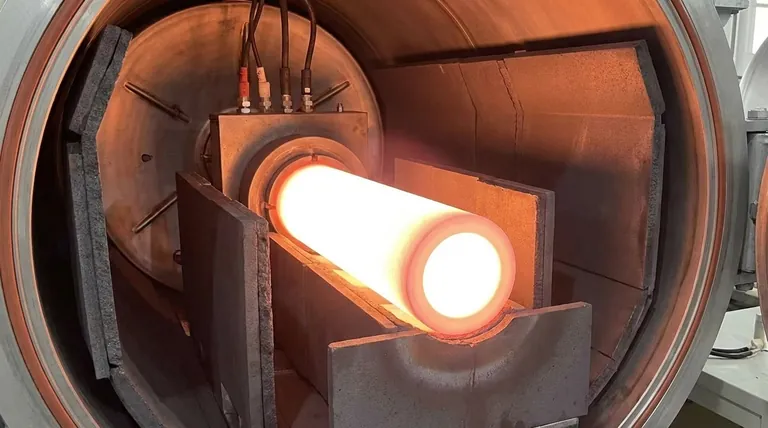
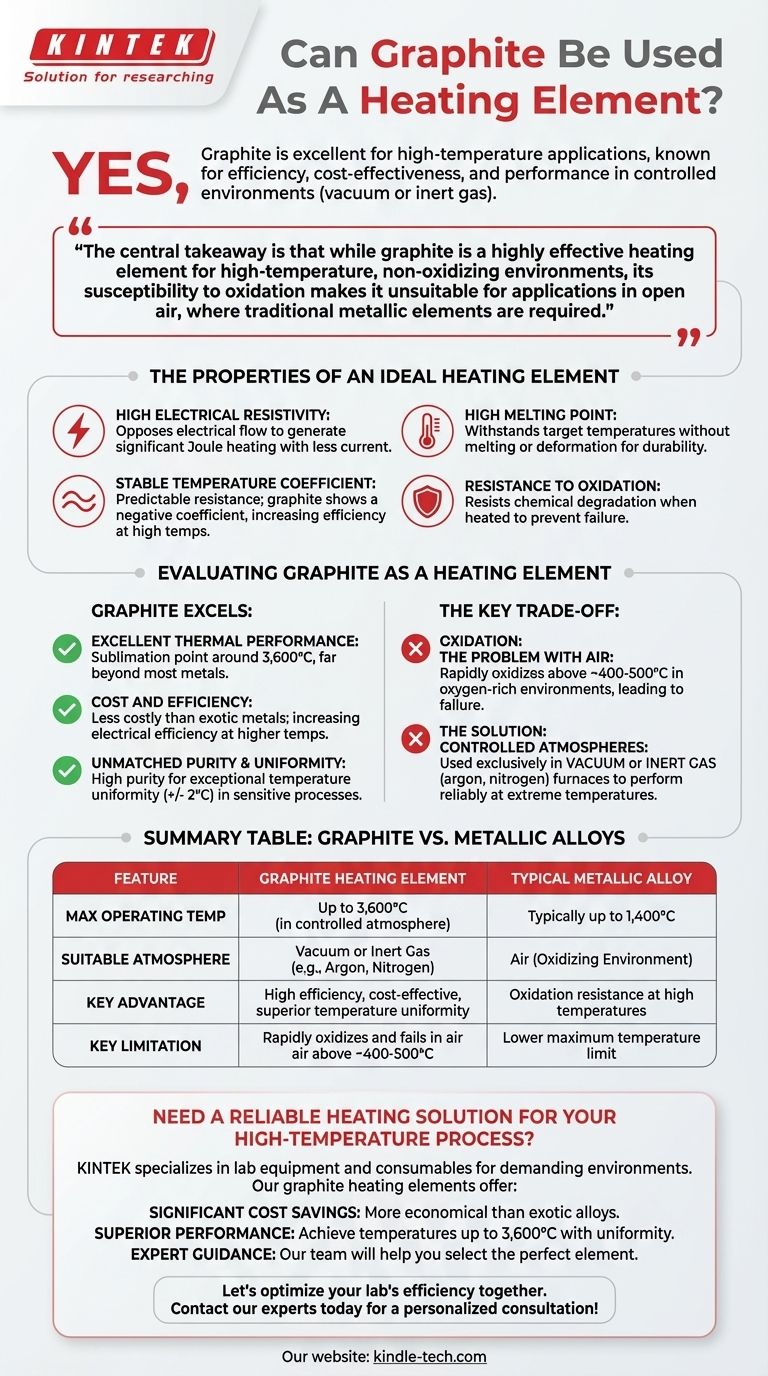
Yes, graphite is an excellent and widely used material for heating elements, particularly in high-temperature applications. It is often chosen for its high efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and superior performance in specific, controlled environments like vacuum or inert gas furnaces.
