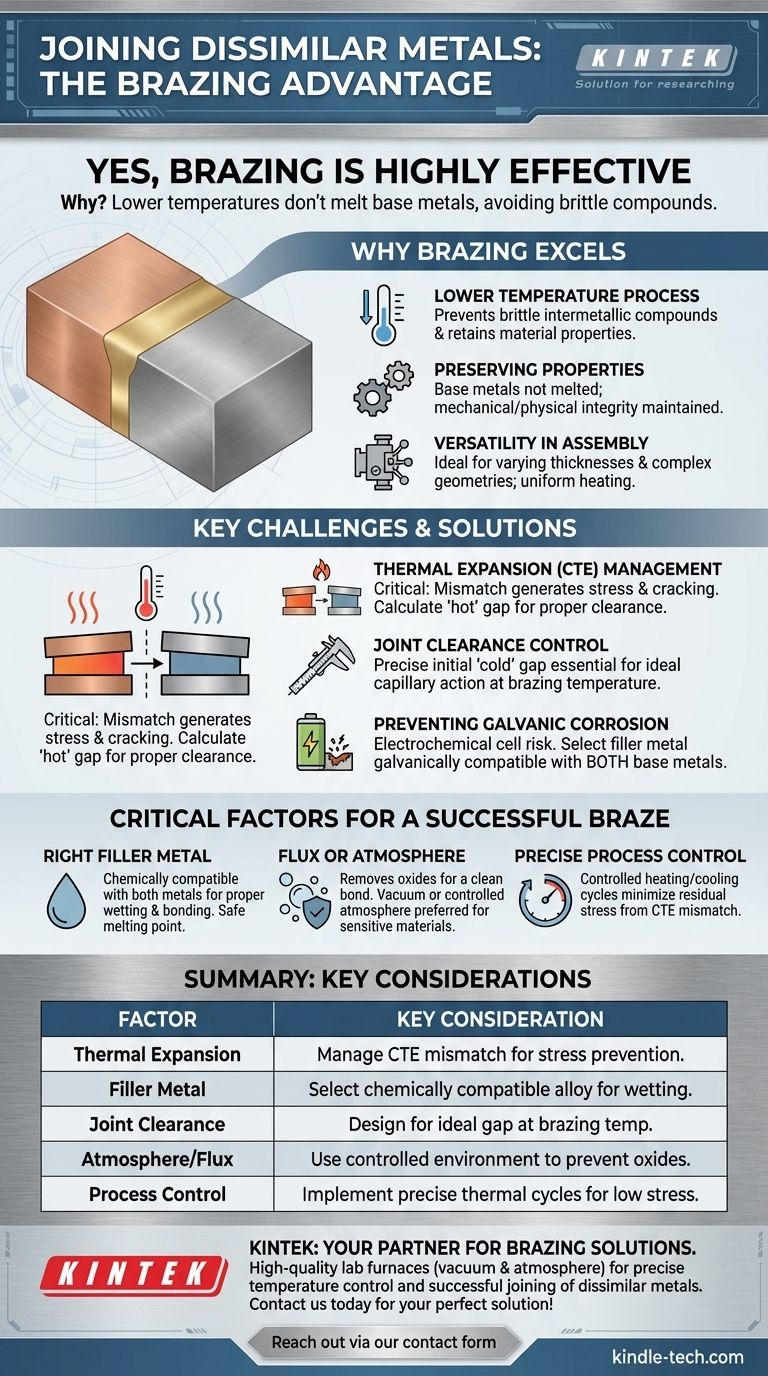
Yes, brazing is an exceptionally effective method for joining dissimilar metals. It is often the preferred technique because the lower process temperatures do not melt the base metals, which avoids many of the difficult metallurgical problems, such as the formation of brittle intermetallic compounds, that can occur when welding different materials together.
Brazing successfully joins dissimilar metals by using a filler metal with a lower melting point, but success is not automatic. The primary challenges lie in managing the different rates of thermal expansion between the base metals and selecting a filler alloy that is chemically compatible with both.

Why Brazing Excels with Dissimilar Metals
Brazing relies on a fundamentally different principle than welding. Instead of melting the base materials to fuse them, brazing uses a filler metal that is drawn into a tight-fitting joint by capillary action, creating a strong metallurgical bond upon solidification.
The Advantage of a Lower Temperature Process
The key to brazing's success is its relatively low temperature. The process is always conducted below the solidus (melting point) of the base metals being joined.
