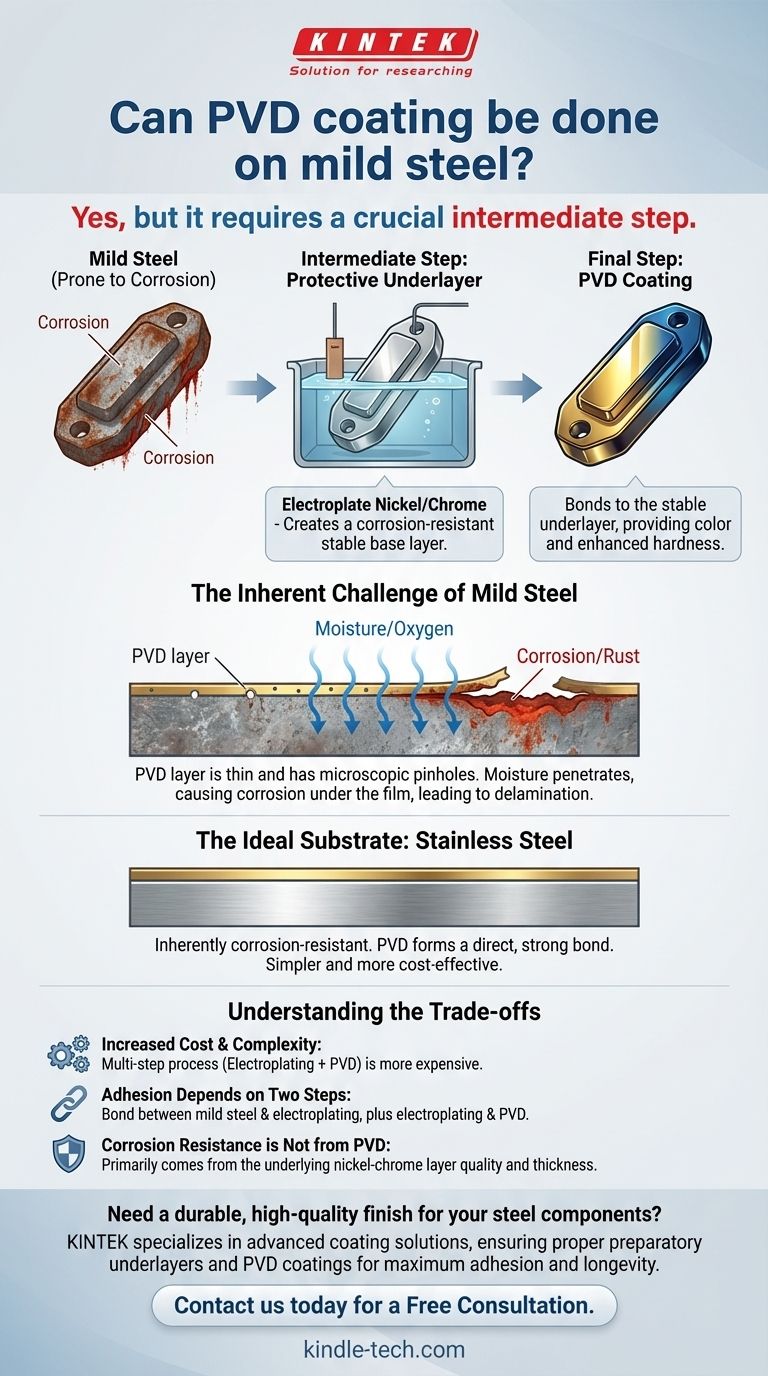
Yes, but it requires a crucial intermediate step. PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) coating can be applied to mild steel, but not directly. Because mild steel is prone to corrosion, it must first be coated with a protective underlayer, such as nickel or chrome, to ensure both proper adhesion and long-term durability.
The success of PVD on mild steel is not determined by the PVD process itself, but by the quality of the protective base layer applied beforehand. Without this foundation, corrosion will form under the PVD film, causing it to fail.