The central takeaway is that while graphite is a highly effective heating element for high-temperature, non-oxidizing environments, its susceptibility to oxidation makes it unsuitable for applications in open air, where traditional metallic elements are required.

The Properties of an Ideal Heating Element
To understand where graphite fits, we must first define what makes any material a good heating element. The choice of material is critical for longevity, efficiency, and the reliability of the entire heating process.
High Electrical Resistivity
A heating element works by converting electrical energy into heat as current passes through it, a phenomenon known as Joule heating. A material with high resistivity opposes the flow of electricity, generating significant heat with less current.
High Melting Point
The material must be able to withstand the target operating temperatures without melting or deforming. A high melting point is a fundamental requirement for durability and safety in high-temperature applications.
Stable Temperature Coefficient
The material's resistance should remain relatively stable as its temperature changes. This ensures predictable and controllable heat output. Interestingly, graphite exhibits a negative temperature coefficient, meaning its resistance decreases by about 20% as it heats up, making it more electrically efficient at high temperatures.
Resistance to Oxidation
The element must resist chemical degradation, primarily oxidation, when heated. Oxidation weakens the material, leading to premature failure and the need for frequent replacement.
Evaluating Graphite as a Heating Element
Graphite excels in several key areas, making it a superior choice for certain demanding processes. However, it also has one critical limitation.
Excellent Thermal Performance
Graphite has an exceptionally high melting point (or more accurately, sublimation point) of around 3,600°C, allowing it to operate at temperatures far beyond the limits of most metallic alloys.
Cost and Efficiency
Graphite elements are generally less costly than those made from exotic metals like molybdenum or tungsten. Combined with its increasing electrical efficiency at higher temperatures, it presents a very economical solution.
Unmatched Purity and Uniformity
Graphite can be manufactured to very high purity levels. When used in a furnace, it provides exceptional temperature uniformity, often within +/- 2°C, which is critical for sensitive processes in electronics and material science.
Understanding the Key Trade-off: Oxidation
Graphite's primary limitation is its behavior in the presence of oxygen. This single factor defines where it can and cannot be used.
The Problem with Air
When heated above approximately 400-500°C in an oxygen-rich environment (like open air), graphite will rapidly oxidize. This process converts the solid carbon into carbon dioxide gas, causing the element to degrade and quickly fail.
The Solution: Controlled Atmospheres
Because of its susceptibility to oxidation, graphite heating elements are used exclusively in vacuum furnaces or furnaces filled with a protective, inert gas (like argon or nitrogen). In these controlled environments, the lack of oxygen allows the graphite to perform reliably up to extremely high temperatures without degrading.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct heating element material comes down to the operating environment of your process.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature operation (>1200°C) in a vacuum or inert gas: Graphite is the ideal choice due to its superior temperature capabilities, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is heating in an open-air environment: Graphite is unsuitable and will fail quickly; you must use an oxidation-resistant metallic alloy like Kanthal (FeCrAl) or Nichrome (NiCr).
Ultimately, matching the material's properties to the operational atmosphere is the key to designing an effective and reliable heating system.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Graphite Heating Element | Typical Metallic Alloy |
|---|---|---|
| Max Operating Temp | Up to 3,600°C (in controlled atmosphere) | Typically up to 1,400°C |
| Suitable Atmosphere | Vacuum or Inert Gas (e.g., Argon, Nitrogen) | Air (Oxidizing Environment) |
| Key Advantage | High efficiency, cost-effective, superior temperature uniformity | Oxidation resistance at high temperatures |
| Key Limitation | Rapidly oxidizes and fails in air above ~400-500°C | Lower maximum temperature limit |
Need a reliable heating solution for your high-temperature process?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing robust heating systems for demanding environments. If your application involves high-temperature operations in a vacuum or inert gas atmosphere, our graphite heating elements can offer you:
- Significant Cost Savings: More economical than exotic metal alloys.
- Superior Performance: Achieve temperatures up to 3,600°C with excellent uniformity.
- Expert Guidance: Our team will help you select the perfect element for your specific furnace and process requirements.
Let's optimize your lab's efficiency together. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What temperature can graphite withstand? Unlocking Its Extreme Heat Potential
- Does graphite have a melting point? Unlocking the Extreme Heat Resistance of Graphite
- What are the applications of graphite material? Leveraging Extreme Heat and Precision for Industrial Processes
- Why is graphite used in furnaces? For Extreme Heat, Purity, and Efficiency
- What is the purpose of a graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme Temperatures for Advanced Materials



















