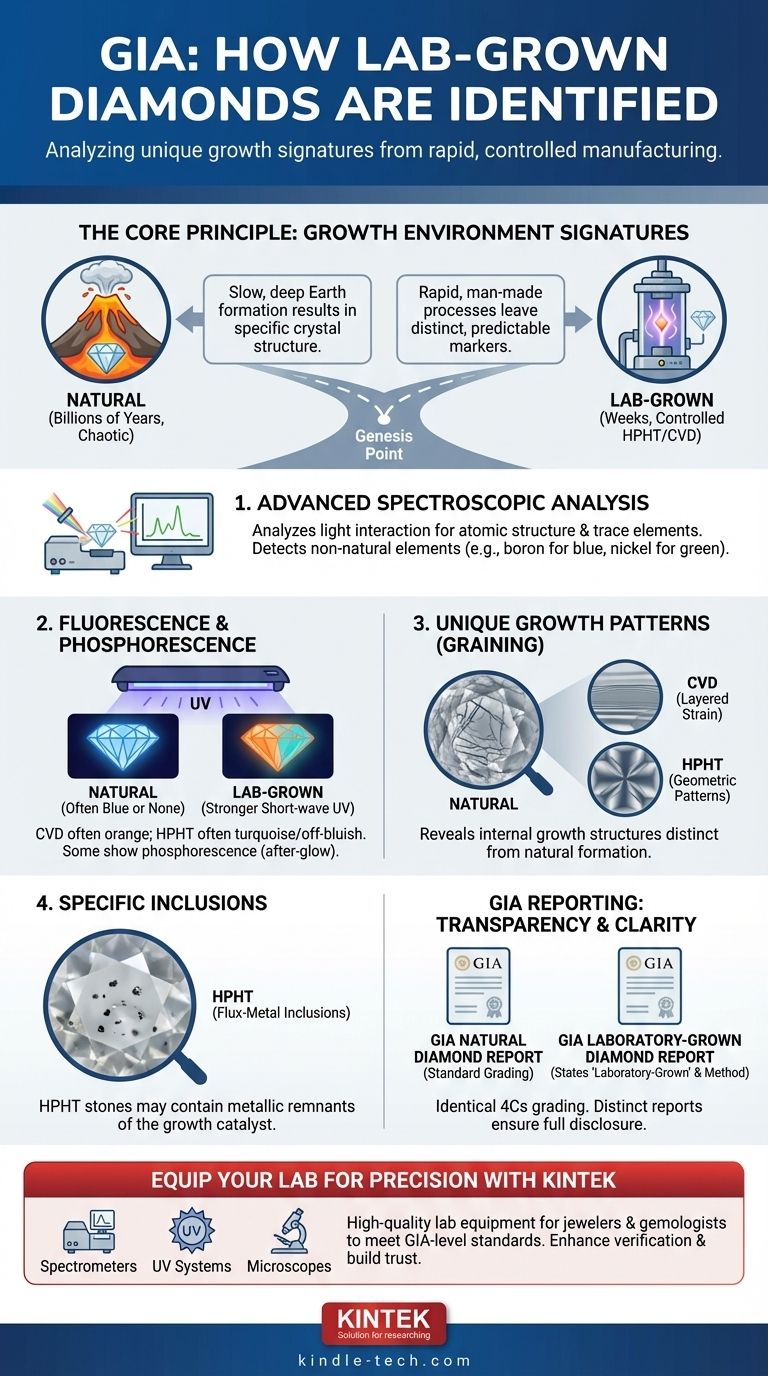
GIA identifies lab-grown diamonds by analyzing their unique growth characteristics. While physically and chemically identical to natural diamonds, lab-grown stones possess subtle markers left behind by their rapid, controlled manufacturing process. GIA's expert gemologists use advanced spectroscopic and gemological equipment to detect these specific growth patterns, fluorescence characteristics, and inclusion types to definitively determine a diamond's origin.
The core principle of identification rests on a simple fact: different creation environments leave different "fingerprints." GIA's methods are designed to spot the microscopic evidence of a rapid, man-made process, which is fundamentally different from the slow, chaotic formation of a natural diamond deep within the Earth.
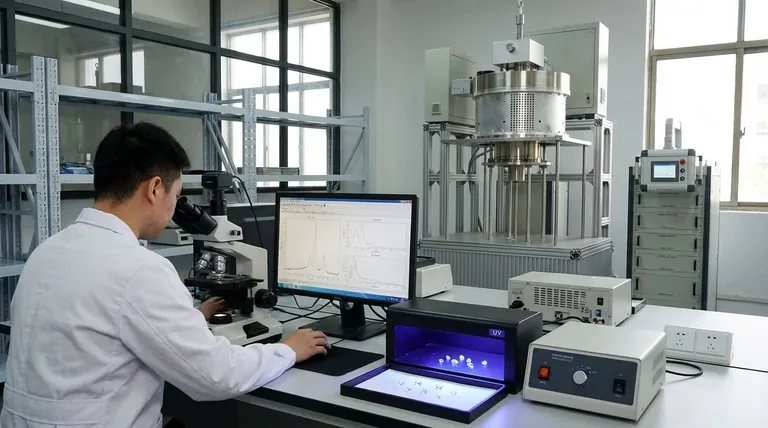

The Core Principle: Growth Environment Signatures
The ability to distinguish between a natural and a lab-grown diamond comes down to identifying the traces left by its unique formation journey.