This prevents the creation of brittle intermetallic compounds that often form when dissimilar metals are melted and mixed together, which is a common failure point in dissimilar metal welding.
Preserving Material Properties
Because the base metals are not melted, their original mechanical and physical properties remain largely unchanged. This is critical when joining a heat-treated alloy to a soft, ductile metal, for example.
Versatility in Assembly
Brazing methods, particularly furnace brazing, are well-suited for joining parts with varying thicknesses or complex, intricate geometries. The slow, uniform heating of the entire assembly helps to minimize thermal distortion and stress.
Key Challenges and Considerations
While brazing is highly effective, joining dissimilar metals requires careful engineering to manage the inherent differences between the materials. Ignoring these factors is a common cause of joint failure.
The Problem of Thermal Expansion
This is the single most critical factor to manage. Different materials expand and contract at different rates when heated and cooled. This is known as the Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE).
A significant CTE mismatch can cause two primary problems. It can generate high internal stresses in the joint during cooling, potentially leading to cracking. It can also cause the carefully prepared joint clearance to either shrink too much or grow too large at the actual brazing temperature, preventing proper capillary action.
Managing Joint Clearance
The success of a braze depends on a precise gap between the parts at brazing temperature. You must calculate the initial "cold" gap so that when the two different metals expand, you achieve the ideal "hot" gap for the filler metal to flow into.
Preventing Galvanic Corrosion
Joining two different metals creates a natural electrochemical cell. In the presence of an electrolyte (like moisture), the more active (less noble) metal can corrode preferentially.
The choice of brazing filler metal is crucial here. An improper filler can accelerate this galvanic corrosion at the joint, leading to premature failure in service.
Critical Factors for a Successful Braze
Success depends on controlling a few key variables. A systematic approach ensures a strong, reliable, and durable joint.
Selecting the Right Filler Metal
The filler metal must be chemically compatible with both base metals. This ensures it will "wet" and flow properly over both surfaces to create a strong metallurgical bond. It must also have a melting point that is safe for both materials.
The Role of Flux or Atmosphere
All metals have a surface layer of oxides that must be removed for the filler metal to bond. This is accomplished either with a chemical flux or by using a controlled atmosphere.
Processes like vacuum brazing or hydrogen furnace brazing use a controlled environment to prevent oxides from forming in the first place, which is ideal for sensitive materials.
Precise Process Control
Controlling the heating and cooling rates is vital, especially to manage the stresses from a thermal expansion mismatch. Slow, uniform heating and controlled cooling help minimize residual stress that could otherwise compromise the joint's integrity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your specific goal will determine which factors you need to prioritize in your design and process control.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity: Prioritize managing thermal expansion by designing the joint and controlling the heating/cooling cycle to minimize residual stress.
- If your primary focus is long-term corrosion resistance: Carefully select a filler metal that is galvanically compatible with both base metals to prevent premature failure.
- If your primary focus is joining complex assemblies: Consider furnace or vacuum brazing, as these methods provide uniform heating that helps accommodate different material thicknesses and geometries.
By understanding and controlling these key variables, you can reliably produce strong and durable joints between a wide range of dissimilar metals.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Key Consideration for Success |
|---|---|
| Thermal Expansion | Manage Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE) mismatch to prevent stress and cracking. |
| Filler Metal | Select an alloy chemically compatible with both base metals to ensure proper wetting and bonding. |
| Joint Clearance | Design the joint gap to account for different expansion rates at brazing temperature. |
| Atmosphere/Flux | Use a controlled atmosphere (e.g., vacuum) or flux to prevent oxide formation for a clean bond. |
| Process Control | Implement precise heating and cooling cycles to minimize residual stress from CTE mismatch. |
Need to join dissimilar metals in your lab or production process? The right equipment is critical for achieving the precise temperature control and atmosphere required for a successful braze. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab furnaces, including vacuum and atmosphere brazing systems, designed to handle the complexities of joining different materials. Our expertise ensures you get the reliable performance needed for strong, durable joints. Contact us today to find the perfect brazing solution for your application. Reach out via our contact form to speak with an expert!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why would you braze instead of solder? For Superior Joint Strength and High-Temperature Performance
- What is a braze repair process? A Low-Heat Solution for Strong, Seamless Metal Joining
- What is the most important factor influencing the strength of the brazed joint? Master Joint Clearance for Maximum Strength
- What is the cost of a vacuum brazing furnace? A guide to key factors and investment strategy
- What is vacuum brazed? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity Metal Joining



















