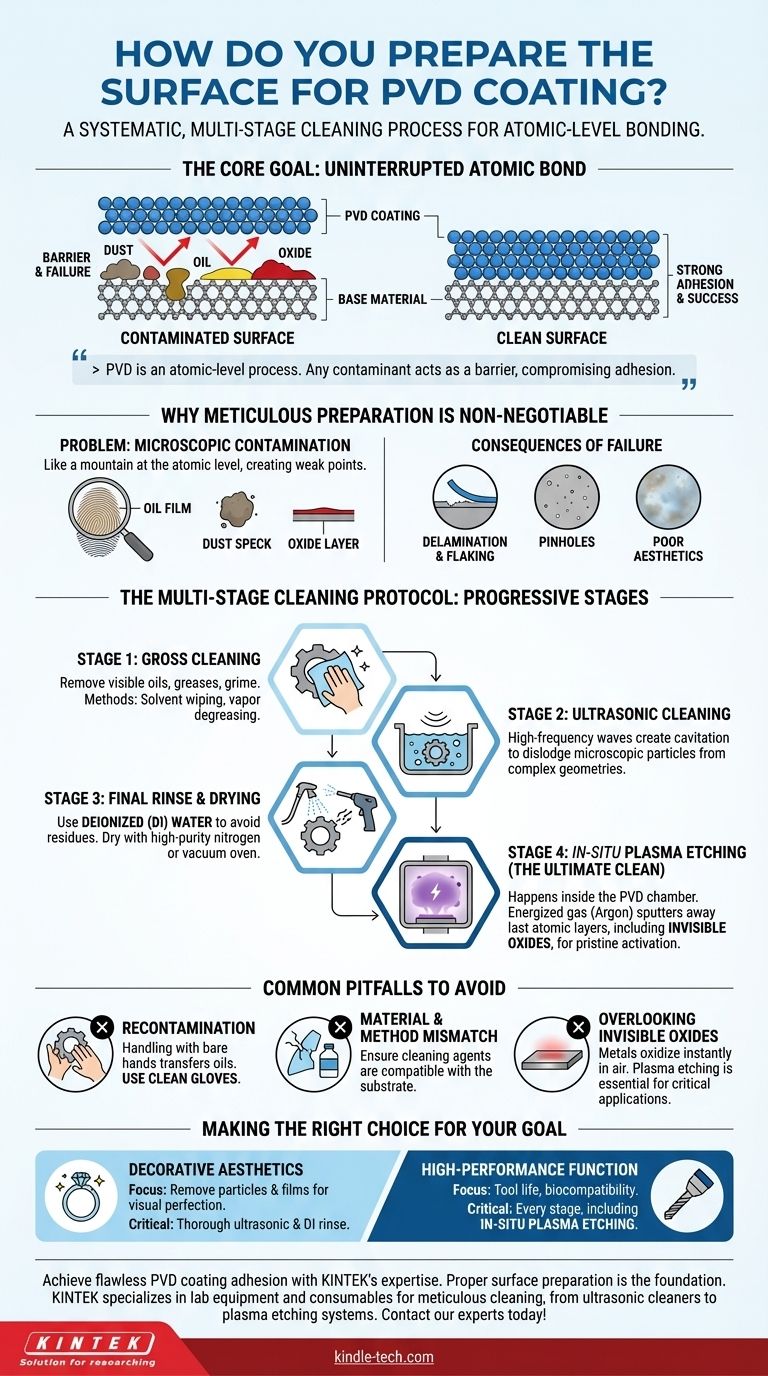
At its core, preparing a surface for Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a systematic, multi-stage cleaning process designed to remove all foreign materials. This is not a simple wipe-down; it involves progressively finer cleaning stages to eliminate everything from visible grease and oils to microscopic particles, fingerprints, and even invisible oxide layers, ensuring the substrate is atomically clean before entering the vacuum chamber.
The ultimate goal of surface preparation is to guarantee a direct, uninterrupted bond between the coating atoms and the substrate atoms. Because PVD is an atomic-level process, any contaminant—no matter how small—acts as a physical barrier that compromises adhesion, leading to coating failure.

Why Meticulous Preparation is Non-Negotiable
PVD coating does not happen in a normal environment. It occurs in a high-vacuum chamber where individual atoms of a material are deposited onto a surface, building a new layer one atom at a time.
The Problem of Contamination
Think of it like painting, but on a microscopic scale. A single speck of dust, an invisible film of oil from a fingerprint, or a faint layer of oxidation on a metal surface becomes a mountain at the atomic level.
