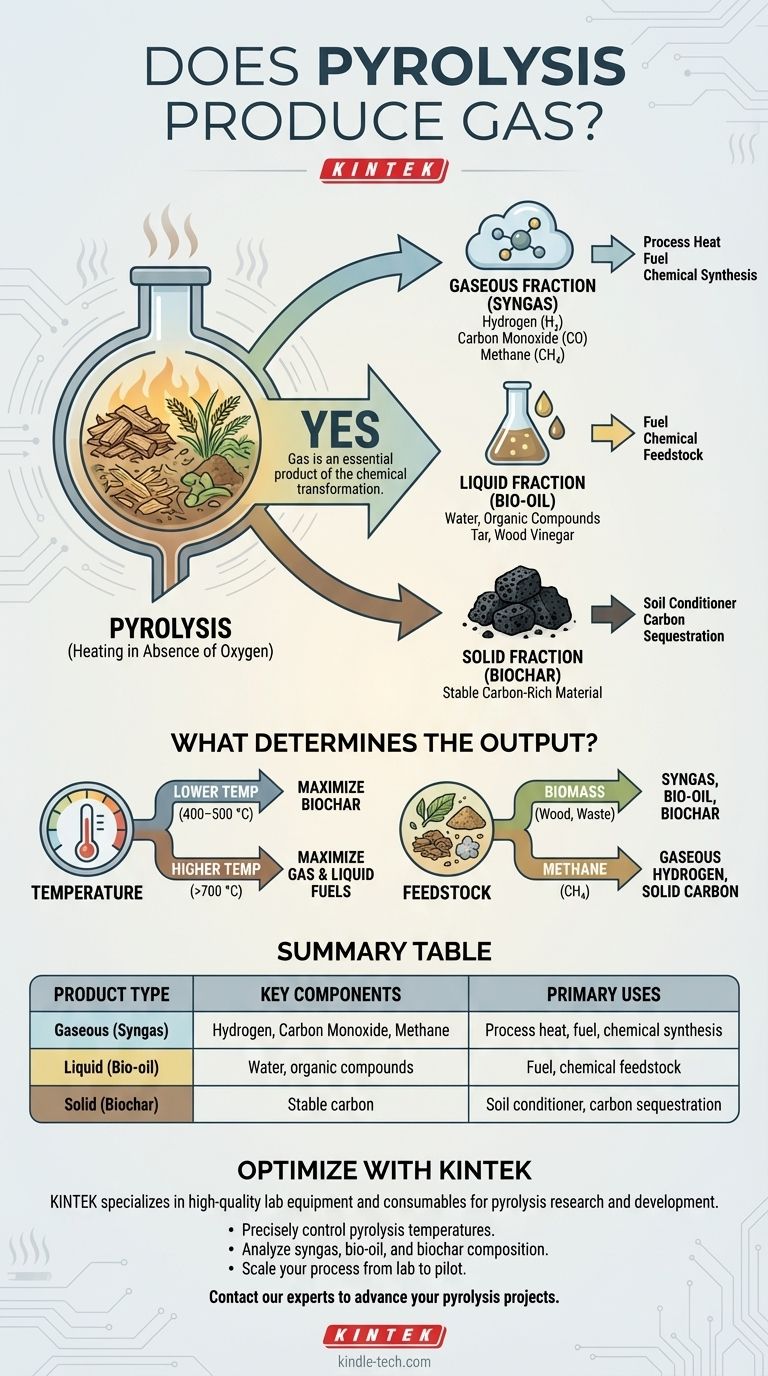
Yes, pyrolysis absolutely produces gas. This process, which involves heating organic materials like biomass in the absence of oxygen, fundamentally breaks them down into three distinct outputs: a solid (biochar), a liquid (bio-oil), and a mixture of combustible gases often called syngas or biogas. The gas is an unavoidable and essential product of the chemical transformation.
Pyrolysis is not a single-output process; it is a decomposition that always yields a combination of solid, liquid, and gaseous products. The critical variable is not if gas is produced, but how much and of what composition, which is directly controlled by the process conditions and the material being heated.