Natural vs. Laboratory Formation
Natural diamonds form over billions of years under immense, inconsistent heat and pressure deep within the Earth's mantle. This chaotic process results in a specific crystal structure and set of characteristics.
In contrast, lab-grown diamonds are created in a matter of weeks using methods like High Pressure/High Temperature (HPHT) or Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). These highly controlled, rapid processes leave behind distinct and predictable markers.
Advanced Spectroscopic Analysis
GIA’s most definitive tool is advanced instrumentation that analyzes how a diamond interacts with different wavelengths of light. This reveals its atomic structure and the presence of trace elements.
This analysis can detect elements deliberately added during the growth process, such as boron to create blue diamonds or nickel for green diamonds, which differ from the trace elements found in natural stones.
Key Observable Markers of Lab-Grown Diamonds
While advanced machinery provides the final verdict, GIA gemologists also look for several key visual indicators that are characteristic of lab-grown stones.
Distinctive Fluorescence and Phosphorescence
Fluorescence, the glow a diamond emits under ultraviolet (UV) light, is a critical indicator.
Lab-grown diamonds often exhibit stronger fluorescence under short-wave UV light compared to long-wave UV light, which is the opposite of most natural diamonds.
Specific colors can also be a clue. CVD-grown diamonds typically fluoresce a bright orange color, while HPHT-grown diamonds often show a turquoise or off-bluish color. Natural diamonds, when they fluoresce, usually emit a blue color.
Additionally, some lab-grown diamonds exhibit phosphorescence, meaning they continue to glow for a short period after the UV light source is turned off.
Unique Growth Patterns (Graining)
The way a diamond crystal grows leaves behind internal graining or patterns.
HPHT diamonds may show geometric or cross-shaped fluorescence patterns, reflecting the cubic nature of the growth environment.
CVD diamonds, which are grown in layers, can display a striped or layered pattern (strain pattern) when viewed from the side. These uniform patterns are distinct from the more irregular growth features seen in natural diamonds.
Specific Types of Inclusions
Inclusions are tiny imperfections within a diamond. While both types of diamonds can have inclusions, their nature often differs.
HPHT diamonds can contain small, dark flux-metal inclusions. These are tiny remnants of the molten metal solution that served as the catalyst for the diamond's growth and are not found in natural stones.
Understanding the GIA Reporting Process
GIA's goal is not to judge quality but to provide full transparency about a diamond's identity and characteristics.
The Rigorous, Identical Grading
It is crucial to understand that all diamonds, regardless of origin, undergo the same rigorous grading process. The assessment of the 4Cs (Cut, Clarity, Color, and Carat) is identical for both natural and lab-grown diamonds.
Separate, Distinct Reports
To ensure complete clarity, GIA issues two different types of reports. Natural diamonds receive a standard GIA Diamond Grading Report, while lab-grown diamonds are issued a GIA Laboratory-Grown Diamond Report.
This report clearly states the diamond's origin as "laboratory-grown" and may even specify the growth method (HPHT or CVD), providing the consumer with unambiguous information.
What This Means for You
Understanding how GIA distinguishes diamond origins empowers you to make an informed choice based on your priorities and values.
- If your primary focus is transparency and verification: Always insist on a GIA report, which will definitively state whether the diamond is natural or laboratory-grown.
- If you are choosing a lab-grown diamond: Appreciate that its unique growth markers are a fascinating part of its story, but they do not impact its beauty, durability, or chemical identity as a genuine diamond.
- If you are concerned about telling them apart visually: Rest assured that to the naked eye, the differences are undetectable; identification requires the expertise and advanced equipment of a gemological lab.
Ultimately, GIA's scientific process provides the market with the critical confidence and clarity needed to value and appreciate both of these genuine sources of diamond.
Summary Table:
| Identification Method | Key Markers for Lab-Grown Diamonds | Common in Growth Method |
|---|---|---|
| Spectroscopic Analysis | Presence of specific trace elements (e.g., boron, nickel) | HPHT & CVD |
| Fluorescence/Phosphorescence | Stronger short-wave UV glow; orange (CVD) or turquoise (HPHT) colors | HPHT & CVD |
| Growth Patterns (Graining) | Geometric patterns (HPHT); layered strain patterns (CVD) | HPHT & CVD |
| Inclusion Types | Flux-metal inclusions (HPHT) | Primarily HPHT |
Ensure Diamond Integrity with Professional Gemological Equipment
Whether you're a jeweler, appraiser, or gemologist, having the right tools is essential for accurate diamond analysis. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to the precise needs of the gemological industry.
- Advanced Spectrometers for detailed compositional analysis
- UV Lighting Systems to detect fluorescence and phosphorescence markers
- Microscopes and Imaging Tools for identifying unique growth patterns and inclusions
Let KINTEK equip your laboratory with reliable, precise instruments that meet GIA-level standards. Enhance your verification processes and build trust with your clients.
Contact our experts today to discuss the perfect equipment for your gemological needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a microwave plasma reactor facilitate the synthesis of diamond? Master MPCVD with Precision Technology
- What are the limitations of diamonds? Beyond the Myth of Perfection
- What is microwave plasma CVD? A Guide to High-Purity Diamond and Material Synthesis
- What is the microwave plasma method? A Guide to High-Purity Material Synthesis
- What are the primary advantages of the CVD method for growing diamonds? Engineering High-Purity Gems and Components



















