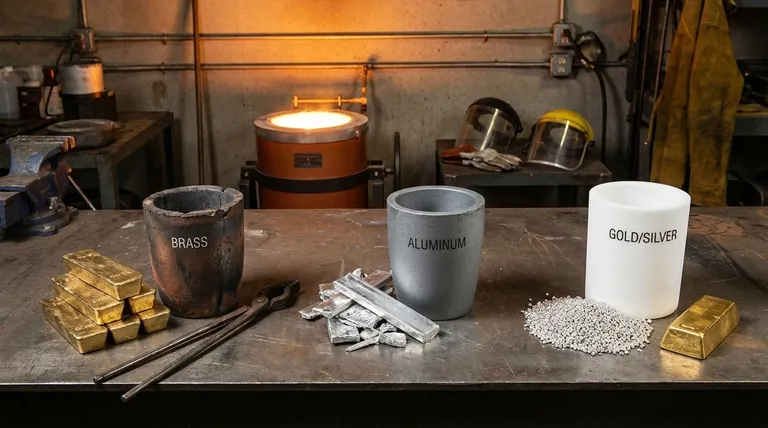
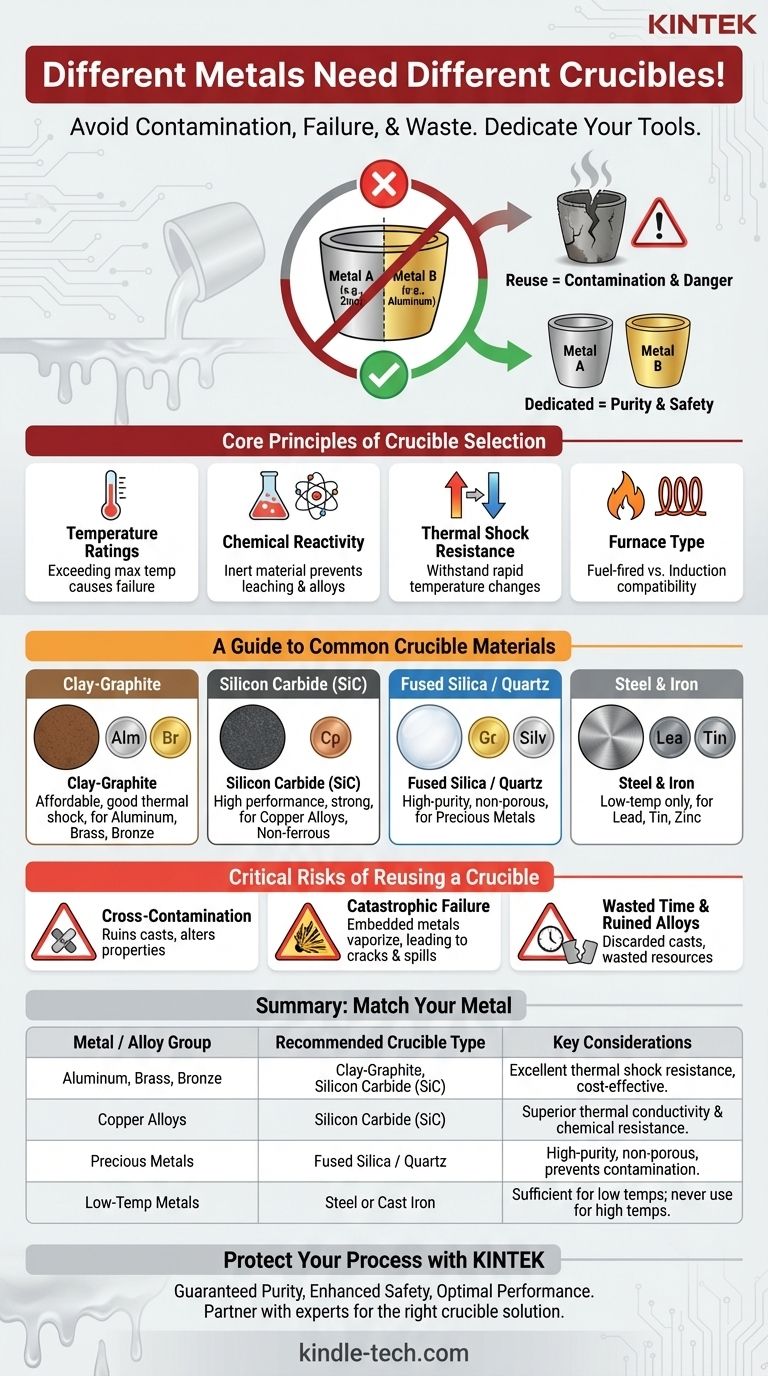
Yes, you absolutely need a different crucible for different metals. While it may seem efficient to reuse a single crucible, doing so is a fundamental error that introduces contamination, compromises the integrity of your metal, and can lead to dangerous equipment failure. Each metal or alloy family requires a dedicated crucible to ensure purity and safety.
