Depositing silicon carbide (SiC) films is fundamentally different from producing SiC powder. For creating thin, uniform coatings on a surface—a process known as deposition—the primary industrial method is Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). This involves reacting specific precursor gases on a heated substrate to grow a SiC layer, a technique distinct from the high-temperature bulk synthesis methods used to create SiC powder for abrasives or ceramics.
The method you choose for producing silicon carbide depends entirely on the final form you need. For thin films and coatings, deposition techniques like CVD are the standard. For creating bulk powder, high-temperature synthesis methods are used instead.
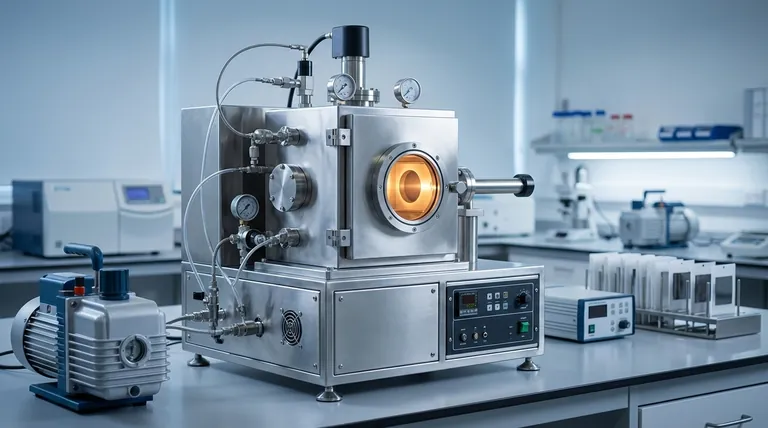

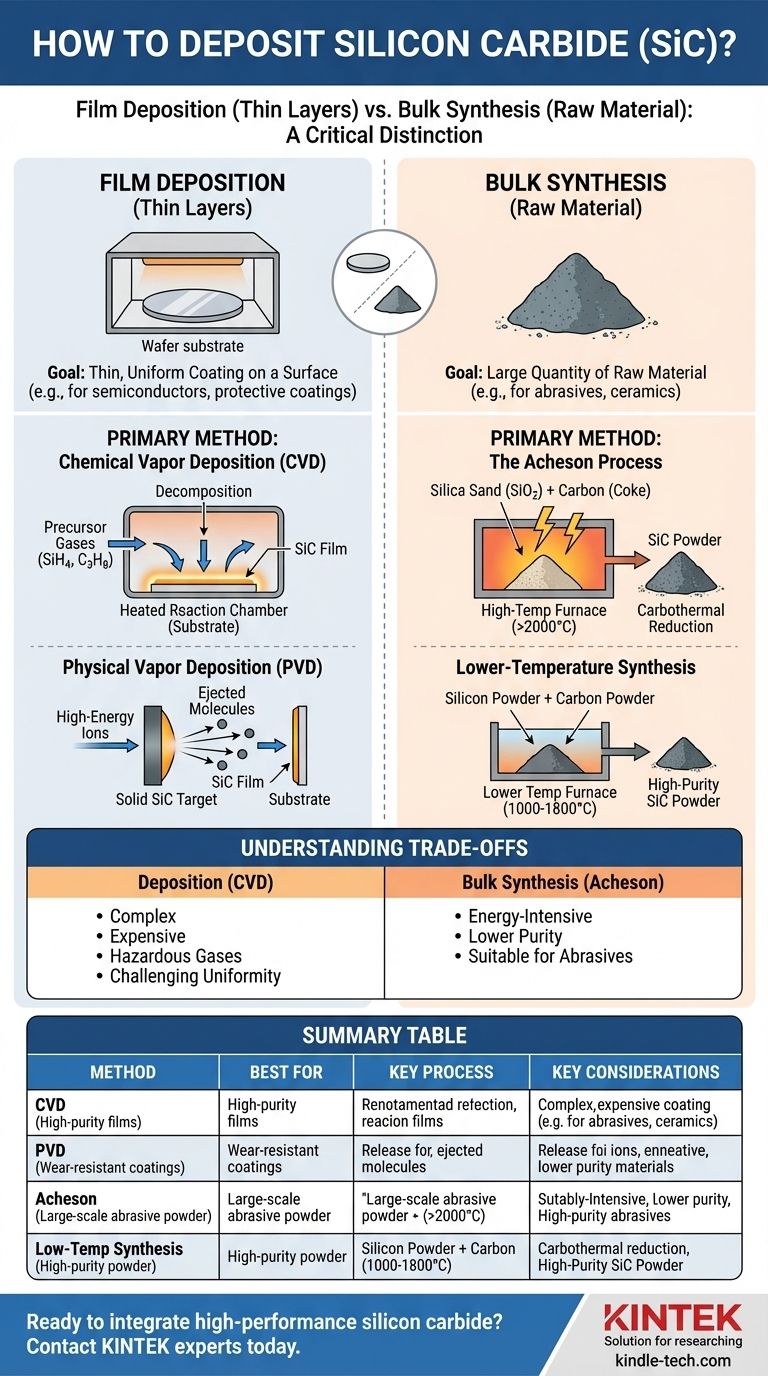
Film Deposition vs. Bulk Synthesis: A Critical Distinction
To select the right process, you must first understand whether you need to create a thin layer on an existing part (deposition) or produce a raw material (synthesis). These two goals require completely different approaches and equipment.
