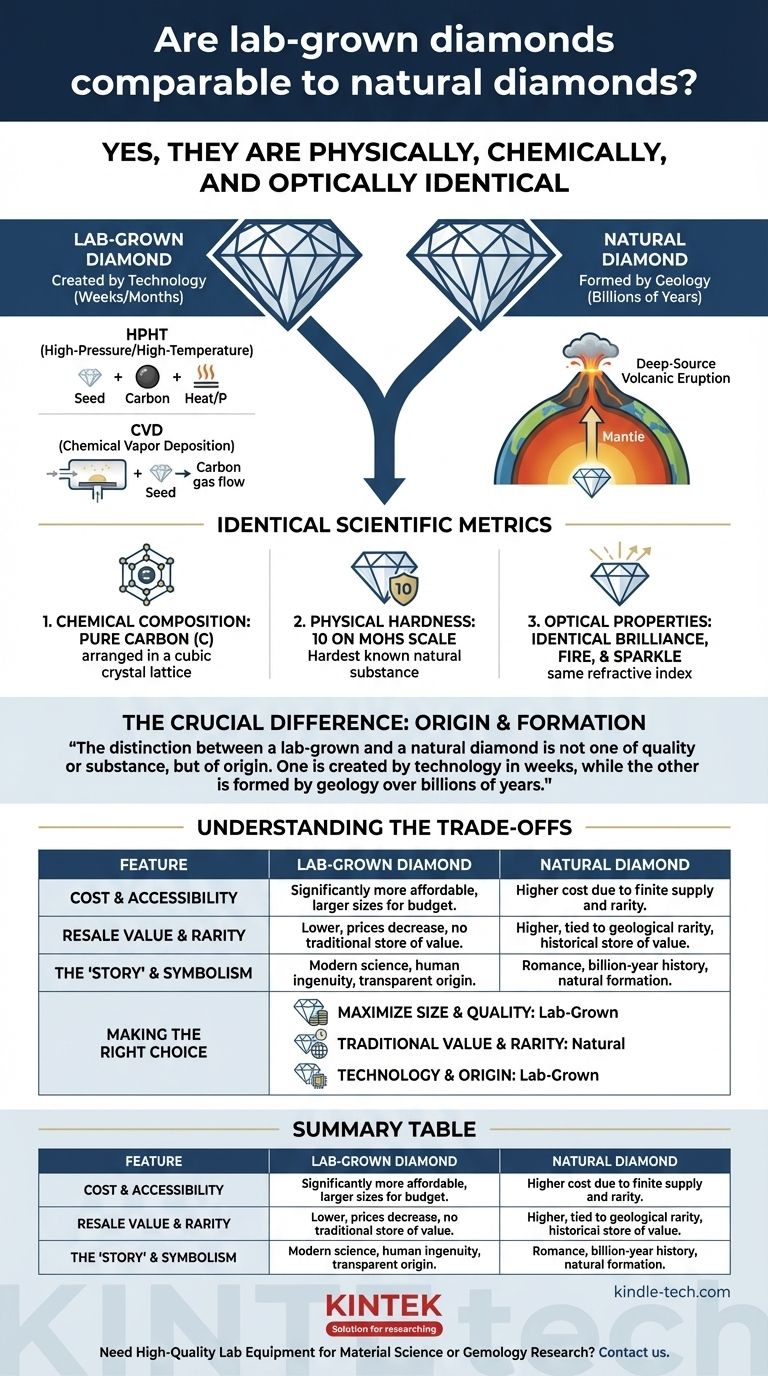
Yes, lab-grown diamonds are physically, chemically, and optically identical to natural diamonds. Both are composed of pure carbon crystallized in the same structure, giving them the same hardness, brilliance, and fire. To the naked eye, even for a trained jeweler, they are indistinguishable. The singular, defining difference between them is not their substance, but their origin.
The distinction between a lab-grown and a natural diamond is not one of quality or substance, but of origin. One is created by technology in weeks, while the other is formed by geology over billions of years. This single difference is the foundation for all other considerations, from price to long-term value.

What Makes a Diamond a Diamond?
To compare the two, we must first establish the objective criteria that define a diamond. On every scientific metric, lab-grown and natural diamonds are the same material.
Identical Chemical Composition
Both natural and lab-grown diamonds are pure carbon. Their atoms are arranged in a rigid cubic crystal lattice, which is responsible for their exceptional properties.