Why the Base Material is Critical for PVD
The Nature of a PVD Coating
PVD is not like paint. It does not add a thick, sealing layer to a surface.
Instead, the PVD process bonds a new material to the substrate at a microscopic level. As the reference material notes, it creates a "surface condition" rather than a coating, with only a minute buildup measured in microns.
The Ideal Substrate: Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is an ideal material for PVD because it is inherently corrosion-resistant.
Its stable surface allows the PVD material to form a direct, strong bond. This creates a durable, hard finish for aesthetic or functional purposes without the need for additional preparatory layers, making the process simpler and more cost-effective.
The Inherent Challenge of Mild Steel
The Core Problem: Corrosion
The fundamental issue with mild steel is its tendency to rust when exposed to oxygen and moisture. This process is relentless and will occur on any unprotected surface.
PVD's Limitation
A PVD layer is extremely thin and is not a perfect hermetic seal. It can have microscopic pinholes or pores.
If applied directly to mild steel, moisture can penetrate these tiny imperfections and reach the steel underneath. Corrosion will begin to form beneath the PVD layer, causing it to bubble, flake, and ultimately delaminate from the surface.
The Solution: A Multi-Layer Approach
The Role of an Underlayer
To successfully coat mild steel with PVD, you must first create a stable, non-corrosive foundation. This is almost always achieved through electroplating.
A layer of a corrosion-resistant material, most commonly nickel-chromium, is electroplated onto the mild steel part first.
The PVD Bonds to the Base Coat
This electroplated layer becomes the new, effective substrate. The PVD coating is then applied on top of the chrome or nickel.
The PVD process bonds with this stable underlayer, not the reactive mild steel. The mild steel simply serves as the structural core of the component.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Increased Cost and Complexity
This multi-step process (electroplating followed by PVD) is more complex, time-consuming, and expensive than applying PVD directly to a substrate like stainless steel.
Adhesion Depends on Two Steps
The final quality depends on two separate bonds: the electroplating to the mild steel and the PVD to the electroplating. A failure at the first step will compromise the entire system.
Corrosion Resistance Is Not from the PVD
It is critical to understand that the final product's resistance to rust comes almost entirely from the quality and thickness of the underlying nickel-chrome layer. The PVD layer primarily provides the desired color and enhanced surface hardness.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When deciding how to proceed, your choice depends on balancing cost, performance, and aesthetic requirements.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and corrosion resistance: Using a stainless steel substrate is the most direct and reliable path to a high-quality PVD finish.
- If you must use a mild steel part for structural or cost reasons: You must factor in the necessity of a high-quality electroplated underlayer before the PVD application.
- If your part is purely for decorative use in a dry, indoor environment: A thinner, less robust underlayer might suffice, but you accept a higher risk of long-term failure if the part is ever exposed to humidity.
Ultimately, successful PVD coating on mild steel is achieved by creating a corrosion-proof foundation for the PVD film to bond with.
Summary Table:
| Step | Process | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Electroplate Nickel/Chrome | Creates a corrosion-resistant base layer on the mild steel. |
| 2 | Apply PVD Coating | Bonds to the stable underlayer, providing color and hardness. |
Need a durable, high-quality finish for your steel components?
KINTEK specializes in advanced coating solutions for laboratory and industrial equipment. Our expertise ensures your mild steel parts receive the proper preparatory underlayer and subsequent PVD coating for maximum adhesion, corrosion resistance, and longevity.
Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your components' performance and aesthetics. Get a Free Consultation
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of hot stamping? Unlock Ultra-High Strength for Automotive Parts
- What is hot press forging? Creating Complex, High-Strength Metal Components
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of hot pressing? Choose the Right Powder Metallurgy Process
- What is the purpose of laminating? Protect and Enhance Your Documents for Long-Term Use
- How does hot pressing work? Achieve Maximum Density for Advanced Materials



