The core principle is that a crucible is not just a pot; it's a piece of technical equipment. Its material must be chosen based on the metal's melting temperature and chemical reactivity, and dedicating one crucible per metal is the only way to guarantee the quality of your cast and the safety of your process.

The Core Principles of Crucible Selection
To understand why dedicated crucibles are non-negotiable, you must first understand the factors that govern their selection. The choice is a careful balance of physics and chemistry under extreme conditions.
Matching Temperature Ratings to Your Metal
Every crucible has a maximum service temperature. Exceeding this limit will cause the crucible to soften, crack, or fail catastrophically.
For example, a steel crucible might work for melting zinc (melting point 787°F / 420°C), but it will melt and fail if you attempt to use it for copper (1984°F / 1084°C). You must always select a crucible with a temperature rating comfortably above the melting point of your target metal.
Preventing Chemical Reactions and Contamination
Molten metals are highly reactive. The crucible material must be chemically inert, meaning it won't react with or dissolve into the molten metal it holds.
More importantly, crucibles are porous on a microscopic level. When you melt a metal like zinc, its vapors and particles become embedded in the crucible walls. If you then try to melt aluminum in that same crucible, the trapped zinc will leach out, creating an unintended and weak zinc-aluminum alloy, ruining your pure aluminum cast.
Understanding Thermal Shock Resistance
Thermal shock is the stress a material endures when it experiences rapid temperature changes. A good crucible must withstand being heated to over 2000°F and then cooling back to room temperature without cracking.
Materials like silicon carbide have excellent thermal shock resistance, making them durable for frequent use. Others, like some ceramics, may require slower, more careful heating and cooling cycles to prevent failure.
Considering Your Furnace Type
The way you heat the crucible also matters. A fuel-fired furnace (propane, gas) heats the crucible from the outside, while an induction furnace heats the crucible's contents directly using a magnetic field.
Graphite-based crucibles (like clay-graphite and silicon carbide) are conductive and work well in induction furnaces. A non-conductive ceramic or quartz crucible would be ineffective in the same furnace without a special conductive sleeve.
A Guide to Common Crucible Materials
Understanding the primary types of crucibles clarifies why a "one-size-fits-all" approach is impossible.
Clay-Graphite Crucibles
These are the affordable workhorses for hobbyists and small foundries. They are a composite of clay (a binder) and graphite (for thermal conductivity and shock resistance). They are excellent for aluminum, brass, and bronze.
Silicon Carbide (SiC) Crucibles
These are a significant step up in performance and cost. Made of silicon carbide with a carbon or clay binder, they offer superior thermal conductivity, high mechanical strength, and excellent resistance to chemical erosion and thermal shock. They are the professional choice for melting copper alloys, aluminum, and other non-ferrous metals.
Fused Silica / Quartz Crucibles
These high-purity ceramic crucibles are the standard for melting precious metals like gold and silver, as well as high-purity lab samples. Their extremely smooth, non-porous surface minimizes contamination and prevents the loss of valuable material that could get trapped in the crucible wall. They are, however, more susceptible to thermal shock.
