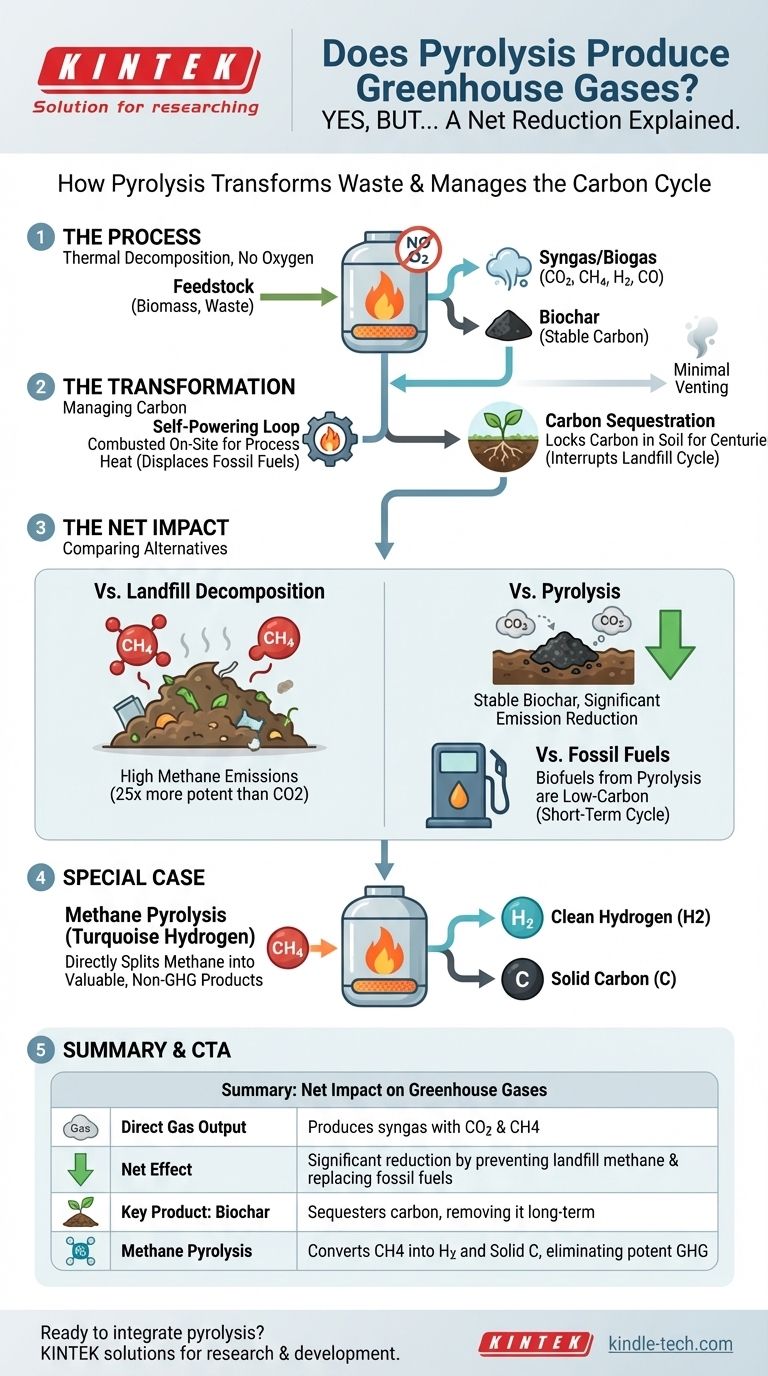
In principle, yes. The process of pyrolysis can produce a mixture of gases, known as syngas or biogas, which often contains greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane (CH4). However, this direct output is only a small part of a much larger picture. The primary purpose and typical application of pyrolysis result in a significant net reduction in overall greenhouse gas emissions compared to other alternatives.
The critical distinction is not whether pyrolysis creates any greenhouse gases, but how it transforms materials that would otherwise release potent GHGs. By converting waste biomass or fugitive methane into stable carbon and low-carbon fuels, pyrolysis serves as a powerful tool for carbon management and emission reduction.

How Pyrolysis Manages the Carbon Cycle
Pyrolysis is best understood as a thermal decomposition process that occurs in the absence of oxygen. This distinction is crucial—it's not burning. Instead, it breaks down a feedstock into new, more valuable forms.
The Gaseous Products: Syngas and Biogas
The gas produced during pyrolysis is a mixture, primarily of hydrogen, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and methane. Both CO2 and methane are greenhouse gases.
However, this gas is rarely vented into the atmosphere.
The Self-Powering Loop
In most modern pyrolysis plants, the produced syngas is captured and immediately combusted on-site.
