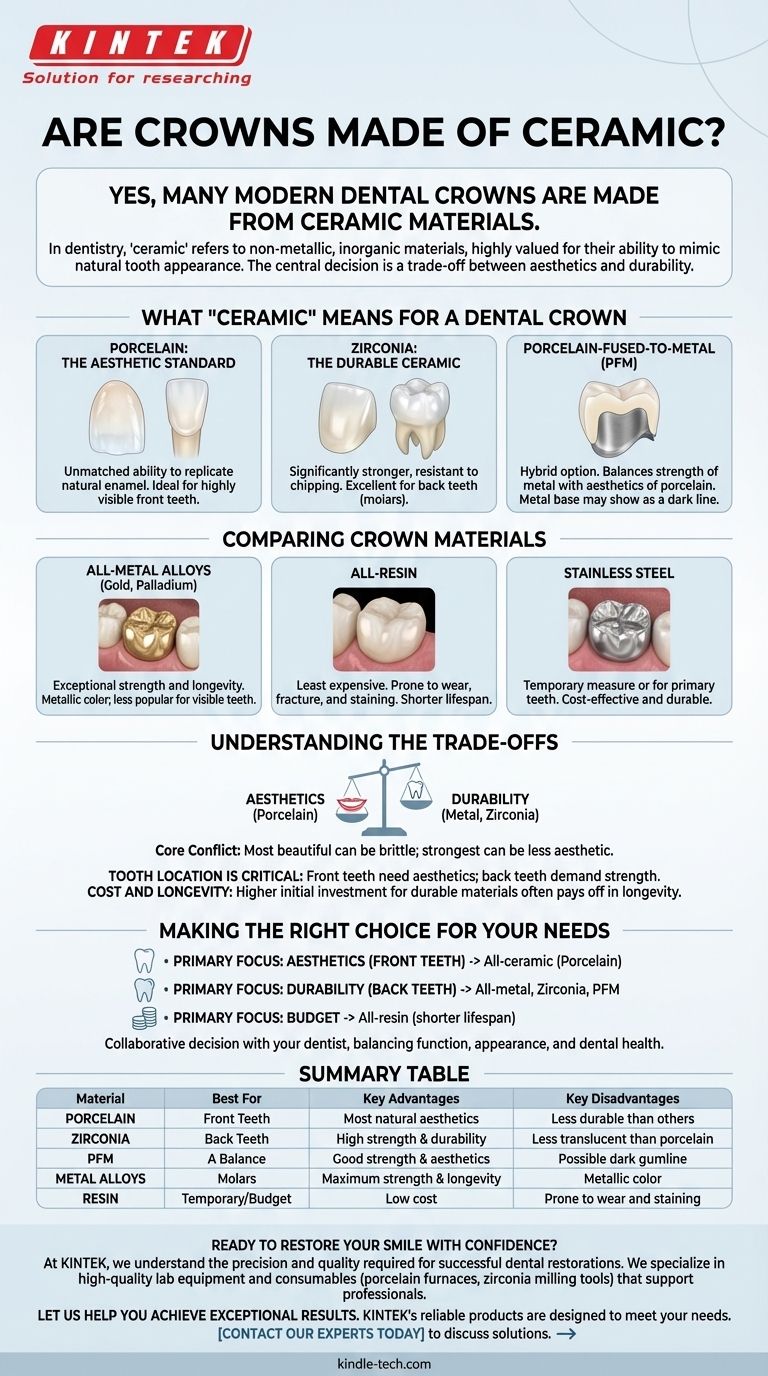
Yes, many modern dental crowns are made from ceramic materials. In dentistry, "ceramic" refers to a class of non-metallic, inorganic materials, with porcelain being the most well-known type. These all-ceramic crowns are highly valued for their ability to perfectly mimic the color, translucency, and overall appearance of a natural tooth.
The central decision in choosing a crown material is a trade-off between aesthetics and durability. While ceramic crowns offer the most natural look, ideal for front teeth, stronger materials like metal or zirconia are often better suited for back teeth that endure immense chewing pressure.
What "Ceramic" Means for a Dental Crown
The term "ceramic" covers several materials used in dentistry, each with specific properties. Understanding these types is key to understanding your options.
Porcelain: The Aesthetic Standard
Porcelain is the classic ceramic material used for dental work. Its primary advantage is its unmatched ability to replicate the look of natural tooth enamel.
This makes all-porcelain crowns the premier choice for restoring highly visible front teeth, where a seamless, natural appearance is the top priority.
