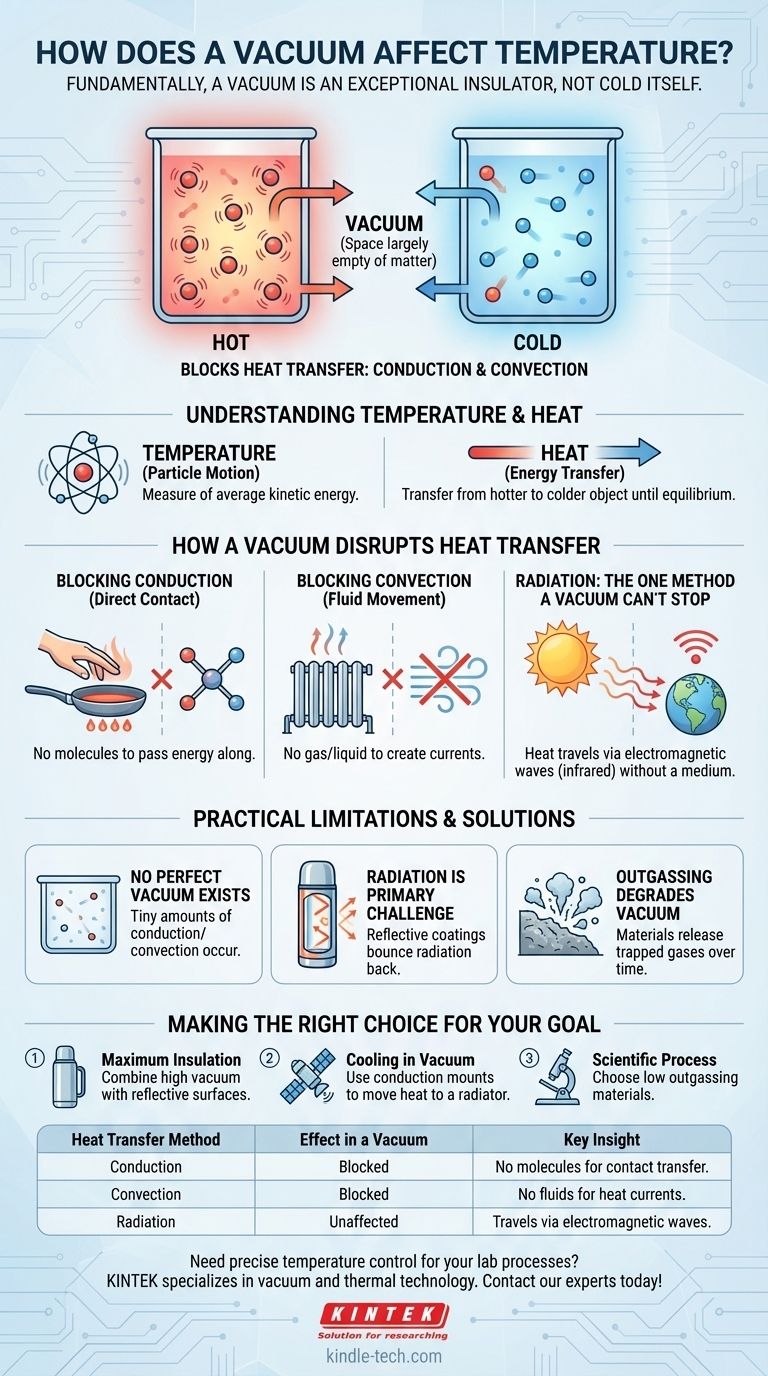
Fundamentally, a vacuum does not have a temperature of its own. Instead, a vacuum is an excellent insulator that dramatically affects the temperature of an object by preventing heat from moving. Because a vacuum is a space largely empty of matter, it blocks the two most common forms of heat transfer: conduction and convection.
A vacuum is neither hot nor cold. It is an empty space that acts as a barrier to heat transfer, making hot objects stay hot and cold objects stay cold by preventing the movement of thermal energy.
What is Temperature, Really?
To understand how a vacuum works, we must first be clear about what temperature and heat are.