This combustion provides the heat energy required to sustain the pyrolysis reaction itself, creating a semi-closed loop. This displaces the need to burn external fossil fuels to power the system, representing an immediate emissions saving.
The Solid Product: Biochar as Carbon Sequestration
A key output of biomass pyrolysis is biochar, a stable, carbon-rich solid. When feedstock like wood or agricultural waste decomposes in a landfill, its carbon is converted into methane—a greenhouse gas over 25 times more potent than CO2 over 100 years.
Pyrolysis interrupts this cycle. It locks that carbon into the stable structure of biochar, which can be added to soil. This not only improves soil health but also effectively sequesters carbon, keeping it out of the atmosphere for hundreds or even thousands of years.
The Net Impact: A Question of Alternatives
Evaluating the emissions of pyrolysis requires comparing it to the alternative fate of its feedstock.
Pyrolysis vs. Landfill Decomposition
Letting organic waste rot in a landfill generates significant methane emissions. By diverting this waste to a pyrolysis facility, you prevent those methane emissions and transform the carbon into stable biochar and useful energy.
Pyrolysis vs. Fossil Fuels
The liquid (bio-oil) and gaseous (syngas) products of pyrolysis can be refined or used as fuel.
These biofuels are considered low-carbon. While burning them releases CO2, that carbon was recently captured from the atmosphere by the biomass feedstock. This is part of the short-term biological carbon cycle, unlike the release of "new" carbon from burning fossil fuels that was locked away for millions of years.
The Special Case: Methane Pyrolysis
A specific application called methane pyrolysis (or "turquoise hydrogen" production) directly targets a potent greenhouse gas.
This process takes methane (CH4) and splits it into two valuable, non-greenhouse products: clean-burning hydrogen gas (H2) and solid carbon. This technology actively removes methane from the system, preventing its release into the atmosphere.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the net effect is positive, a complete assessment requires acknowledging potential drawbacks.
Feedstock Sourcing and Transport
The carbon footprint of sourcing and transporting the feedstock (e.g., wood chips, agricultural waste) to the pyrolysis plant must be considered in a full lifecycle analysis.
Process Inefficiency and Fugitive Emissions
A poorly designed, maintained, or operated pyrolysis unit could potentially have leaks. These "fugitive emissions" could release methane or other volatile organic compounds, undermining the environmental benefits.
Initial Energy Input
While many systems are self-powering once operational, they require an initial energy input to reach the necessary temperature. The source of this start-up energy contributes to the overall carbon accounting.
Making the Right Evaluation for Your Goal
To properly assess pyrolysis, you must focus on its net impact within a specific system.
- If your primary focus is waste management: Pyrolysis is an excellent strategy for diverting organic waste from landfills, drastically reducing methane emissions while creating valuable biochar.
- If your primary focus is fuel production: The biofuels produced offer a much lower-carbon alternative to traditional fossil fuels, and hydrogen from methane pyrolysis is a zero-emission energy carrier.
- If your primary focus is carbon sequestration: The creation of stable biochar is a direct and measurable method for removing carbon from the atmospheric cycle and storing it long-term.
Ultimately, viewing pyrolysis through a full lifecycle lens reveals it as a transformative technology that reduces net greenhouse gas emissions by design.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Impact on Greenhouse Gases |
|---|---|
| Direct Gas Output | Produces syngas containing CO2 and CH4 |
| Net Effect | Significant reduction by preventing landfill methane and replacing fossil fuels |
| Key Product: Biochar | Sequesters carbon, removing it from the atmosphere long-term |
| Methane Pyrolysis | Converts CH4 into hydrogen and solid carbon, eliminating potent GHG |
Ready to integrate pyrolysis into your sustainability strategy? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and development. Whether you're focused on waste management, biofuel production, or carbon sequestration, our solutions help you optimize processes and achieve your environmental goals. Contact our experts today to explore how our products can support your laboratory's innovative work in reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
People Also Ask
- How thick should coating be? Achieve the Perfect Balance for Performance and Cost
- What role does a Laboratory Centrifuge play in the production of succinic acid? Critical Solid-Liquid Separation Guide
- What are the benefits of using ultrasonic homogenization for green synthesis of carbon nanomaterials? Boost Lab Results
- Is graphite used in aerospace? Discover the Power of Carbon Fiber Composites
- How much does biomass cost per kWh? Understanding the True Price of Renewable Power
- How do you extract distillate? A Step-by-Step Guide to High-Purity Cannabis Oil
- What are the 4 main types of casting? A Guide to Choosing the Right Process
- What is sinter metal? A Guide to Cost-Effective, Complex Metal Parts



