The coating material cannot bond to the substrate where these contaminants exist. This creates a weak point from the very beginning.
The Consequences of Poor Preparation
Poor surface preparation is the leading cause of PVD coating failure. The results are predictable and costly:
- Delamination & Flaking: The coating peels away from the substrate because it never achieved a proper bond.
- Pinholes: Tiny uncoated spots caused by microscopic dust or particles that were not removed.
- Poor Aesthetics: Hazy finishes, stains, or inconsistencies caused by residual films and fingerprints.
The Multi-Stage Cleaning Protocol
A professional PVD preparation process is a disciplined protocol that moves from coarse cleaning to atomically fine cleaning. The exact steps may vary based on the substrate material and its initial condition, but the principles remain the same.
Stage 1: Gross Cleaning
The first step is to remove all visible, large-scale contaminants. This includes machining oils, greases, polishing compounds, and general shop grime. Common methods include solvent wiping and vapor degreasing.
Stage 2: Ultrasonic Cleaning
Next, parts are typically submerged in a tank for ultrasonic cleaning. This process uses high-frequency sound waves to create and implode microscopic bubbles in a cleaning solution, a phenomenon called cavitation. This action provides a powerful yet gentle scrubbing effect that dislodges tiny particles from complex geometries, seams, and threaded holes that manual cleaning cannot reach.
Stage 3: Final Rinse and Drying
After ultrasonic cleaning, parts must be rinsed thoroughly to remove any detergent or cleaning agent residue. This is almost always done with deionized (DI) water, as regular tap water would leave behind mineral deposits upon drying.
Drying must be just as clean. Parts are often dried using high-purity nitrogen gas guns or placed in a vacuum oven to ensure no moisture or new contaminants are introduced.
Stage 4: In-Situ Plasma Etching (The Ultimate Clean)
For high-performance applications, the final cleaning step happens inside the PVD chamber just before coating begins. This process, often called ion etching or sputter cleaning, uses an energized gas (like Argon) to create a plasma.
This plasma bombards the substrate's surface, physically sputtering away the last few atomic layers. This removes any final, stubborn organic films and, most importantly, any thin, naturally occurring oxide layers that form instantly on metals exposed to air. This leaves a pristine, activated surface ready for maximum coating adhesion.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Success with PVD is often about avoiding common mistakes during preparation.
The Risk of Recontamination
A part is only as clean as its last point of contact. Handling a perfectly cleaned part with bare hands will instantly transfer oils and ruin the preparation. Clean, powder-free gloves and a controlled environment are mandatory after the final cleaning stage.
Material and Method Mismatch
The cleaning process must be compatible with the substrate. Using a harsh solvent that works for stainless steel could easily damage or destroy a plastic part. Always verify that your cleaning agents and methods will not harm the substrate itself.
Overlooking Invisible Oxides
Many teams perform excellent external cleaning but forget that most metals (like titanium, aluminum, and steel) form an invisible oxide layer within seconds of being exposed to oxygen. For critical applications requiring the strongest possible bond, skipping the in-situ plasma etch is a primary cause of latent adhesion failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Not all PVD applications require the same level of stringent preparation. Your end goal dictates the necessary rigor.
- If your primary focus is decorative aesthetics: Your main concern is removing all particles and films that cause visual defects. A thorough ultrasonic cleaning, DI water rinse, and careful handling are critical.
- If your primary focus is high-performance function (e.g., tool life, biocompatibility): You cannot compromise. Every stage, including in-situ plasma etching to remove oxide layers, is essential for achieving the required adhesion and coating durability.
Ultimately, successful PVD coating is built upon the foundation of a perfectly prepared surface.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Process | Key Goal |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Gross Cleaning | Remove visible oils, greases, and grime |
| 2 | Ultrasonic Cleaning | Dislodge microscopic particles from complex geometries |
| 3 | Final Rinse & Drying | Eliminate residues using deionized water and clean drying |
| 4 | Plasma Etching (In-Situ) | Sputter away oxide layers for atomic-level bonding |
Achieve flawless PVD coating adhesion with KINTEK's expertise.
Proper surface preparation is the foundation of a durable, high-performance coating. Whether you're working on decorative pieces or high-stakes functional components, KINTEK specializes in the lab equipment and consumables needed for meticulous cleaning—from ultrasonic cleaners to plasma etching systems. Let us help you eliminate contamination risks and ensure your coatings bond perfectly.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific substrate and coating requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications



















