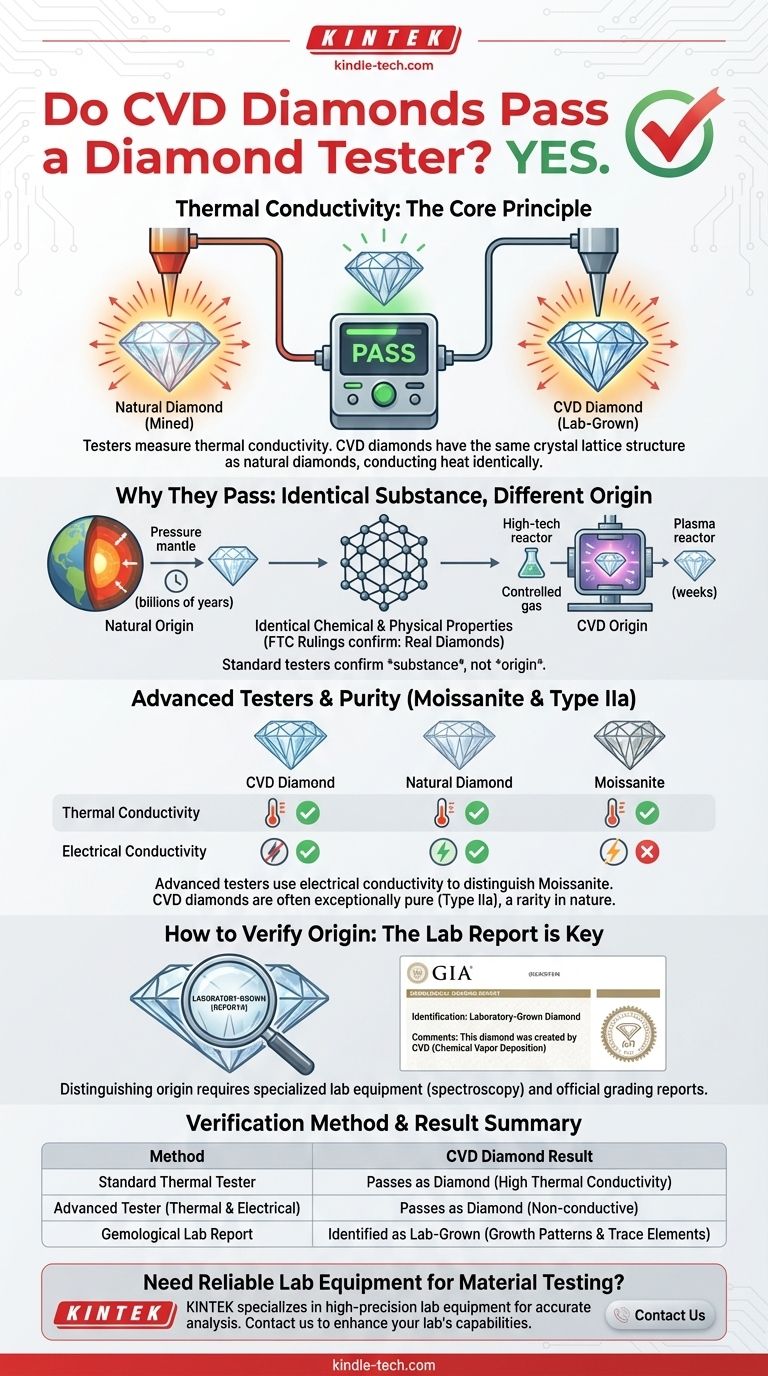
Yes, a CVD diamond will pass a standard diamond tester. These testers are designed to measure thermal conductivity—how quickly a material conducts heat. Because CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) diamonds are chemically and physically identical to natural diamonds, they possess the same exceptional thermal properties and will be correctly identified as a diamond.
Your question isn't just about a tool; it's about authenticity. A standard diamond tester confirms a stone's substance, not its origin. Since CVD diamonds are real diamonds, they pass the test, proving they are not fakes or simulants like cubic zirconia.
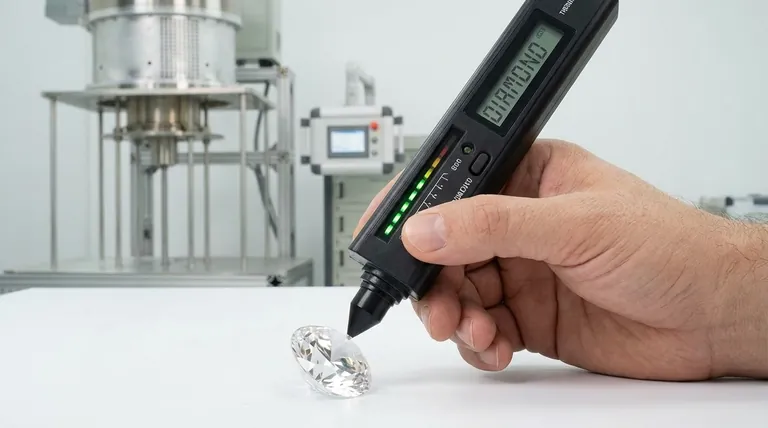

What a Diamond Tester Actually Measures
To understand why CVD diamonds pass the test, you must first understand what the test is actually looking for. It's a test of physics, not history.
