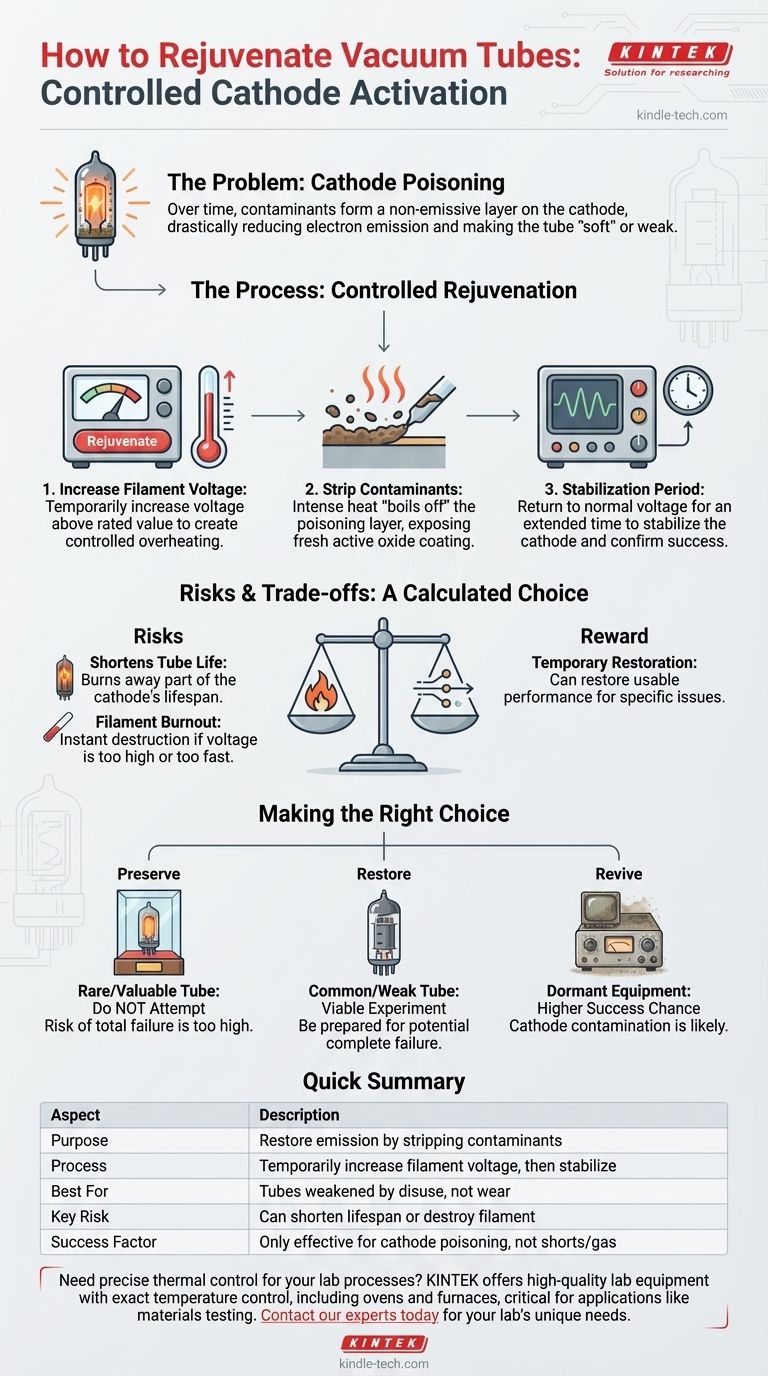
To rejuvenate a vacuum tube, you perform a controlled procedure of temporarily increasing its filament voltage. This higher-than-normal heat strips contaminants from the cathode, which is the element that emits electrons. After this "reactivation," the tube is operated at its normal voltage for a stabilization period to see if a usable level of performance has been restored.
The core concept of tube rejuvenation is using controlled stress—excess heat—to fix a specific problem known as cathode poisoning. It is not a magical cure for all tube failures but rather a last-resort technique that trades a portion of the tube's remaining life for a temporary restoration of function.
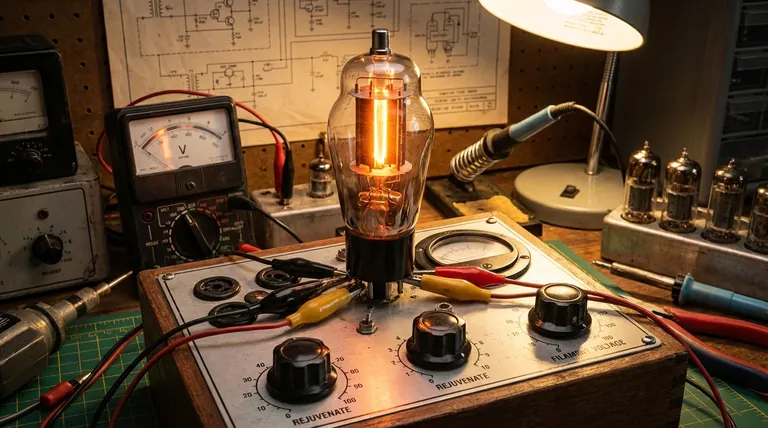

What Causes a Tube to Need Rejuvenation?
