Yes, fundamentally, a crucible is designed to withstand extremely high temperatures. This capability is its core purpose in metallurgical, chemical, and laboratory applications. Its effectiveness, however, is entirely dependent on its specific material composition being correctly matched to the temperature and chemical properties of the substance it is intended to hold.
A crucible's ability to handle intense heat is not a universal guarantee. It is a carefully engineered property determined by its material, which must have a melting point far higher than the substance being heated and remain chemically stable to prevent contamination and failure.

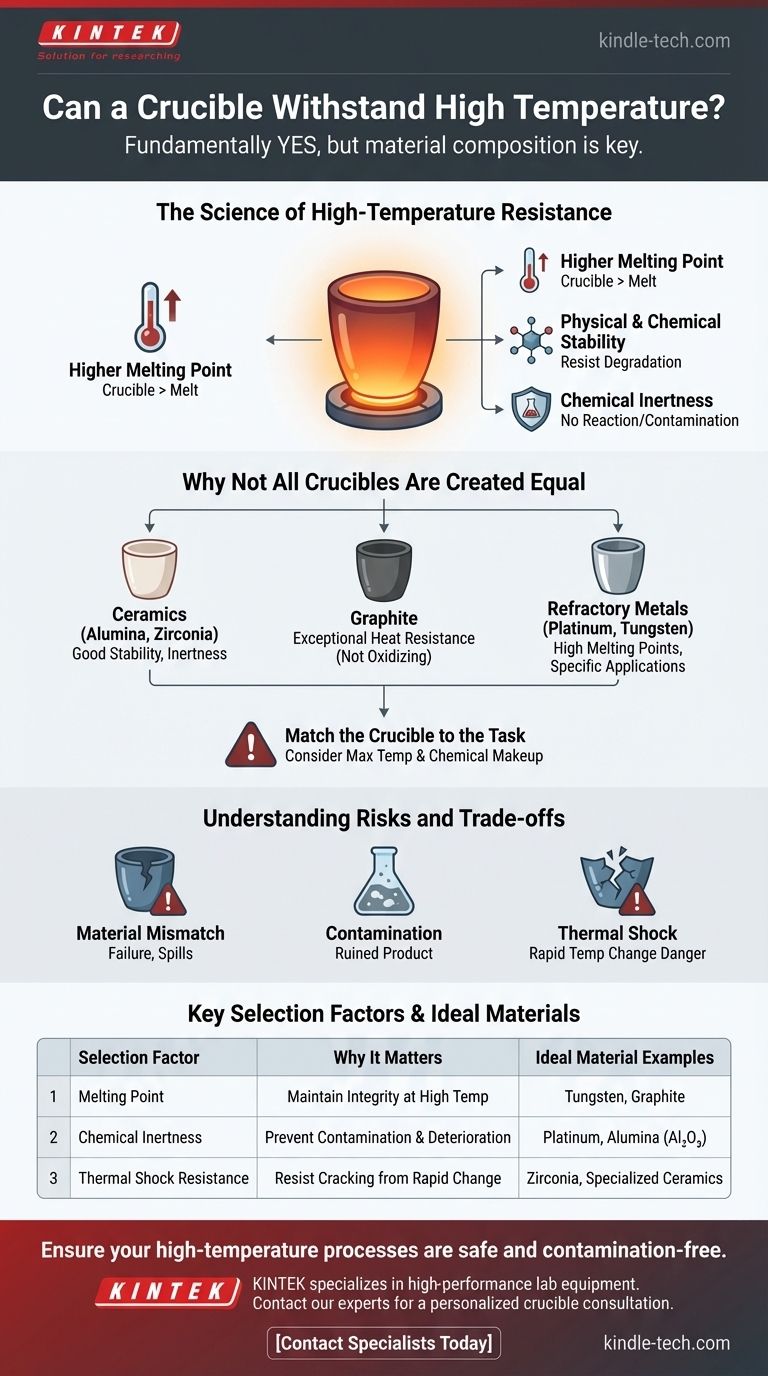
The Science of High-Temperature Resistance
A crucible's performance under extreme heat is governed by a few fundamental principles. Understanding these is key to using them safely and effectively.
