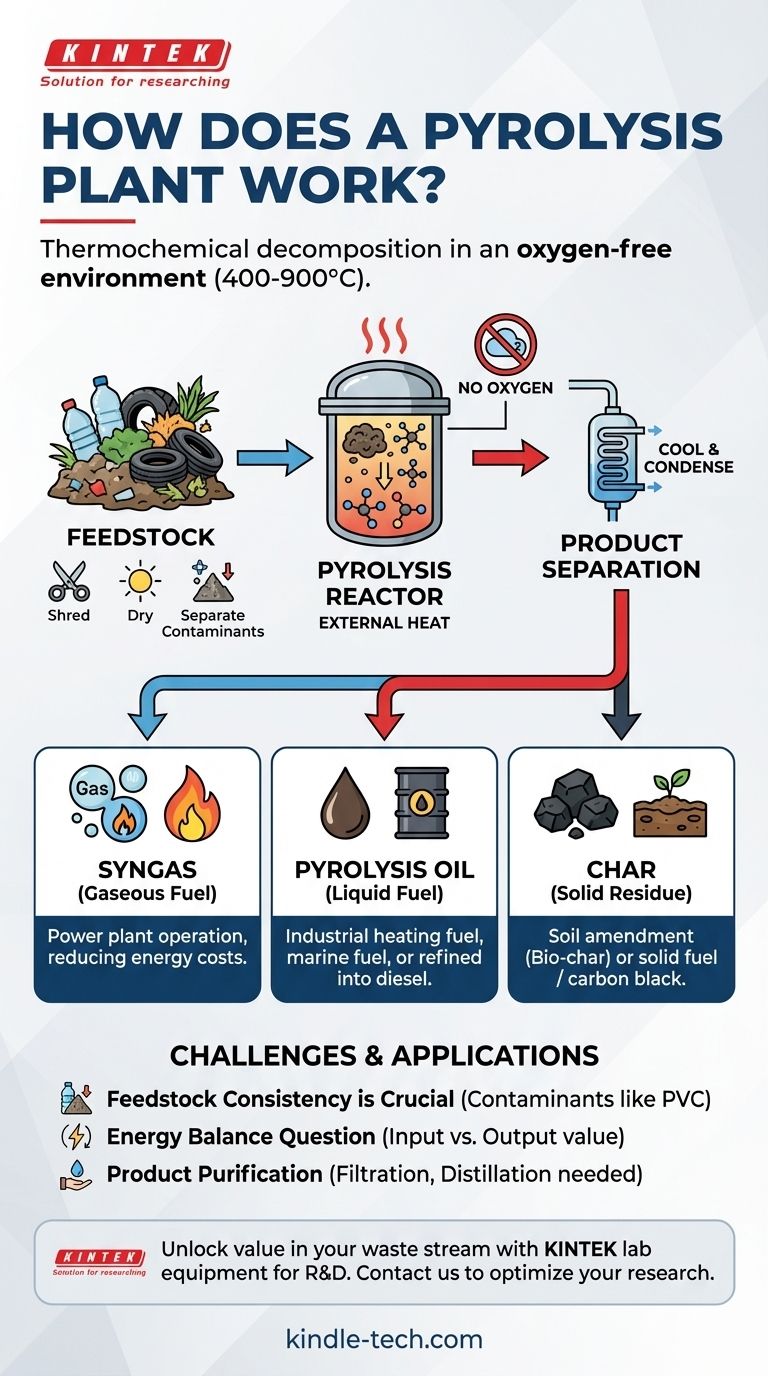
At its core, a pyrolysis plant is a facility that chemically decomposes materials like plastic, tires, or biomass using high heat in an oxygen-free environment. This process, distinct from burning, breaks down complex organic polymers into simpler, valuable substances. The primary outputs are a synthetic gas (syngas), a liquid oil (pyrolysis oil), and a solid, carbon-rich residue (char).
The fundamental purpose of a pyrolysis plant is not to destroy waste but to transform it. By preventing combustion, it acts as a form of chemical recycling, converting low-value materials into usable fuels, chemicals, and soil amendments.

The Core Principle: Decomposition Without Burning
Pyrolysis is often called thermal cracking or depolymerization. It relies on a simple principle: intense heat can break the chemical bonds within large molecules without the presence of oxygen to cause a fire.
What is Thermochemical Decomposition?
Every organic material, from a plastic bottle to a wood chip, has a limit to its thermal stability. A pyrolysis plant exploits this.
Inside a sealed reactor, material is heated to temperatures between 400°C and 900°C (750°F to 1650°F). This intense energy causes the long polymer chains in the material to vibrate and break apart into smaller, lighter, and more volatile molecules.