To understand the fix, we must first understand the failure. A vacuum tube's performance relies on a delicate chemical and physical balance, which degrades over time.
The Role of the Cathode
The heart of most vacuum tubes is the cathode. It's a metal sleeve coated with a special mixture (typically of barium and strontium oxides) that releases a cloud of electrons when heated. The flow of these electrons is what the tube amplifies or switches.
The Problem: Cathode Poisoning
Over time, or especially during long periods of disuse, the cathode's surface can become contaminated. Molecules from residual gas inside the tube or impurities from the cathode itself can form a passive, non-emissive layer. This "cathode poisoning" or "sleeping sickness" effectively smothers the active coating, drastically reducing the number of electrons it can emit. The tube becomes weak or "soft."
Natural Wear vs. Poisoning
It's crucial to distinguish this from a tube that is simply worn out. In a worn-out tube, the active oxide coating has been physically depleted through thousands of hours of normal use. Rejuvenation cannot restore material that is no longer there.
The Rejuvenation Process Explained
Rejuvenation is an aggressive procedure designed specifically to combat cathode poisoning. It is typically performed with a specialized tube tester that has a "rejuvenate" or "reactivate" function.
The Core Principle: Controlled Overheating
The fundamental step is to slowly increase the filament voltage above its rated value. This makes the filament—and by extension, the cathode sleeve around it—glow hotter than it was designed to.
Stripping the Contaminants
This intense heat provides enough thermal energy to "boil off" or strip away the layer of contaminants that has poisoned the cathode. This process exposes a fresh, underlying layer of the active oxide coating, allowing the cathode to emit electrons freely once again.
The Stabilization Period
After reaching a peak emission reading on the tester, the filament voltage must be returned to its normal, rated value. As the reference material notes, the tube should then be operated for an extended period, often several hours. This stabilizes the cathode and gives a true indication of whether the procedure was successful. Consistent readings over time signal the tube is as rejuvenated as it will get.
Understanding the Inherent Risks and Trade-offs
Rejuvenation is not a gentle process. It should be approached with a clear understanding of the potential downsides.
It Is a Life-Shortening Procedure
You are essentially burning away part of the cathode's life to restore immediate function. The process can strip away not just contaminants but also some of the valuable emissive coating itself, shortening the tube's overall lifespan.
The Danger of Filament Burnout
The most significant risk is applying too much voltage or applying it too quickly. This can instantly destroy the tube's filament, rendering the tube completely useless. This is an irreversible failure.
Success Is Not Guaranteed
Rejuvenation only works for cathode poisoning. It will not fix other common tube failures, such as internal shorts between elements, a loss of vacuum (a "gassy" tube), or a physically exhausted cathode.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding whether to attempt rejuvenation requires weighing the potential reward against the very real risk of destroying the tube.
- If your primary focus is preserving a rare or valuable tube: Do not attempt rejuvenation. The risk of total failure is too high for an irreplaceable component.
- If your primary focus is restoring a common, weak tube in a guitar amp or radio: This can be a viable, low-risk experiment, but you must be prepared for the tube to fail completely.
- If your primary focus is reviving equipment that has been dormant for decades: Rejuvenation has a higher chance of success, as cathode contamination is a very likely cause for weakness in tubes that have sat unused.
Ultimately, viewing rejuvenation as a specific tool for a specific problem is the key to using it wisely.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Restore electron emission by stripping contaminants from the cathode. |
| Process | Temporarily increase filament voltage, then stabilize at normal voltage. |
| Best For | Tubes weakened by cathode poisoning from disuse, not natural wear. |
| Key Risk | Can shorten tube lifespan or instantly destroy the filament if done incorrectly. |
| Success Factor | Only effective for cathode poisoning, not other failures like shorts or gas leaks. |
Need precise thermal control for your lab processes? The controlled heating principles behind tube rejuvenation are critical in many laboratory applications. At KINTEK, we specialize in high-quality lab equipment, including ovens and furnaces that offer the exact temperature control and reliability your work demands. Whether you're working with materials testing or specialized heating procedures, our solutions are designed for accuracy and longevity. Contact our experts today to find the perfect equipment for your laboratory's unique needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
People Also Ask
- What are the sizes of autoclaves? A Guide to Choosing the Right Capacity for Your Lab
- What temperature must be reached for sterilization in 10-12 minutes? Achieve Rapid, Reliable Sterility with Flash Autoclaving
- Why is it important to autoclave the prepared reagents before using? Ensure Sterility and Reliable Results
- How do you sterilize glassware by autoclave? Master the 3-Step Process for Reliable Sterility
- Do you need to autoclave glassware? A Guide to Sterilization vs. Cleaning



















