In short, yes, but not in the way you might think. While platinum is exceptionally resistant to corrosion and does not rust or tarnish under normal conditions, it can be forced to form a thin oxide layer under very specific circumstances, primarily at high temperatures or through electrochemical processes. This oxidation is fundamentally different from the destructive rusting seen on iron.
Platinum's reputation as a "noble metal" is well-earned. Its resistance to oxidation at room temperature is nearly absolute, and while it can form an oxide at high heat, this layer is unstable and decomposes at even higher temperatures, a property that sets it apart from almost all other metals.
What "Oxidation" Means for a Noble Metal
For most people, oxidation brings to mind the reddish-brown, flaky rust on iron. Platinum's interaction with oxygen is a far more subtle and controlled process that only occurs when significant energy is introduced into the system.
Redefining Tarnish and Corrosion
The oxidation of platinum does not result in tarnish or destructive corrosion. Instead, it forms an exceptionally thin, adherent, and often dark-colored surface layer of platinum dioxide (PtO₂).
Unlike the rust on steel, this layer does not flake off to expose fresh metal to further attack. It is a surface-level phenomenon that requires specific, non-everyday conditions to occur.
The Stability of Platinum
Platinum is a noble metal because it is thermodynamically stable in its elemental form. The reaction to form platinum oxide is not energetically favorable under normal conditions.
This inherent stability is why platinum, along with gold, sits at the top of the hierarchy of corrosion-resistant metals, making it invaluable for applications where reliability is paramount.
The Conditions Required for Platinum Oxidation
While resistant, platinum is not entirely inert. There are two primary pathways through which it can be made to oxidize, both of which are common in industrial and scientific settings but rare in daily life.
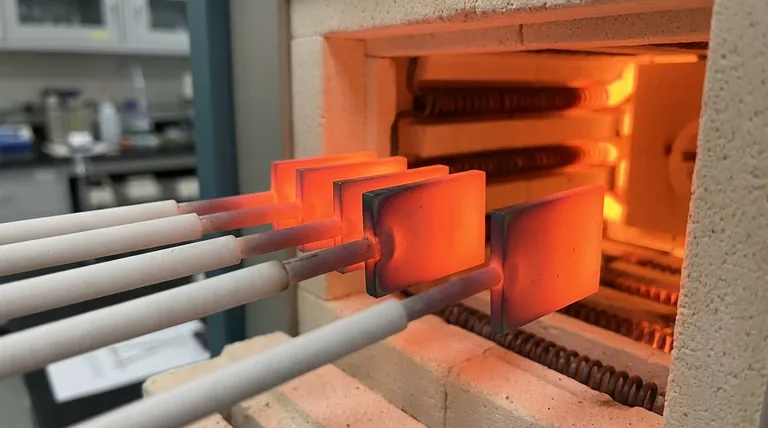
1. High-Temperature Oxidation
The most common way to oxidize platinum is by heating it in the presence of oxygen. A volatile oxide layer begins to form on the surface at temperatures between 500°C and 900°C (approx. 930°F to 1650°F).
Interestingly, if you continue to heat the metal above this range, the process reverses. At temperatures exceeding 1000°C, the platinum oxide becomes unstable and decomposes back into pure, metallic platinum and oxygen gas. This unique behavior is critical in applications like high-temperature sensors and catalytic converters.
2. Electrochemical Oxidation
Platinum can also be oxidized in a liquid solution by applying a strong positive voltage. This process is fundamental to the field of electrochemistry, where platinum is often used as an electrode.
Even in this scenario, the oxide layer formed is typically only a few atoms thick. Its formation and reduction can be precisely controlled, a property leveraged in advanced sensors and chemical research.
Understanding the Trade-offs vs. Other Metals
Comparing platinum's behavior to other metals highlights its exceptional nature and helps clarify when its properties are most valuable.
Against Gold
Gold is even more resistant to oxidation than platinum. It is one of the few metals that will not oxidize under high heat in the air. However, platinum often has superior mechanical properties, such as hardness and durability, making it better for applications involving wear.
Against Silver and Copper
Silver readily tarnishes by reacting with sulfur compounds in the air, and copper forms a green patina. Platinum's resistance to any form of tarnishing or corrosion in ambient air is absolute, making it far superior for jewelry or electrical contacts where a clean surface is essential.
Against Iron and Steel
The oxidation of iron (rust) is an aggressive, destructive process that flakes away, continuously exposing new metal to corrosion. Platinum's oxidation is a stable, non-destructive surface effect, making the two processes fundamentally incomparable.
Is Platinum Oxidation a Concern for You?
Understanding whether this phenomenon matters depends entirely on your application. For the vast majority of uses, it is not a practical concern.
- If your primary focus is jewelry: Platinum's resistance to oxidation means it is a premier material that will not tarnish, corrode, or change color over a lifetime of wear.
- If you are using it in high-temperature industrial settings: You must account for the formation and decomposition of platinum oxide, as this can lead to material loss and affect component longevity within its specific temperature window.
- If you are using it for medical implants or electrodes: Platinum's extreme resistance to electrochemical corrosion in the human body is precisely why it is a benchmark for biocompatibility and safety.
Ultimately, platinum's immense stability is its defining feature, making it a benchmark material for performance in the most demanding environments.
Summary Table:
| Condition | Oxidation Behavior | Key Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Room Temperature / Air | No oxidation or tarnish | Premier choice for jewelry and electronics. |
| High Heat (500-900°C) | Forms thin, stable PtO₂ layer | Layer decomposes above 1000°C, a key property for industrial use. |
| Electrochemical Process | Forms a controlled, atomic-scale oxide layer | Essential for electrochemical sensors and research. |
| Comparison to Iron (Rust) | Non-destructive surface effect vs. destructive flaking | Platinum's oxidation does not compromise the metal's integrity. |
Need Reliable, High-Performance Lab Equipment?
Understanding material properties like platinum's oxidation resistance is crucial for precision work. At KINTEK, we specialize in supplying high-quality lab equipment and consumables designed for reliability and accuracy. Whether your research involves high-temperature processes, electrochemistry, or requires corrosion-resistant materials, we have the solutions to support your success.
Let's discuss your specific laboratory needs. Contact our experts today to find the perfect equipment for your application.
Visual Guide

Related Products
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Platinum Auxiliary Electrode for Laboratory Use
- Custom-Made Alumina Zirconia Special-Shaped Ceramic Plates for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Processing
- Zirconia Ceramic Gasket Insulating Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- High Temperature Wear-Resistant Alumina Al2O3 Plate for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- How does a Hot Isostatic Press (HIP) facilitate the transformation of CVD-ZnS? From Standard to Multispectral Grade
- What are the properties of the sintering process? Achieve High-Strength, Complex Parts from Powder
- What is the DC sputtering mechanism? A Guide to Physical Vapor Deposition for Thin Films
- Is biomass a sustainable energy option? Unlocking a Truly Sustainable Energy Future
- What are the cons of pyrolysis? The High Costs and Hidden Challenges of Waste-to-Energy
- How do you test for filtration? Measure Upstream vs. Downstream for True Efficiency
- Is annealing done in a furnace? Mastering the Thermal Process for Material Properties
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of bio-oil? A Guide to This Renewable Fuel



















