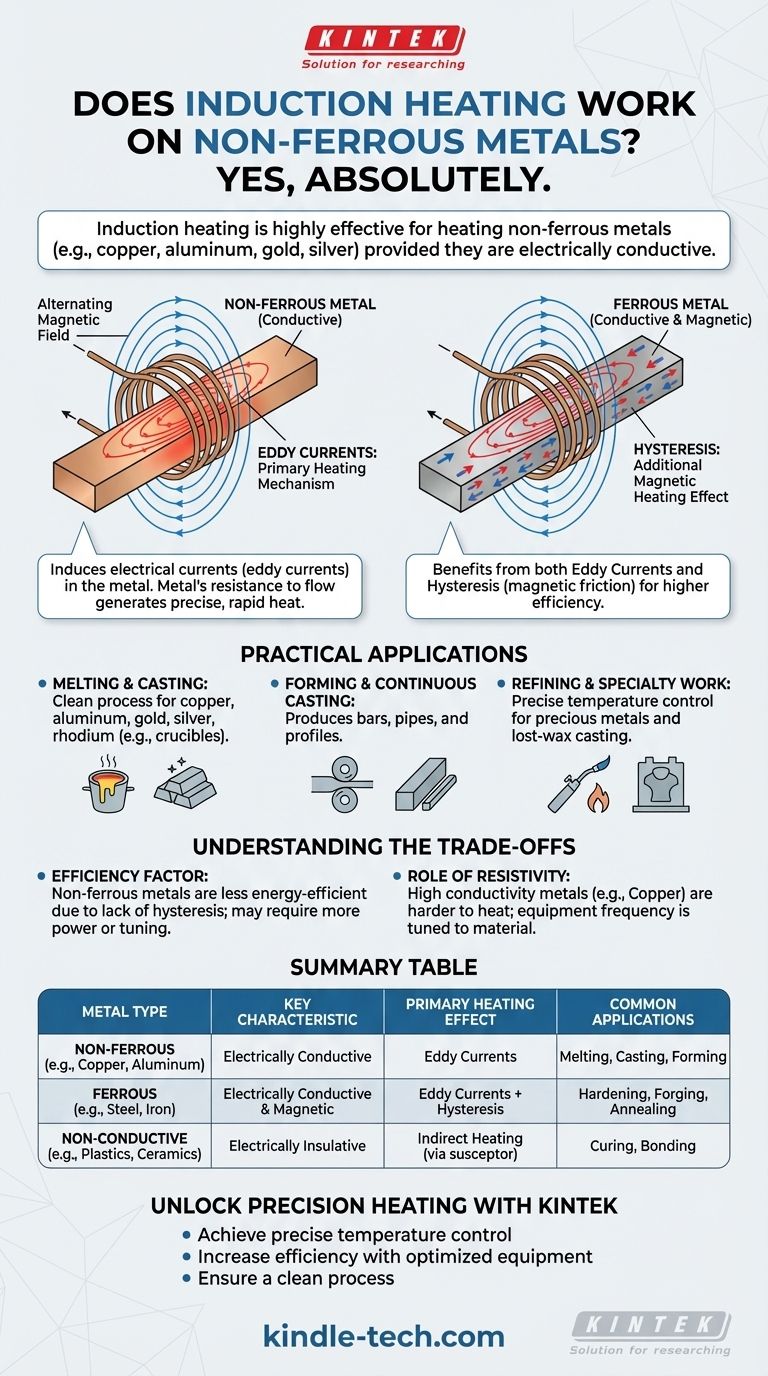
Yes, absolutely. Induction heating is a highly effective method for heating non-ferrous metals, provided they are electrically conductive. This process is widely used across industries for melting, casting, and forming materials like copper, aluminum, gold, and silver.
The core principle is simple: induction works on any material that can conduct electricity. While it's famously efficient with ferrous metals like iron due to an added magnetic effect, its ability to generate heat in non-ferrous metals through electrical currents makes it a versatile and widely-used technology.

The Core Principle: How Induction Heats Any Conductive Metal
To understand why induction works on such a broad range of materials, you must grasp the two fundamental heating effects it can produce.
The Universal Effect: Eddy Currents
An induction heater creates a powerful, rapidly alternating magnetic field. When a conductive material like aluminum or copper is placed inside this field, it induces electrical currents within the metal.