The Critical Role of an Oxygen-Free Environment
The absence of oxygen is the defining feature of pyrolysis. If oxygen were present, the material would simply burn (combust), releasing its energy as heat and producing ash and flue gases like carbon dioxide.
By removing oxygen, the process forces a chemical transformation instead of combustion. This allows for the recovery of the carbon and hydrogen locked within the waste material in the form of new, usable products.
Anatomy of a Pyrolysis Plant: From Waste to Resource
A pyrolysis plant is a multi-stage system designed to carefully control the transformation process from start to finish.
Step 1: Feedstock Preparation
The process begins before the material ever enters the reactor. The raw waste, or feedstock, is prepared to ensure efficiency.
This typically involves shredding the material into smaller, uniform pieces for even heating and drying to remove moisture. It also includes preprocessing to separate out non-pyrolyzable contaminants like metals or glass.
Step 2: The Pyrolysis Reactor
This is the heart of the plant. The prepared feedstock is fed into a sealed vessel, the pyrolysis reactor, which is heated externally.
Different reactor designs exist, such as fixed-bed reactors, where the material sits in a static pile, or ablative reactors, which press the material against a hot surface. The goal of any design is to transfer heat efficiently and consistently into the feedstock.
Step 3: Product Separation and Refinement
As the material decomposes in the reactor, it separates into three states: gas, liquid, and solid.
The hot vapors (gas and vaporized oil) are drawn out of the reactor and cooled. The cooling causes the liquid components to condense into pyrolysis oil. The remaining non-condensable gases are collected as syngas. The solid material left behind in the reactor is the char.
The Three Key Outputs and Their Uses
The value of a pyrolysis plant lies in its ability to create multiple useful products from a single stream of waste.
Syngas: The Gaseous Fuel
This mixture of gases, primarily hydrogen and carbon monoxide, has caloric value. It is often captured and used to power the pyrolysis plant itself, creating a partially self-sustaining energy loop and reducing operational costs.
Pyrolysis Oil: The Liquid Fuel
Also known as bio-oil or tire-derived fuel (TDF), this liquid is the main product. It can be refined and used as an industrial heating oil, a marine fuel, or further processed into higher-grade fuels like diesel or gasoline.
Char: The Solid Residue
This stable, carbon-rich solid is similar to charcoal. When derived from biomass, it is called bio-char and is highly valued as a soil amendment that improves water retention and sequesters carbon. When derived from plastics or tires, it can be used as a solid fuel or processed into an industrial material called carbon black.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While powerful, pyrolysis technology is not a magic bullet and comes with important operational considerations.
Feedstock Consistency is Crucial
The process is highly sensitive to the type and quality of the input material. Contaminants like PVC plastic, metals, or excessive moisture can damage equipment or create undesirable byproducts, requiring rigorous pre-sorting.
The Energy Balance Question
A pyrolysis plant requires a significant energy input to reach and maintain its high operating temperatures. For a plant to be economically and environmentally viable, the energy value of its outputs must justify the energy consumed.
Product Purification is Often Necessary
The raw pyrolysis oil and char are rarely pure enough for high-value applications directly out of the reactor. They often require additional steps like filtration, distillation, or chemical treatment, which adds complexity and cost to the overall operation.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Understanding the outputs of pyrolysis is key to seeing its potential application for specific challenges.
- If your primary focus is managing plastic waste: Pyrolysis is a powerful tool for handling mixed or contaminated plastics that are difficult to mechanically recycle, turning them into a valuable liquid fuel.
- If your primary focus is generating renewable energy: The technology effectively converts low-value biomass (wood waste, agricultural scraps) into a storable and transportable liquid fuel (bio-oil).
- If your primary focus is soil health and carbon sequestration: Pyrolysis of biomass is one of the most effective methods for producing bio-char, a product that directly improves soil structure and locks carbon away for centuries.
Ultimately, a pyrolysis plant serves as a critical bridge in the circular economy, unlocking the inherent value in materials that would otherwise be considered waste.
Summary Table:
| Pyrolysis Plant Output | Primary Use |
|---|---|
| Syngas | Fuel for plant operation, reducing energy costs |
| Pyrolysis Oil | Industrial heating fuel, marine fuel, or refined into diesel |
| Char / Bio-char | Soil amendment (bio-char) or solid fuel / carbon black |
Ready to unlock the value in your waste stream?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for researching and developing pyrolysis processes. Whether you are exploring plastic recycling, renewable energy from biomass, or soil health with bio-char, our precise and reliable equipment can support your R&D goals.
Contact our experts today via our contact form to discuss how our solutions can help you optimize your pyrolysis research and development.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
People Also Ask
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process



















