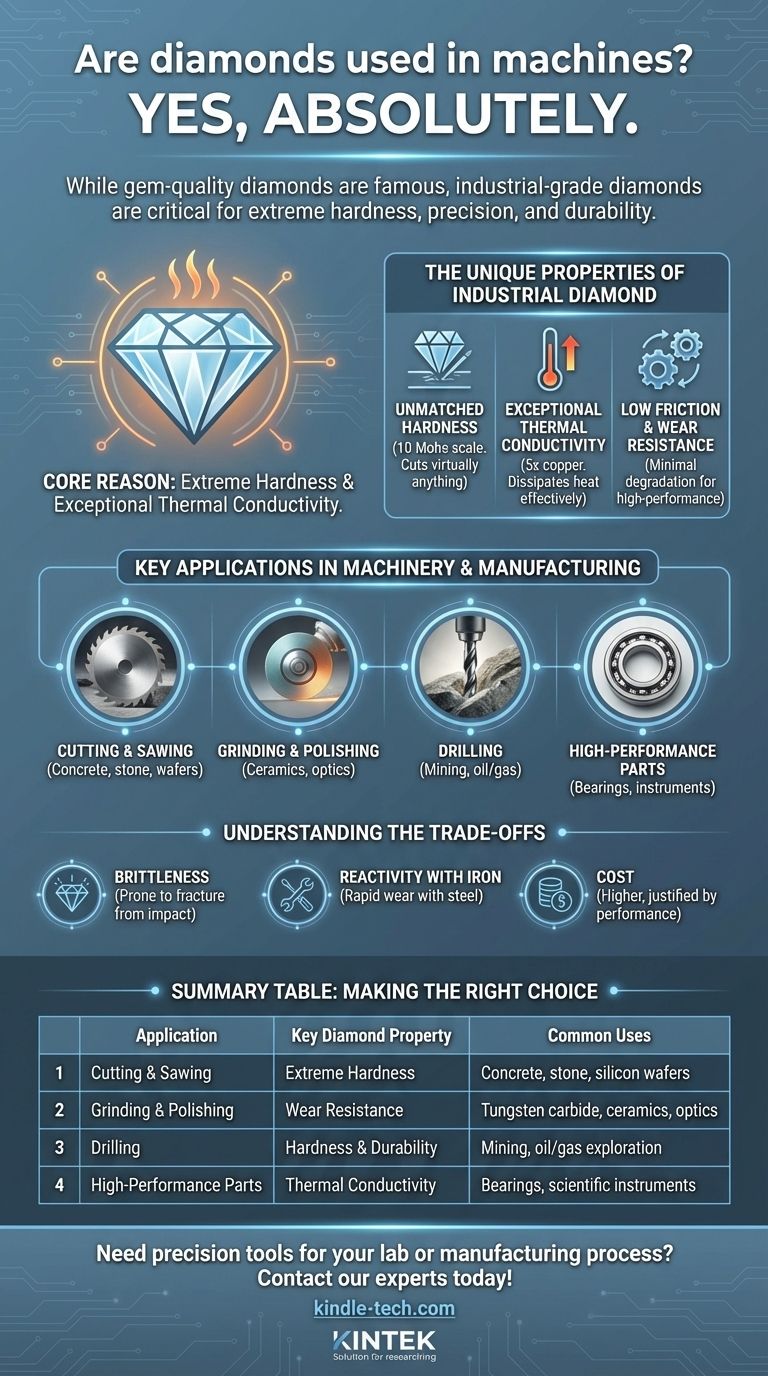
Yes, absolutely. While gem-quality diamonds are famous for their brilliance, industrial-grade diamonds are a critical component in a vast range of modern machinery and manufacturing processes. Their unparalleled physical properties make them the material of choice for tasks that demand extreme hardness, precision, and durability.
The core reason diamonds are used in machines is not for their beauty, but for their extreme hardness and exceptional thermal conductivity. These two properties solve critical challenges in cutting, grinding, and machining materials that no other substance can handle as effectively.

The Unique Properties of Industrial Diamond
To understand why diamond is so vital, we must look beyond its appearance and focus on its material science. The diamonds used in industry are often synthetic or natural stones not suitable for jewelry, prized for their function over their form.
Unmatched Hardness
Diamond is the hardest known natural material, scoring a 10 on the Mohs scale of hardness. This means it can scratch or cut virtually any other material, including rock, concrete, ceramics, and other superhard alloys. This property is the basis for its most common industrial applications.
Exceptional Thermal Conductivity
Less known but equally important is diamond's ability to conduct heat. It is the best thermal conductor of any bulk material at room temperature, transferring heat five times more effectively than copper. This allows it to dissipate the intense heat generated during high-friction processes like cutting and grinding, preventing damage to both the tool and the workpiece.