Steel & Iron Crucibles
For very low-temperature metals, a simple steel or cast iron pot is often sufficient. They are used exclusively for melting lead, tin, zinc, and pewter. Using them for anything hotter, like aluminum, will destroy the crucible and contaminate your melt.
The Critical Risks of Reusing a Crucible
Attempting to save money by using one crucible for multiple metals is a false economy that introduces significant risks.
The Inevitability of Cross-Contamination
This is the most common and immediate problem. Using a crucible that once held zinc to melt aluminum will contaminate the aluminum. Even trace amounts of a foreign metal can dramatically alter the properties of your final cast, making it brittle, weak, or prone to cracking.
The Danger of Catastrophic Failure
Contamination isn't just about purity; it's about safety. If a low-temperature metal like zinc is embedded in a crucible wall and you then heat it to the temperature required for copper, the zinc will rapidly vaporize inside the crucible's structure. This can cause internal pressure to build, leading to cracks or an explosive failure, spilling molten metal.
Wasted Time and Ruined Alloys
The result of cross-contamination is, at best, a ruined cast that must be discarded. This wastes the metal, the fuel used for the melt, and hours of your time. The cost of a dedicated crucible is minor compared to the cost of repeated failures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Metal
Your decision should be guided by your specific goals and the metals you work with. Always mark your crucibles clearly to avoid mix-ups.
- If your primary focus is low-temp metals (lead, zinc): A dedicated, inexpensive steel pot for each metal is a perfectly safe and effective solution.
- If your primary focus is aluminum, brass, or bronze: Invest in a separate clay-graphite or silicon carbide crucible for each distinct alloy to ensure professional results.
- If your primary focus is precious metals (gold, silver): A high-purity fused silica crucible is the only acceptable choice to protect the value and integrity of your material.
Treating each crucible as a dedicated tool for a single metal is the mark of a skilled and safe practitioner.
Summary Table:
| Metal / Alloy Group | Recommended Crucible Type | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum, Brass, Bronze | Clay-Graphite, Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Excellent thermal shock resistance, cost-effective for non-ferrous metals. |
| Copper Alloys | Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Superior thermal conductivity and resistance to chemical erosion. |
| Precious Metals (Gold, Silver) | Fused Silica / Quartz | High-purity, non-porous surface to prevent contamination and material loss. |
| Low-Temp Metals (Lead, Tin, Zinc) | Steel or Cast Iron | Sufficient for low melting points; never use for higher temperature metals. |
Protect Your Materials and Processes with the Right Crucible from KINTEK
Choosing the correct crucible is not just a recommendation—it's a critical step for ensuring the purity of your materials, the integrity of your results, and the safety of your lab. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including a comprehensive range of crucibles designed for specific metals and applications.
By partnering with KINTEK, you gain:
- Guaranteed Purity: Prevent cross-contamination and ensure accurate, reliable results for every melt.
- Enhanced Safety: Minimize the risk of crucible failure and dangerous accidents with equipment rated for your specific thermal and chemical requirements.
- Optimal Performance: Maximize the efficiency and lifespan of your furnaces with compatible, high-performance crucibles.
Don't compromise your work. Let our experts help you select the perfect crucible for your laboratory's unique needs.
Contact KINTEK today for a consultation and ensure your next project is a success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of selecting an alumina crucible for TGA? Ensure High-Precision Thermal Analysis Data
- Why Use Alumina Crucibles for TGA of Bicyclic Carbonates? Ensure Data Purity & Chemical Inertness
- What is a crucible material for a furnace? A Guide to Choosing the Right High-Temperature Container
- What are the advantages of using alumina crucibles for the TGA of modified alkyd resins? Ensure Accurate Results
- What temperature is an Al2O3 crucible? Key Factors for High-Temperature Success Up to 1700°C



