Zirconia: The Durable Ceramic
Zirconia is another type of ceramic material that is significantly stronger and more resistant to chipping than traditional porcelain.
While slightly more opaque, its supreme durability makes it an excellent all-ceramic option for crowns on back teeth (molars), which handle the most chewing force.
Porcelain-Fused-to-Metal (PFM)
This is a hybrid crown. It features a strong metal alloy base that fits over the tooth, which is then covered with a layer of tooth-colored porcelain.
PFM crowns offer a good balance of the strength of metal with the aesthetic appeal of porcelain, though the metal base can sometimes be visible as a dark line at the gumline.
Comparing Crown Materials
Ceramics are just one option. Your dentist will consider the tooth's location, your budget, and your specific needs when making a recommendation.
All-Metal Alloys
Crowns made from metal alloys (such as gold or palladium) are known for their exceptional strength and longevity. They require the least amount of healthy tooth removal.
Their obvious metallic color is the primary disadvantage, making them a practical but less popular choice for any visible teeth.
All-Resin
Resin crowns are the least expensive option. They are made from a composite material similar to what is used for tooth-colored fillings.
However, they are the most prone to wear, fracture, and staining over time, and they generally do not last as long as ceramic or metal crowns.
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel crowns are typically used as a temporary measure to protect a tooth while a permanent crown is being made.
They are also commonly used to restore primary (baby) teeth in children, as they are cost-effective and durable enough to last until the permanent tooth erupts.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right crown material involves balancing several competing factors. There is no single "best" material for every situation.
Aesthetics vs. Durability
This is the core conflict. The most beautiful materials, like porcelain, can be more brittle than the strongest materials, like metal. Your choice depends on whether the tooth needs to look perfect or withstand heavy force.
Tooth Location is Critical
A crown for a front incisor has a very different job than a crown for a rear molar. Front teeth require aesthetics, while back teeth demand strength. This is the single most important factor in material selection.
Cost and Longevity
Generally, more durable and aesthetic materials like zirconia or porcelain command a higher price than resin or metal. This initial investment often pays off in longevity, as they may not need to be replaced as frequently.
Making the Right Choice for Your Needs
Consult with your dental professional to determine the ideal solution for your specific clinical situation.
- If your primary focus is aesthetics (front teeth): All-ceramic crowns, particularly porcelain, are the clear choice for the most natural and seamless look.
- If your primary focus is durability (back teeth): Consider strong materials like all-metal alloys, zirconia, or porcelain-fused-to-metal (PFM) crowns.
- If your primary focus is budget: All-resin crowns offer the most affordable upfront option, but be mindful of their shorter expected lifespan.
Ultimately, the best crown material is a collaborative decision between you and your dentist, balancing function, appearance, and your specific dental health.
Summary Table:
| Material | Best For | Key Advantages | Key Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Porcelain | Front Teeth | Most natural aesthetics | Less durable than other options |
| Zirconia | Back Teeth | High strength & durability | Less translucent than porcelain |
| Porcelain-Fused-to-Metal (PFM) | A Balance | Good strength & aesthetics | Possible dark gumline |
| Metal Alloys | Molars | Maximum strength & longevity | Metallic color |
| Resin | Temporary/Budget | Low cost | Prone to wear and staining |
Ready to Restore Your Smile with Confidence?
Choosing the right crown material is crucial for both the health and appearance of your smile. At KINTEK, we understand the precision and quality required for successful dental restorations. We specialize in providing high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables that support dental professionals in creating perfect ceramic crowns, from precise porcelain furnaces to durable zirconia milling tools.
Let us help you achieve exceptional results. Whether you are a dental lab technician crafting the restoration or a clinician seeking the best outcome for your patient, KINTEK's reliable products are designed to meet your needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your dental lab's capabilities and ensure patient satisfaction.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- Horizontal High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Bottom Discharge Graphitization Furnace for Carbon Materials
People Also Ask
- What are the key differences between incineration and gasification? Explore Waste Management Solutions
- What function does a high-temperature sintering furnace serve in biomass carbonization? Unlock Superior MFC Performance
- What is the difference between oxidizing and reducing environments? Key Insights for Chemical Reactions
- What are the disadvantages of biomass conversion? High Costs, Logistical Hurdles, and Environmental Trade-offs
- What is the sputtering voltage of a magnetron? Optimize Your Thin Film Deposition Process