Low Friction and Wear Resistance
Diamond has a very low coefficient of friction, especially when polished. Combined with its hardness, this translates to extraordinary wear resistance. Diamond-coated parts or diamond bearings can operate for long periods with minimal degradation, making them ideal for high-performance and mission-critical applications.
Key Applications in Machinery and Manufacturing
These properties translate directly into specific, high-value uses across many industries.
Cutting and Sawing
The most widespread use is in cutting tools. Diamond-tipped saw blades are standard for cutting concrete, asphalt, stone, and tile. Similarly, diamond-wire saws provide incredibly precise cuts for delicate materials like silicon wafers in the semiconductor industry.
Grinding and Polishing
As an abrasive, diamond is unmatched. Diamond grinding wheels are used to shape and finish extremely hard materials like tungsten carbide, ceramics, and sapphire glass. Diamond pastes and slurries are used for lapping and polishing to achieve a mirror-like, super-smooth surface finish required in optics and electronics.
Drilling
In mining, oil and gas exploration, and geotechnical engineering, diamond-impregnated drill bits are essential. These bits have small industrial diamonds embedded in a metal matrix, allowing them to grind through rock formations that would destroy conventional steel bits.
High-Performance Components
In more specialized machinery, diamond is used for its durability. Diamond-coated bearings can operate in harsh environments without lubrication. In scientific instruments, diamond anvil cells are used to create immense pressures to study materials under extreme conditions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Despite its advantages, diamond is not a universal solution. Its application has clear limitations that engineers must consider.
Brittleness
While extremely hard, diamond is also brittle. Hardness is resistance to scratching, while toughness is resistance to fracture. A sharp impact can cause a diamond tool to chip or shatter, making it unsuitable for applications with heavy, intermittent shocks where a tougher material like tungsten carbide might be preferred.
Reactivity with Iron
At the high temperatures generated when machining steel, diamond undergoes a chemical reaction with iron. Carbon atoms from the diamond diffuse into the steel, causing rapid tool wear. For this reason, another superhard material, Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN), is typically the preferred choice for machining hardened steel and other ferrous alloys.
Cost
Even industrial-grade and synthetic diamonds are more expensive than conventional tool materials. The cost must be justified by significant performance gains, such as longer tool life, faster processing speeds, or the ability to work with otherwise un-machinable materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right superhard material depends entirely on the specific application and materials involved.
- If your primary focus is cutting concrete, stone, or hard ceramics: Diamond tooling is the industry standard and the most effective choice.
- If your primary focus is high-speed machining of hardened steel or cast iron: Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN) is the superior material due to diamond's chemical reactivity with iron.
- If your primary focus is achieving an ultra-fine surface finish on hard materials: Diamond abrasives, slurries, and pastes are essential for precision polishing.
- If your primary focus is creating a wear-resistant surface for a non-ferrous material: A Polycrystalline Diamond (PCD) coating can dramatically extend component life.
Ultimately, the use of diamonds in machinery is a testament to how a material's fundamental properties can be harnessed to solve our most demanding engineering challenges.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Diamond Property | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Cutting & Sawing | Extreme Hardness | Concrete, stone, silicon wafers |
| Grinding & Polishing | Wear Resistance | Tungsten carbide, ceramics, optics |
| Drilling | Hardness & Durability | Mining, oil/gas exploration |
| High-Performance Parts | Thermal Conductivity | Bearings, scientific instruments |
Need precision tools for your lab or manufacturing process? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including diamond-based solutions for cutting, grinding, and material analysis. Our expertise ensures you get the right tooling for your specific materials—whether you're working with ceramics, composites, or other challenging substrates. Contact our experts today to enhance your operational efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Precision Diamond Wire Cutting Machine Laboratory Saw Precision Wire EDM Cutting Machine
- 12 Inch 24 Inch High Precision Automatic Diamond Wire Cutting Machine Laboratory Saw Precision Wire EDM Cutting Machine
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type
- Precision Wire Saw Laboratory Cutting Machine with 800mm x 800mm Workbench for Diamond Single Wire Circular Small Cutting
- Liquid Nitrogen Cryogenic Grinder Mill Cryomill Airflow Ultrafine Pulverizer
People Also Ask
- What machine do I need to make diamonds? HPHT vs. CVD Equipment Explained
- What are the environmental issues with diamond mining? Uncover the True Ecological and Human Cost
- What is the carbon footprint of diamond mining? Uncovering the True Environmental and Ethical Cost
- What are 5 negative impacts of diamond mines on the environment? The Hidden Environmental Cost of Diamond Mining
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of cold working over hot working? A Guide to Choosing the Right Metal Forming Process



