Temperature as Particle Motion
Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy—or movement—of atoms and molecules within a substance. Hot objects have fast-moving, vibrating particles, while cold objects have slow-moving particles.
Heat is the transfer of this energy from a hotter object to a colder one. This transfer happens until both objects reach the same temperature, a state known as thermal equilibrium.
The Void of a Vacuum
A vacuum is a space where matter (those atoms and molecules) has been almost entirely removed. It is not "cold"; it is simply empty.
How a Vacuum Disrupts Heat Transfer
Heat moves in three ways. A vacuum is so effective because it stops two of them almost completely.
Blocking Conduction
Conduction is the transfer of heat through direct physical contact. Imagine a hot pan handle: the heat travels from the pan's body to your hand molecule by molecule.
A vacuum has virtually no molecules. Without particles to touch each other and pass the energy along, conduction cannot occur.
Blocking Convection
Convection is the transfer of heat through the movement of fluids (liquids or gases). A radiator heats the air around it, causing that hot air to rise and be replaced by cooler air, creating a current.
Since a vacuum contains no gas or liquid to create these currents, heat transfer by convection is impossible.
The One Method a Vacuum Can't Stop: Radiation
Thermal radiation is the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves, primarily infrared radiation. Unlike conduction and convection, it does not need a medium to travel.
This is how the Sun's heat reaches Earth across the vacuum of space. Any object with a temperature above absolute zero emits thermal radiation. This is the only way heat can cross a perfect vacuum.
Understanding the Limitations
A vacuum is an exceptional insulator, but it's important to recognize its practical limits.
No Perfect Vacuum Exists
Creating a perfect vacuum—a space with zero atoms—is physically impossible. Real-world vacuums, even in deep space or a laboratory, contain some stray particles.
These few particles allow for a tiny amount of conduction and convection, though it is usually negligible.
Radiation Is the Primary Challenge
In a high-quality vacuum, radiation becomes the dominant form of heat transfer. This is why a thermos or Dewar flask has a silvered coating on its inner surfaces.
The reflective lining bounces thermal radiation back to its source, preventing heat from radiating out of a hot liquid or into a cold one.
Outgassing Degrades the Vacuum
Materials themselves can be a problem. When placed in a vacuum, solids and liquids can slowly release trapped gases in a process called outgassing.
This process degrades the quality of the vacuum over time, reducing its insulating properties by adding more particles back into the space.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding these principles allows you to apply them to your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum insulation (e.g., a thermos): Combine a high-quality vacuum with highly reflective internal surfaces to block both convection/conduction and radiation.
- If your primary focus is cooling in a vacuum (e.g., a satellite): You must use conduction through physical mounts or dedicated thermal straps to move heat to a radiator, which then sheds the heat as radiation into space.
- If your primary focus is a scientific process: Be aware that radiation is always a factor, and choose materials with low outgassing properties to maintain the integrity of your vacuum.
By removing the matter that carries heat, a vacuum empowers you to control and isolate temperature with remarkable efficiency.

Summary Table:
| Heat Transfer Method | Effect in a Vacuum | Key Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Conduction | Blocked | No molecules to transfer heat by contact. |
| Convection | Blocked | No fluids (gas/liquid) to create heat currents. |
| Radiation | Unaffected | Heat travels via electromagnetic waves (infrared). |
Need precise temperature control for your lab processes? KINTEK specializes in vacuum and thermal technology for laboratories. Our equipment, including vacuum ovens and furnaces, leverages these insulating principles to provide unparalleled temperature stability and energy efficiency for your research or production needs. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the temperature control system of a vacuum hot press furnace influence the mechanical properties of tungsten and copper joints? | Optimize Joint Strength
- Why is the vacuum environment provided by a vacuum hot pressing furnace necessary for Diamond/Al-Cu composites?
- What are the primary functions of a vacuum hot press furnace? Optimize Densification of CNT/Al Matrix Composites
- What role does the Laboratory Vacuum Hot Press Furnace play in the production of ZnS ceramics? Unlock Optical Excellence
- How does a vacuum hot-press sintering furnace enhance WC/Cu material density? Achieving Superior Structural Integrity



















