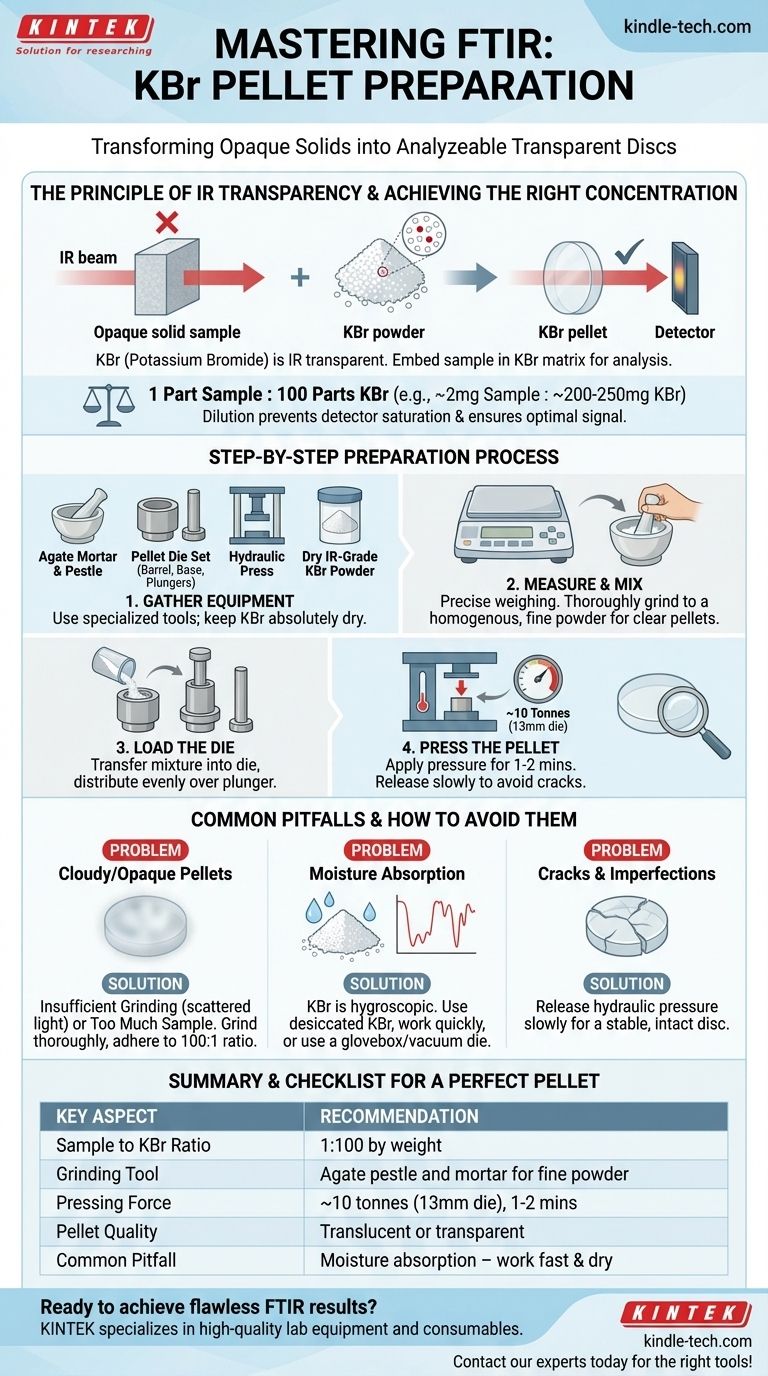
To prepare a KBr pellet for FTIR, you thoroughly mix a small amount of your solid sample with a much larger amount of dry, infrared-grade potassium bromide (KBr) powder. This mixture is then ground to a fine consistency and compressed under several tons of pressure in a specialized die using a hydraulic press. The result is a thin, semi-transparent solid disc suitable for infrared analysis.
The core objective is not simply to make a pellet, but to disperse your sample at a very low concentration within a solid matrix that is transparent to infrared light. This transforms an opaque solid into a sample that can be analyzed using transmission FTIR spectroscopy.

Why the KBr Pellet Method is Used
Fourier-Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy works by passing an infrared beam through a sample. For this to work with solids, the material must be thin and uniform enough for the beam to pass through without being completely absorbed or scattered.
The Principle of IR Transparency
Most solid samples are too thick or opaque for the IR beam. Potassium bromide (KBr) is an alkali halide salt that has no molecular vibrations in the mid-infrared range, making it effectively transparent to IR radiation. By embedding the sample in a KBr matrix, we can analyze it.
Achieving the Right Concentration
The goal is to dilute the sample so that its absorbance falls within the detector's optimal range. A typical ratio is 1 part sample to 100 parts KBr by weight. Too much sample will result in peaks that are too intense ("flat-topped"), while too little will produce a weak signal with poor signal-to-noise.
