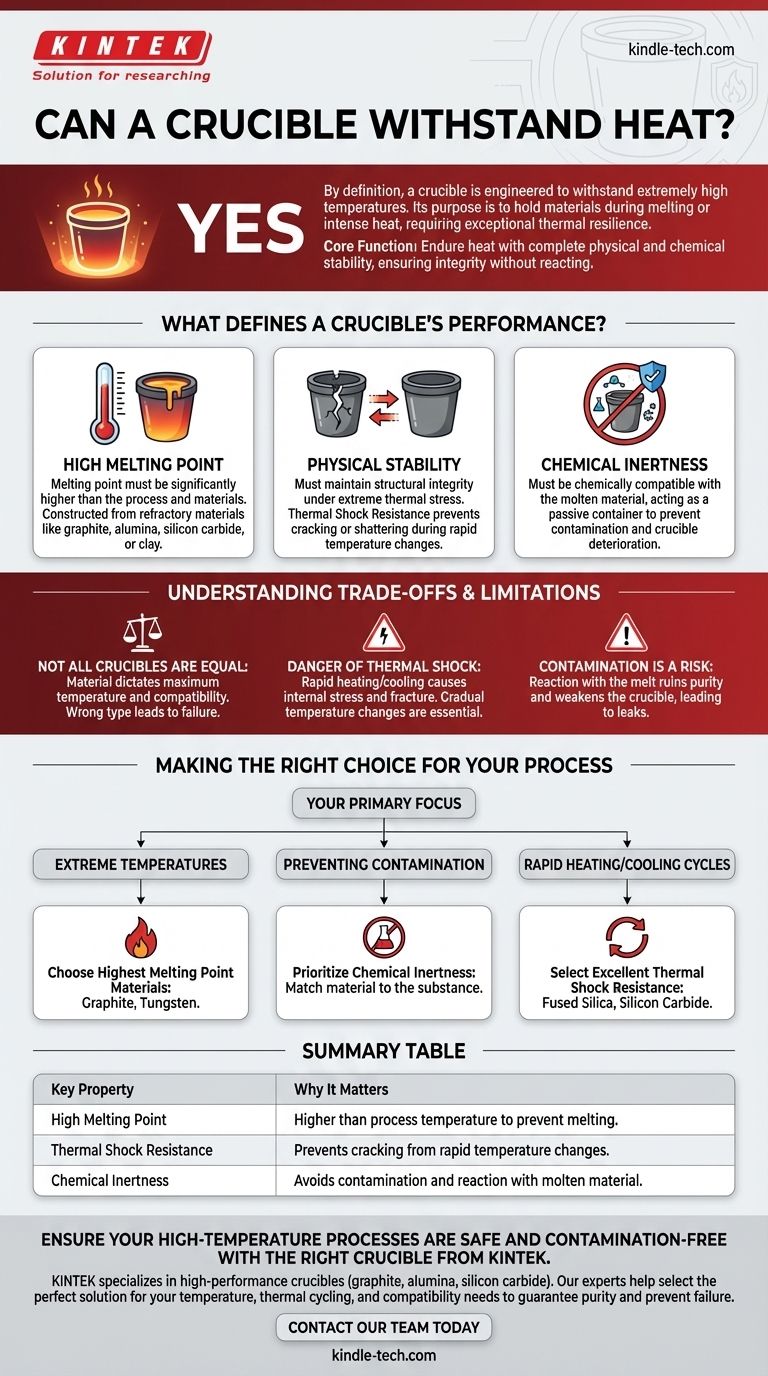
Yes, by its very definition, a crucible is a container engineered to withstand extremely high temperatures. Its entire purpose is to hold materials as they are melted or subjected to intense heat, a task that requires exceptional thermal resilience. A crucible's effectiveness, however, goes far beyond simply not melting.
The core function of a crucible isn't just to endure heat, but to do so with complete physical and chemical stability, ensuring the integrity of the material it holds without reacting with it or breaking down.

What Defines a Crucible's Performance?
A crucible's ability to handle heat is a result of several critical properties working in concert. Understanding these factors is key to appreciating its function in high-temperature processes.
The Foundation: High Melting Point
The most fundamental requirement is that a crucible's melting point must be significantly higher than the temperature of the process and the melting point of the materials inside it. This is achieved by constructing crucibles from specialized refractory materials like graphite, alumina, silicon carbide, or clay.
Critical Factor: Physical Stability
Beyond simply not melting, a crucible must maintain its structural integrity under extreme thermal stress. This property, known as thermal shock resistance, prevents the crucible from cracking or shattering when temperatures change rapidly. Poor stability can lead to catastrophic failure.
The Goal: Chemical Inertness
A crucible must be chemically compatible with the molten material it contains. Its job is to be a passive container, not an active ingredient. Any chemical reaction between the crucible and its contents can lead to contamination of the melt and the deterioration of the crucible itself.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While designed for heat, no crucible is universally perfect. The specific material and application introduce critical limitations that must be respected.
Not All Crucibles Are Equal
The material a crucible is made from dictates its maximum operating temperature and chemical compatibility. A porcelain crucible cannot be used for the same high-temperature applications as a tungsten or graphite crucible. Using the wrong type for a given process will result in failure.
The Danger of Thermal Shock
Even the most robust crucible can be compromised by thermal shock. Heating or cooling a crucible too quickly creates internal stresses that can cause it to fracture. Proper, gradual temperature changes are essential for longevity.
Contamination is a Constant Risk
Choosing a crucible that reacts with your melt is a common failure point. This not only ruins the purity of your material but can also weaken the crucible's structure, leading to leaks or a complete breach over time.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct crucible is a matter of matching its properties to the demands of your specific application.
- If your primary focus is reaching extreme temperatures: Choose a crucible made from materials with the highest melting points, such as graphite or tungsten.
- If your primary focus is preventing contamination: Prioritize chemical inertness by carefully matching the crucible material to the substance you are melting.
- If your primary focus is rapid heating and cooling cycles: Select a crucible with excellent thermal shock resistance, like one made from fused silica or silicon carbide.
Ultimately, a crucible's ability to withstand heat is the baseline requirement, not the final measure of its value.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| High Melting Point | Must be higher than the process temperature to prevent melting. |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Prevents cracking from rapid temperature changes. |
| Chemical Inertness | Avoids contamination and reaction with the molten material. |
Ensure your high-temperature processes are safe and contamination-free with the right crucible from KINTEK.
Choosing the correct crucible is critical for the success and safety of your melting, ashing, or heat treatment applications. KINTEK specializes in supplying high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including a comprehensive range of crucibles made from materials like graphite, alumina, and silicon carbide. Our experts can help you select the perfect crucible based on your specific temperature requirements, thermal cycling needs, and material compatibility to guarantee purity and prevent failure.
Contact our team today to discuss your application and find the ideal crucible solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Custom Machined and Molded PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer with PTFE Crucible and Lid
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- What role do high-purity alumina crucibles play in high-temperature steam oxidation? Ensure Data Integrity up to 1350°C
- Why is a high-purity alumina crucible preferred for high-temperature oxidation? Ensure Unmatched Data Integrity
- What are the functional advantages of using high-purity alumina crucibles? Achieve Precise Oxidation Data
- Why are high-purity alumina crucibles used for LATP? Preserve Purity and Conductivity in Sintering
- What is the function of alumina crucibles in Na3V2(PO4)2F3 synthesis? Ensure Purity in NVPF Production



