Identical Physical Hardness
Both types of diamonds score a 10 on the Mohs scale of hardness, making them the hardest known natural substance on Earth. A lab-grown diamond is just as durable and resistant to scratching as a natural one.
Identical Optical Properties
The brilliance, fire, and sparkle of a diamond are products of its refractive index and crystal structure. Because lab-grown diamonds share the exact same structure as natural ones, they bend and reflect light in the exact same way.
The Crucial Difference: Origin and Formation
The entire debate and value difference between these two products comes down to their creation story.
The Geological Story of Natural Diamonds
Natural diamonds were formed deep within the Earth's mantle between 1 and 3.3 billion years ago. Immense pressure and extreme heat caused carbon atoms to crystallize. These diamonds were then carried to the surface in a matter of hours through deep-source volcanic eruptions. Their story is one of geological rarity and ancient history.
The Technological Process of Lab-Grown Diamonds
Lab-grown diamonds are created in highly controlled environments that replicate the conditions of the Earth's mantle. The two primary methods are:
- HPHT (High-Pressure/High-Temperature): A small diamond "seed" is placed with pure carbon and subjected to intense pressure and heat, causing the carbon to melt and crystallize onto the seed.
- CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition): A seed is placed in a sealed chamber filled with carbon-rich gas. The gases are heated, causing the carbon atoms to break away and deposit onto the seed, growing a diamond layer by layer.
This entire process takes from a few weeks to a few months. The result is not a "fake" diamond, but a diamond synthesized by human technology.
How Experts Tell Them Apart
While they look identical to the naked eye, gemological laboratories can distinguish between them. Using advanced spectroscopic equipment, experts can identify minute differences in their internal growth patterns and trace elements. HPHT diamonds, for example, often show cubic growth faces not typically seen in natural octahedral crystals.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between a natural and lab-grown diamond involves weighing a clear set of trade-offs.
Cost and Accessibility
This is the most significant factor for many buyers. Because they can be produced on demand, lab-grown diamonds are significantly more affordable than natural diamonds of the same size and quality. This allows you to purchase a larger or higher-grade stone for the same budget.
Resale Value and Rarity
A natural diamond's value is intrinsically tied to its finite supply and geological rarity. Historically, this has allowed natural diamonds to act as a store of value. Lab-grown diamonds, being a technological product with a potentially unlimited supply, do not share this characteristic. Their prices have steadily decreased as technology improves and are not expected to hold value in the same way.
The "Story" and Symbolism
The choice also carries an emotional weight. Some value the romance and billion-year history of a stone formed by nature. Others are drawn to the story of modern science and human ingenuity represented by a lab-grown diamond, often viewing it as a more transparent and modern choice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "better" diamond is entirely dependent on your priorities.
- If your primary focus is maximizing size and visual quality for your budget: A lab-grown diamond offers an undeniable advantage, providing a physically identical stone for a significantly lower cost.
- If your primary focus is traditional symbolism and long-term value retention: A natural diamond's geological rarity and established market history make it the conventional choice.
- If your primary focus is celebrating technology and a clear chain of custody: A lab-grown diamond represents human innovation and offers a straightforward origin story without the complexities of traditional mining.
Ultimately, the best choice is the one that aligns with your personal values, budget, and the story you wish the diamond to tell.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Lab-Grown Diamond | Natural Diamond |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Pure Carbon (C) | Pure Carbon (C) |
| Hardness (Mohs Scale) | 10 | 10 |
| Optical Properties | Identical Brilliance & Fire | Identical Brilliance & Fire |
| Origin | Created in a lab (weeks/months) | Formed in Earth's mantle (billions of years) |
| Cost | Significantly lower | Higher due to rarity |
| Resale Value | Lower, technology-driven supply | Higher, tied to geological rarity |
Need High-Quality Lab Equipment for Material Science or Gemology Research?
Whether you're analyzing diamond properties or developing new materials, KINTEK provides the precise, reliable lab equipment and consumables your work demands. Our furnaces, spectrometers, and sample preparation tools are trusted by researchers worldwide for accurate, repeatable results.
Let us equip your lab for success. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the fluorescence of a CVD diamond? A Guide to Its Unique Glow and Purpose
- What is the process of lab created diamonds? A Clear Guide to HPHT & CVD Methods
- What is the future of CVD diamond? Unlocking Next-Gen Electronics & Thermal Management
- Are CVD diamonds fake? Discover the Truth About Lab-Grown Diamonds
- What is the difference between CVD and original diamond? Choose the Right Diamond for Your Needs



