The Step-by-Step Preparation Process
Achieving a high-quality pellet requires careful attention to detail at each stage.
Step 1: Gather Your Equipment
You will need a few specialized tools:
- Agate pestle and mortar: For grinding and mixing. Agate is preferred for its hard, non-porous surface that minimizes contamination.
- Pellet die set: This consists of a barrel, a base, and two polished plungers for compressing the powder. A common size is 13 mm in diameter.
- Hydraulic press: Capable of applying several tons of force.
- Infrared-grade KBr powder: Must be kept exceptionally dry.
Step 2: Measure and Mix
Precision is key. For a standard 13 mm pellet, you will use approximately 200-250 mg of KBr powder. Based on the 100:1 ratio, this means you only need about 2-2.5 mg of your sample.
Place both the sample and KBr into the agate mortar. Grind the mixture thoroughly for several minutes until it becomes a homogenous, fine powder. This step is critical for reducing the particle size of the sample, which minimizes light scattering and produces a clear pellet.
Step 3: Load the Die
Carefully transfer the powder mixture into the pellet die barrel, ensuring the bottom plunger is in place. Distribute the powder as evenly as possible over the polished face of the plunger. Place the top plunger into the barrel on top of the powder.
Step 4: Press the Pellet
Place the assembled die into the hydraulic press. A common "rule of thumb" is to apply a load of around 10 tonnes for a 13 mm die. Hold this pressure for a minute or two to allow the KBr to fuse into a solid disc. Release the pressure slowly, and carefully disassemble the die to retrieve your pellet.
A good pellet will appear translucent or even transparent.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
The quality of your spectrum is directly dependent on the quality of your pellet. Understanding common failures is essential for troubleshooting.
Cloudy or Opaque Pellets
A cloudy pellet is the most frequent issue. This is typically caused by one of two things:
- Insufficient Grinding: Large sample particles scatter infrared light, reducing signal and distorting the baseline. The solution is to grind the KBr/sample mixture more thoroughly.
- Too Much Sample: An excessively high sample concentration makes the pellet opaque. Always adhere to the ~100:1 ratio.
The Problem with Moisture
KBr is hygroscopic, meaning it readily absorbs water from the atmosphere. Water has very strong IR absorption bands that can obscure important regions of your sample's spectrum. To avoid this, always use desiccated KBr and prepare your pellet quickly. In humid environments, using a glovebox or a vacuum die is highly recommended.
Cracks and Imperfections
Pellets that crack upon removal from the die are often the result of releasing the hydraulic pressure too quickly. A slow, controlled pressure release is crucial for creating a stable, intact disc.
A Checklist for a Perfect Pellet
Use this checklist to guide your preparation based on your analytical needs.
- If your primary focus is a high-quality, quantitative spectrum: Be meticulous with weighing your sample and KBr, ensure the mixture is ground into an exceptionally fine powder, and take every precaution to keep the components dry.
- If your primary focus is a quick qualitative identification: A slightly imperfect or cloudy pellet may still provide a usable spectrum, but you must still grind the sample well enough to minimize baseline slope from light scattering.
- If your primary focus is a moisture-sensitive or hygroscopic sample: Working in a dry atmosphere, such as inside a glovebox, is not optional—it is essential for obtaining meaningful data.
Mastering this technique transforms a wide range of solid materials from intractable to analyzable, unlocking a wealth of molecular information.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Sample to KBr Ratio | 1:100 by weight (e.g., 2 mg sample to 200 mg KBr) |
| Grinding Tool | Agate pestle and mortar for fine, homogeneous powder |
| Pressing Force | ~10 tonnes for a 13 mm die, held for 1-2 minutes |
| Pellet Quality | Should be translucent or transparent for optimal IR transmission |
| Common Pitfall | Moisture absorption (KBr is hygroscopic)—work quickly and in dry conditions |
Ready to achieve flawless FTIR results? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including infrared-grade KBr powder, durable pellet dies, and reliable hydraulic presses. Our products are designed to help you prepare perfect pellets every time, ensuring accurate and reproducible spectroscopic data. Contact our experts today to find the right tools for your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
- kbr pellet press 2t
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press Machine for Lab Use
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a bench-top laboratory hydraulic press for XRF? Maximize Accuracy in Prosopis juliflora Analysis
- What is the function of a laboratory hydraulic press for Li10GeP2S12 pellets? Optimize Solid-State Battery Performance
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in preparing solid model materials? Standardize for Precise Data.
- How do laboratory hydraulic presses facilitate biomass pelletization? Optimize Biofuel Density and Prevent Slagging
- What is KBr disc method? A Complete Guide to IR Spectroscopy Sample Prep



