Thermal Conductivity is Key
Most handheld diamond testers work on a simple principle: thermal conductivity. They have a small, heated metal tip that is placed on the gemstone. The device then measures how quickly heat is pulled away from the tip.
Diamonds are among the most effective thermal conductors on the planet, pulling heat away far more rapidly than common simulants like glass or cubic zirconia.
Why CVD Diamonds Pass
A CVD diamond is made of carbon atoms arranged in the same crystal lattice structure as a mined diamond. This specific structure is what gives a diamond its hardness, brilliance, and high thermal conductivity.
Since the physical structure is identical, a CVD diamond conducts heat identically to a natural diamond. The tester cannot distinguish between them.
What About Moissanite Testers?
Some advanced testers also measure electrical conductivity to differentiate diamonds from moissanite. Moissanite looks very similar to diamond and has high thermal conductivity, but it is also electrically conductive.
Most diamonds (both natural and CVD) are not electrically conductive. Therefore, even on these more advanced testers, a CVD diamond will correctly register as a diamond.
If a Tester Can't Tell, What's the Difference?
The inability of a standard tester to differentiate between CVD and natural diamonds highlights the core truth: the difference is one of origin, not substance.
The Question of Origin, Not Composition
The only difference between a CVD diamond and a natural diamond is its formation process. One grew over billions of years deep within the Earth's mantle, while the other was grown in a highly controlled laboratory environment over a few weeks.
Identical Properties
As ruled by the FTC in 2018, lab-grown diamonds are real diamonds. They share the same chemical, physical, and optical properties as their mined counterparts. A trained jeweler cannot tell them apart with the naked eye or a standard loupe.
The Role of Gemological Labs
Distinguishing a CVD diamond from a natural one requires specialized equipment found only in major gemological laboratories like the GIA (Gemological Institute of America) or IGI (International Gemological Institute).
These labs use advanced spectroscopic instruments to detect microscopic differences in crystal growth patterns and the presence (or absence) of certain trace elements like nitrogen.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Knowing that a CVD diamond is physically a "real" diamond, the decision to purchase one comes down to a clear set of trade-offs.
The Purity Factor
CVD diamonds are almost always classified as Type IIa, a category that represents the most chemically pure diamonds. In nature, Type IIa diamonds are exceptionally rare (less than 2% of all mined diamonds). The consistent purity of CVD diamonds is a direct result of the controlled environment in which they are grown.
Certification Is Your Proof of Origin
For the consumer, the only reliable way to know a diamond's origin is to review its official grading report. Reputable labs will clearly state if a diamond is "Laboratory-Grown" in the comments section and often laser-inscribe the diamond's girdle with the report number and a lab-grown identifier.
The Value Proposition
The primary trade-off is cost. A CVD diamond offers the exact same visual and physical performance as a natural diamond of equivalent size, cut, color, and clarity for a significantly lower price. Your choice is between the geological history of a mined diamond and the technological achievement and value of a lab-grown one.
How to Verify Your Diamond's Origin
Use the right tool for the right question. Your verification method should match your goal.
- If your primary focus is confirming you have a real diamond (and not a simulant): A standard thermal diamond tester is a reliable tool for this purpose.
- If your primary focus is determining the diamond's origin (lab-grown vs. natural): You must rely on the official grading report (certificate) from a reputable gemological lab.
- If you are purchasing a diamond: Always demand the certificate and verify that the laser inscription on the diamond's girdle matches the report number.
Understanding these distinctions empowers you to make an informed choice based on authenticity, origin, and value.
Summary Table:
| Verification Method | What It Detects | CVD Diamond Result |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Thermal Tester | Thermal Conductivity | Passes as Diamond |
| Advanced Tester (Thermal & Electrical) | Thermal & Electrical Conductivity | Passes as Diamond (non-conductive) |
| Gemological Lab Report | Crystal Growth & Trace Elements | Identified as Lab-Grown |
Need reliable lab equipment for material testing or research? KINTEK specializes in high-precision lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratories with trusted solutions for accurate analysis. Contact us today to enhance your lab's capabilities with our expert support and premium products.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- Filter Testing Machine FPV for Dispersion Properties of Polymers and Pigments
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
People Also Ask
- What are the primary advantages of the CVD method for growing diamonds? Engineering High-Purity Gems and Components
- What is MPCVD method? A Guide to High-Purity Diamond Synthesis
- How does MPCVD work? A Guide to Low-Temperature, High-Quality Film Deposition
- How difficult is it to grow a diamond? The Immense Challenge of Atomic-Level Precision
- How does a microwave plasma reactor facilitate the synthesis of diamond? Master MPCVD with Precision Technology



















