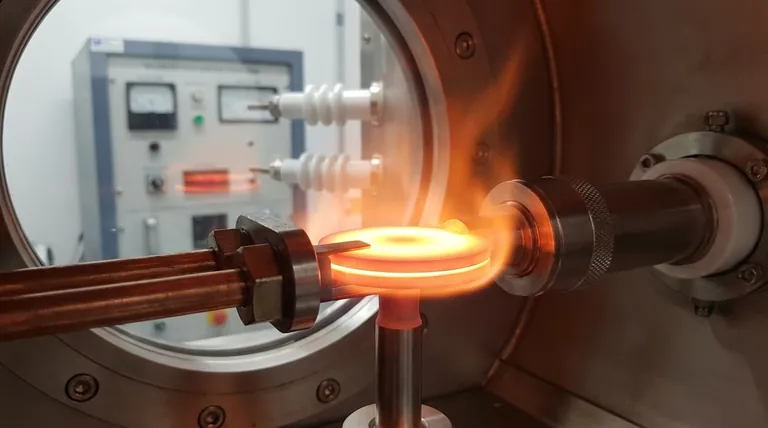
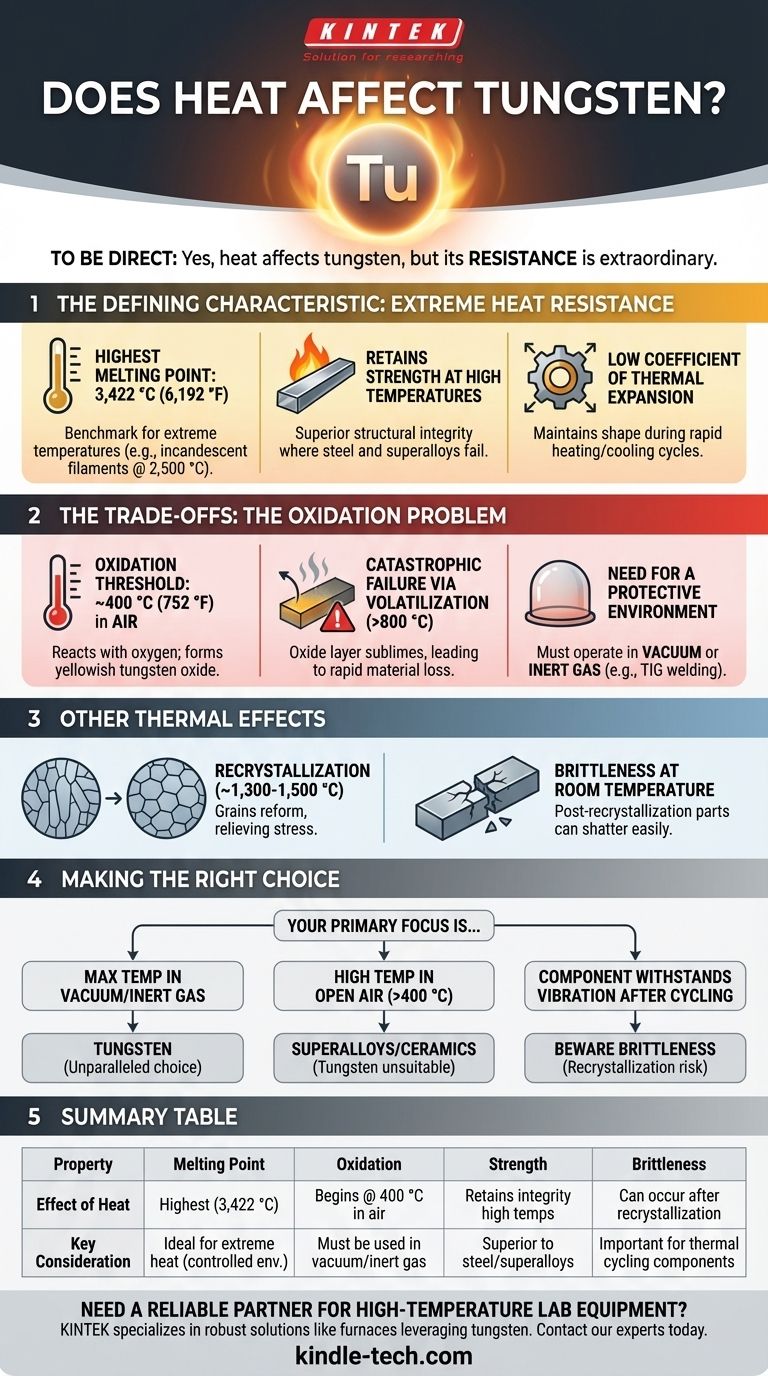
To be direct, yes, heat absolutely affects tungsten, but its defining characteristic is its extraordinary resistance to those effects. Tungsten has the highest melting point of any pure metal, making it the benchmark material for applications involving extreme temperatures. However, its behavior under heat is more nuanced than just its melting point.
While tungsten boasts the highest melting point of any metal (3,422 °C / 6,192 °F), its practical use at high temperatures is critically dependent on the environment. Its Achilles' heel is oxidation, which begins in air at temperatures far below its melting point.