These swirling currents are called eddy currents. Due to the metal's natural electrical resistance, the flow of these currents generates precise and rapid heat. This is the primary mechanism for heating non-ferrous metals.
The Ferrous Metal Advantage: Hysteresis
Ferrous metals (like iron and steel) benefit from a second, powerful heating effect called hysteresis. These materials are magnetic.
When exposed to the alternating magnetic field, their internal magnetic domains rapidly flip back and forth. This microscopic friction generates a significant amount of additional heat. Non-ferrous metals do not experience this effect.
Practical Applications for Non-Ferrous Metals
The ability to heat non-ferrous metals with precision and speed makes induction essential for many high-value applications. The references confirm its use across several key industrial processes.
Melting and Casting
Induction furnaces are a standard choice for melting base metals like copper and aluminum and precious metals like gold, silver, and rhodium. The clean, contained heating process minimizes contamination.
Forming and Continuous Casting
The technology is also used to produce semi-finished goods. By heating metals, they can be formed into bars, pipes, and profiles through processes like continuous casting.
Refining and Specialty Work
For precious metals, induction is used for refining raw materials and for creating intricate objects through lost-wax casting, where precise temperature control is critical.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While induction works on non-ferrous metals, there are key differences in performance compared to ferrous metals that you must consider.
The Efficiency Factor
Because non-ferrous metals are heated only by eddy currents and not hysteresis, the process can be less energy-efficient. It may require more power or different equipment settings to achieve the same heating rate you would see in a piece of steel.
The Role of Resistivity
A material's electrical resistivity plays a crucial role. Metals with very high conductivity, like copper, can be more challenging to heat because they allow eddy currents to flow with less resistance, thus generating less heat.
Conversely, metals with slightly higher resistivity heat more effectively from eddy currents. This is why equipment frequency is often tuned specifically for the target material.
Indirect Heating for Non-Conductive Materials
For materials that are not electrically conductive at all, such as plastics or ceramics, direct induction is impossible. However, they can be heated indirectly by first using induction to heat a conductive metal susceptor, which then transfers its heat to the non-conductive material via conduction or radiation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your approach should be guided by the material you are working with and your ultimate goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum heating efficiency for steel or iron: You are leveraging both hysteresis and eddy currents, making induction an ideal and highly efficient choice.
- If your primary focus is heating non-ferrous metals like aluminum or copper: The process is absolutely viable, but be prepared for different power requirements and ensure your equipment is tuned for the material's specific properties.
- If your primary focus is working with precious metals like gold or silver: Induction offers a clean, precise, and rapid melting method perfectly suited for high-value applications where control is paramount.
Ultimately, induction heating's versatility makes it a powerful tool for nearly any conductive metal, provided the system is properly matched to the material's unique characteristics.
Summary Table:
| Metal Type | Key Characteristic | Primary Heating Effect | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Ferrous (e.g., Copper, Aluminum) | Electrically Conductive | Eddy Currents | Melting, Casting, Forming |
| Ferrous (e.g., Steel, Iron) | Electrically Conductive & Magnetic | Eddy Currents + Hysteresis | Hardening, Forging, Annealing |
| Non-Conductive (e.g., Plastics, Ceramics) | Electrically Insulative | Indirect Heating (via a susceptor) | Curing, Bonding |
Unlock Precision Heating for Your Lab or Production Line
Whether you are refining precious metals, casting aluminum components, or developing new materials, having the right heating equipment is critical. KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including induction heating systems tailored for both ferrous and non-ferrous metals.
Partner with us to:
- Achieve precise temperature control for consistent, high-quality results.
- Increase efficiency with equipment optimized for your specific material's properties.
- Ensure a clean process with our contamination-minimizing solutions, ideal for sensitive applications.
Ready to enhance your capabilities? Contact our experts today to discuss your project needs and discover the perfect heating solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why do you heat treat in a vacuum? Achieve Perfect Surface Finish and Material Integrity
- What are the parts of a vacuum furnace? A Guide to the 5 Core Systems
- What are the different types of heat treatment process for steel? Tailor Strength, Hardness & Toughness
- How does heat treatment process work? Tailor Material Properties for Your Application
- What is a vacuum heat treatment furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Controlled Atmosphere Processing



