What is Film Deposition?
Film deposition is the process of applying a thin, uniform layer of a material onto a surface, known as a substrate.
The goal is typically to give the substrate new properties, such as enhanced hardness, chemical resistance, or specific electronic characteristics. This is common in semiconductors and for creating protective coatings.
What is Bulk Synthesis?
Bulk synthesis is the process of creating a large quantity of a material, often in powder, ingot, or crystal form.
This material is not yet a final product but a raw ingredient to be used later. For example, SiC powder is used to make industrial abrasives or can be formed and sintered into solid ceramic parts.
Primary Methods for Silicon Carbide Deposition (Thin Films)
When your goal is to coat a surface, you will use a deposition technique. The most common and versatile method for SiC is Chemical Vapor Deposition.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
CVD is the workhorse for high-quality SiC films. In this process, precursor gases containing silicon and carbon are introduced into a reaction chamber with a heated substrate.
The high temperature causes the gases to react and decompose on the substrate's surface, forming a solid, high-purity SiC film. Common precursors include silane (SiH4) for the silicon source and a hydrocarbon like propane (C3H8) for the carbon source.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)
PVD, particularly sputtering, is another method for depositing SiC films. It is a physical process, not a chemical one.
In sputtering, a solid SiC target is bombarded with high-energy ions in a vacuum. This impact ejects SiC molecules, which then travel and deposit onto a nearby substrate, forming a thin film. PVD is often chosen when the lower process temperatures are an advantage.
Methods for Bulk SiC Powder Synthesis
If you need to produce silicon carbide as a raw material, you will use a bulk synthesis method. These processes are designed for volume production, not for creating precise layers.
The Acheson Process
This is the traditional, large-scale industrial method for producing SiC powder, primarily for abrasives.
A mixture of silica sand (SiO2) and carbon (in the form of petroleum coke) is heated to extremely high temperatures—often above 2000°C—in an electric furnace. This high-temperature carbothermal reduction yields large quantities of α-SiC crystals.
Lower-Temperature Synthesis
For higher-purity β-SiC powder, often used in more advanced applications, other methods are employed.
These include the direct reaction of silicon powder and carbon powder or the carbothermal reduction of very fine silica powder at temperatures between 1000°C and 1800°C. These processes offer better control over purity but at a smaller scale than the Acheson process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single method is universally superior; the choice depends on balancing cost, quality, and application requirements.
Deposition (CVD) Challenges
CVD systems are complex and expensive. The process uses hazardous and flammable gases that require stringent safety protocols. Achieving a perfectly uniform film thickness across a large or complex-shaped substrate can also be challenging.
Bulk Synthesis (Acheson) Limitations
The Acheson process is extremely energy-intensive due to the very high temperatures required. The resulting SiC powder is suitable for abrasives but often lacks the purity needed for high-performance electronics.
Quality vs. Rate
In nearly all SiC processes, there is a trade-off between speed and quality. Faster deposition or synthesis rates, typically achieved at higher temperatures or pressures, can sometimes lead to lower crystal quality, higher internal stress, or less purity in the final material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your specific goal will determine the correct path forward. The key is to match the process to the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is creating high-performance semiconductor devices: You will use Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) to grow a high-purity, crystalline SiC film on a wafer.
- If your primary focus is applying a hard, wear-resistant coating: Both CVD and PVD (sputtering) are viable, with the choice depending on your temperature budget and required film properties.
- If your primary focus is producing raw material for industrial abrasives or rough ceramics: You will use a bulk synthesis method, most likely the Acheson process, for its high volume.
- If your primary focus is synthesizing high-purity powder for advanced materials: You should investigate lower-temperature synthesis routes like direct reaction to achieve better control over purity and particle size.
Understanding the fundamental difference between depositing a film and synthesizing a powder is the first step toward mastering silicon carbide applications.
Summary Table:
| Method | Best For | Key Process | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | High-purity semiconductor films, protective coatings | Reacting precursor gases on a heated substrate | High quality, but complex and uses hazardous gases |
| Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) | Wear-resistant coatings, lower-temperature processes | Sputtering from a solid SiC target in a vacuum | Lower temperatures, but may have lower purity than CVD |
| Acheson Process | Large-scale production of abrasive powder | High-temperature reaction of sand and carbon | High volume, but energy-intensive and lower purity |
| Lower-Temperature Synthesis | High-purity β-SiC powder | Direct reaction of Si/C or carbothermal reduction | Better purity control, but smaller scale |
Ready to integrate high-performance silicon carbide into your lab's workflow?
Whether you need to deposit thin films for semiconductor research or require high-purity SiC powder for advanced materials development, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to support your project. Our specialized lab equipment and consumables are designed to meet the precise demands of modern laboratories.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your research and development outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between plasma CVD and thermal CVD? Choose the Right Method for Your Substrate
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- Why is a Matching Network Indispensable in RF-PECVD for Siloxane Films? Ensure Stable Plasma and Uniform Deposition
- What are the process capabilities of ICPCVD systems? Achieve Low-Damage Film Deposition at Ultra-Low Temperatures
- Can plasma enhanced CVD deposit metals? Why PECVD is rarely used for metal deposition



