The Defining Characteristic: Extreme Heat Resistance
Tungsten is synonymous with high-temperature performance. This reputation is built on a few key physical properties that set it apart from nearly all other materials.
The Highest Melting Point
The most famous property of tungsten is its melting point of 3,422 °C (6,192 °F). This is higher than any other pure metal on the periodic table.
This property alone is why it was the material of choice for the filaments in incandescent light bulbs, which operate at searing temperatures of around 2,500 °C (4,500 °F).
Retaining Strength at High Temperatures
Unlike many metals that become soft and lose structural integrity long before they melt, tungsten exhibits excellent high-temperature strength.
It remains strong and rigid at temperatures where steel and even superalloys would have failed. This makes it essential for applications like high-temperature furnace components, rocket engine nozzles, and welding electrodes.
Low Coefficient of Thermal Expansion
Tungsten has one of the lowest rates of thermal expansion among pure metals. This means it expands and contracts very little when its temperature changes dramatically.
This stability is crucial for precision components that must maintain their shape and avoid internal stress or cracking when subjected to rapid heating and cooling cycles.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Oxidation Problem
The remarkable properties of tungsten come with a significant limitation that dictates how and where it can be used. Its performance in the presence of oxygen is its most critical weakness.
The Oxidation Threshold
In open air, tungsten begins to oxidize at approximately 400 °C (752 °F). This is a stark contrast to its melting point of over 3,400 °C.
Above this threshold, it reacts with oxygen to form a yellowish layer of tungsten oxide on its surface.
Catastrophic Failure via Volatilization
This oxidation becomes rapidly destructive at higher temperatures. Above roughly 800 °C (1,472 °F), the tungsten oxide layer becomes volatile, meaning it turns directly into a gas and floats away.
This process, called sublimation, causes the material to literally evaporate, leading to rapid material loss and component failure. This is why a tungsten filament in a light bulb must be encased in a vacuum or filled with an inert gas.
The Need for a Protective Environment
To leverage tungsten's incredible melting point, it must be shielded from oxygen.
This is achieved by operating it in a vacuum or surrounding it with a non-reactive inert gas, such as argon or nitrogen. This is the fundamental principle behind its use in TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding.
Other Thermal Effects on Tungsten
Beyond melting and oxidation, heat can induce other important changes in tungsten's structure and properties.
Recrystallization and Brittleness
When tungsten is worked and formed, its internal grain structure is elongated and tough. If it is heated above its recrystallization temperature (around 1,300-1,500 °C), these grains reform into a more uniform, unstressed state.
While this relieves internal stresses, the downside is that a recrystallized tungsten part becomes very brittle at room temperature. A filament that was flexible before use can shatter with a simple tap after being run at high heat.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting tungsten requires understanding its environmental limitations as much as its thermal strengths.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature resistance in a vacuum or inert gas: Tungsten is the unparalleled choice, with a service ceiling far beyond nearly any other metal.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature operation in open air: Tungsten is unsuitable above 400 °C without specialized protective coatings; you should consider nickel-based superalloys or ceramics instead.
- If your primary focus is a component that must withstand vibration after thermal cycling: Be aware of recrystallization, as the part may become extremely brittle at room temperature after being exposed to very high heat.
Ultimately, harnessing tungsten's power is about controlling its environment to prevent its single greatest weakness.
Summary Table:
| Property | Effect of Heat on Tungsten | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Melting Point | Highest of all pure metals (3,422 °C) | Ideal for extreme heat in controlled environments |
| Oxidation | Begins in air at 400 °C; leads to failure | Must be used in a vacuum or inert gas atmosphere |
| Strength | Retains structural integrity at high temperatures | Superior to steel and superalloys for high-heat applications |
| Brittleness | Can become brittle after recrystallization (above 1,300 °C) | Important for components subject to thermal cycling |
Need a reliable partner for high-temperature lab equipment?
Tungsten's exceptional properties make it a cornerstone material for demanding applications. At KINTEK, we specialize in designing and supplying robust lab equipment, including high-temperature furnaces and components that leverage materials like tungsten for superior performance.
Our expertise ensures you get the right solution for your specific thermal processing needs, whether it's for research, production, or quality control.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's high-temperature challenges with precision equipment and consumables.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Metal Disc Electrode Electrochemical Electrode
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Gold Disc Electrode
- RRDE rotating disk (ring disk) electrode / compatible with PINE, Japanese ALS, Swiss Metrohm glassy carbon platinum
- Graphite Disc Rod and Sheet Electrode Electrochemical Graphite Electrode
People Also Ask
- What is the expected lifespan of a metal disk electrode? Extend Its Life with Proper Care
- How should a metal disk electrode be handled during an experiment? Ensure Accurate Electrochemical Measurements
- What are the key performance characteristics of a metal disk electrode? Ensuring Accurate Electrochemical Measurements
- What is the typical shape and size of a metal disk electrode? A Guide to Standard and Custom Dimensions
- What materials can be used for metal disk electrodes? Selecting the Right Metal for Your Electrochemical Experiment



