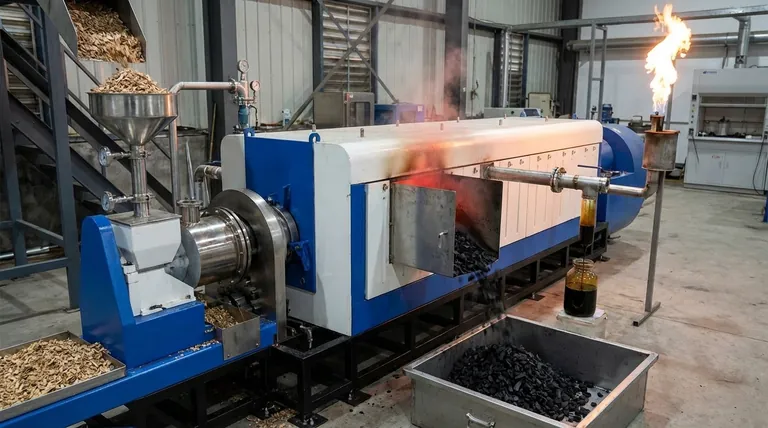

The Three Core Products of Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis deconstructs complex organic matter into simpler, more valuable components. This transformation results in products in all three states of matter.
The Gaseous Fraction (Syngas)
The gas produced is typically a mixture of combustible components, including hydrogen (H₂), carbon monoxide (CO), and methane (CH₄). This mixture is commonly referred to as syngas (synthesis gas).
This gas can be collected in a tank or, in many systems, is used directly to provide the heat needed to sustain the pyrolysis reaction, making the process more energy-efficient.
The Liquid Fraction (Bio-oil)
The liquid fraction is a complex blend of water and hundreds of different organic compounds. Depending on the source material, it is also known as pyrolysis oil, tar, or wood vinegar.
This bio-oil can be burned for heat, refined into transportation fuels, or serve as a source for specialty chemicals.
The Solid Fraction (Biochar)
The remaining solid is a stable, carbon-rich material called biochar or biocoal. It is the carbon backbone of the original organic material.
Biochar has significant value as a soil conditioner to improve fertility and water retention, or as a stable method for long-term carbon sequestration.
What Determines the Output?
You cannot maximize the yield of all three products simultaneously. The specific output is a direct result of two key factors: temperature and the initial material, or feedstock.
The Role of Temperature
Temperature is the primary lever for controlling the outcome of pyrolysis.
Lower temperatures, typically in the range of 400–500 °C, favor the production of the solid fraction, maximizing the biochar yield.
Higher temperatures, above 700 °C, cause more aggressive thermal cracking, breaking down larger molecules into smaller ones and maximizing the yield of liquid and gaseous fuels.
The Impact of Feedstock
The material you start with fundamentally changes the composition of the products.
Pyrolysis of biomass, such as wood or agricultural waste, will produce the classic trio of biochar, bio-oil, and syngas.
However, the pyrolysis of a different feedstock like methane is a more specialized process. It is specifically designed to split the methane molecule, producing only two products: solid carbon and gaseous hydrogen.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The core challenge in applying pyrolysis is deciding which output you value most and tuning the process to achieve it.
Balancing Product Yields
An operator must make a strategic choice. A process optimized for high-quality biochar will inherently produce less gas and oil. Conversely, a high-temperature system designed to maximize syngas production will leave behind very little char.
Managing Product Complexity
While the gas is relatively simple to handle and use as fuel, the liquid bio-oil is corrosive and chemically complex, often requiring further processing before it can be used effectively. The intended application of each product must be considered from the start.
Optimizing Pyrolysis for Your Goal
To apply this process effectively, you must align the operational parameters with your desired primary product.
- If your primary focus is maximizing gas production: Operate at high temperatures (above 700 °C) to favor the thermal cracking that generates syngas.
- If your primary focus is producing stable biochar: Use slower pyrolysis at lower temperatures (around 400–500 °C) to maximize the solid carbon yield.
- If your primary focus is creating pure hydrogen gas: You must use a specific feedstock like methane, as methane pyrolysis is designed to split it into valuable hydrogen and solid carbon.
Ultimately, controlling pyrolysis is about precisely managing temperature and feedstock to produce your desired mix of valuable solid, liquid, and gaseous products.
Summary Table:
| Product Type | Key Components | Primary Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Gaseous (Syngas) | Hydrogen (H₂), Carbon Monoxide (CO), Methane (CH₄) | Process heat, fuel, chemical synthesis |
| Liquid (Bio-oil) | Water, organic compounds (tar, wood vinegar) | Fuel, chemical feedstock |
| Solid (Biochar) | Stable carbon | Soil conditioner, carbon sequestration |
Ready to optimize your pyrolysis process for maximum gas, bio-oil, or biochar yield?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and development. Whether you're developing new biofuels, studying carbon sequestration, or optimizing process parameters, our reliable ovens, reactors, and analytical tools are designed to meet the rigorous demands of your laboratory.
We help you:
- Precisely control pyrolysis temperatures for your target product.
- Analyze the composition of your syngas, bio-oil, and biochar outputs.
- Scale your process from lab to pilot with confidence.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can advance your pyrolysis projects and help you achieve your specific product goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
People Also Ask
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output



