A Higher Melting Point is Non-Negotiable
The most basic requirement is that a crucible must have a melting point significantly higher than the material it contains. This ensures the crucible maintains its structural integrity and does not become part of the melt itself.
Ensuring Physical and Chemical Stability
Beyond simply not melting, the crucible material must remain physically and chemically stable at the target temperature. It cannot degrade, soften, or undergo a phase change that would compromise its structure. This includes resistance to thermal shock, the tendency to crack when subjected to rapid temperature changes.
The Critical Role of Chemical Inertness
A crucible must be chemically inert, meaning it does not react with the molten contents. Any chemical reaction can lead to two critical failures: deterioration of the crucible itself and, just as importantly, contamination of the melt, which can ruin a sensitive experiment or an entire industrial batch.
Why Not All Crucibles Are Created Equal
The term "crucible" refers to a function, not a single type of object. The material used to construct a crucible dictates its specific capabilities and limitations.
The Impact of Material Composition
Crucibles are made from a variety of materials, including ceramics (like alumina or zirconia), graphite, and refractory metals (like platinum or tungsten). Each material offers a different balance of properties. For example, graphite offers exceptional heat resistance but may not be suitable for oxidizing environments, while a ceramic like alumina provides excellent stability and inertness for many applications.
Matching the Crucible to the Task
The selection process is therefore critical. You must know the maximum temperature you need to achieve and the chemical makeup of the substance you are melting. Choosing a crucible rated for 1200°C for a process that requires 1500°C will inevitably lead to failure.
Understanding the Risks and Trade-offs
Using the wrong crucible or using the right one improperly can lead to catastrophic failure, wasted materials, and significant safety hazards.
The Danger of a Material Mismatch
The primary risk is selecting a crucible with an insufficient melting point or poor chemical compatibility. This can cause the crucible to crack, leak, or melt completely, spilling its molten contents.
Contamination from Chemical Reactions
Even if a crucible does not structurally fail, a subtle chemical reaction with the melt can introduce impurities. For high-purity alloys, semiconductors, or scientific samples, this contamination renders the final product useless.
Thermal Shock: The Silent Cracker
Heating or cooling a crucible too quickly can cause it to crack or shatter due to thermal shock. This is especially true for many ceramic materials. A controlled heating and cooling cycle is essential for extending the life of your equipment and ensuring safety.
How to Select the Right Crucible
Your choice must be guided by the specific demands of your application.
- If your primary focus is reaching the absolute highest temperatures: Prioritize crucibles made from materials with the highest melting points, such as graphite or tungsten.
- If your primary focus is ensuring the chemical purity of your melt: Select a crucible material known for its chemical inertness with your specific substance, such as high-purity alumina or platinum.
- If your primary focus is durability and resistance to rapid temperature changes: Look for materials specifically engineered for high thermal shock resistance.
Ultimately, a crucible is a specialized tool whose reliability is a direct result of making an informed material choice for the task at hand.
Summary Table:
| Key Selection Factor | Why It Matters | Ideal Material Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Melting Point | Must be significantly higher than the melt's temperature to maintain integrity. | Tungsten, Graphite |
| Chemical Inertness | Prevents contamination of the melt and deterioration of the crucible. | Platinum, Alumina (Al₂O₃) |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Resists cracking from rapid temperature changes for longer life. | Zirconia, Specialized Ceramics |
Ensure your high-temperature processes are safe and contamination-free with the right crucible.
At KINTEK, we specialize in supplying high-performance lab equipment and consumables. Our experts can help you select the perfect crucible—whether you need extreme temperature capability, superior chemical purity, or excellent thermal shock resistance—to match your specific laboratory or industrial application.
Contact our specialists today for a personalized consultation and get the reliable performance your work demands.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the function of alumina crucibles in Na3V2(PO4)2F3 synthesis? Ensure Purity in NVPF Production
- What are the advantages of high-purity alumina crucibles for molten ZnNaK//Cl salts? Ensure Experimental Purity
- What role do high-purity alumina crucibles play in high-temperature steam oxidation? Ensure Data Integrity up to 1350°C
- Why is the use of high-purity alumina crucibles necessary for NMC powders? Ensure Purity in Cathode Synthesis
- What are the advantages of selecting an alumina crucible for TGA? Ensure High-Precision Thermal Analysis Data



















