Fundamentally, temperature alters hydraulic oil's viscosity, or its resistance to flow. As the oil gets hotter, it becomes thinner (less viscous), which can compromise its ability to lubricate and protect components. Conversely, as it gets colder, it becomes thicker (more viscous), which can strain the system's pump and lead to sluggish performance.
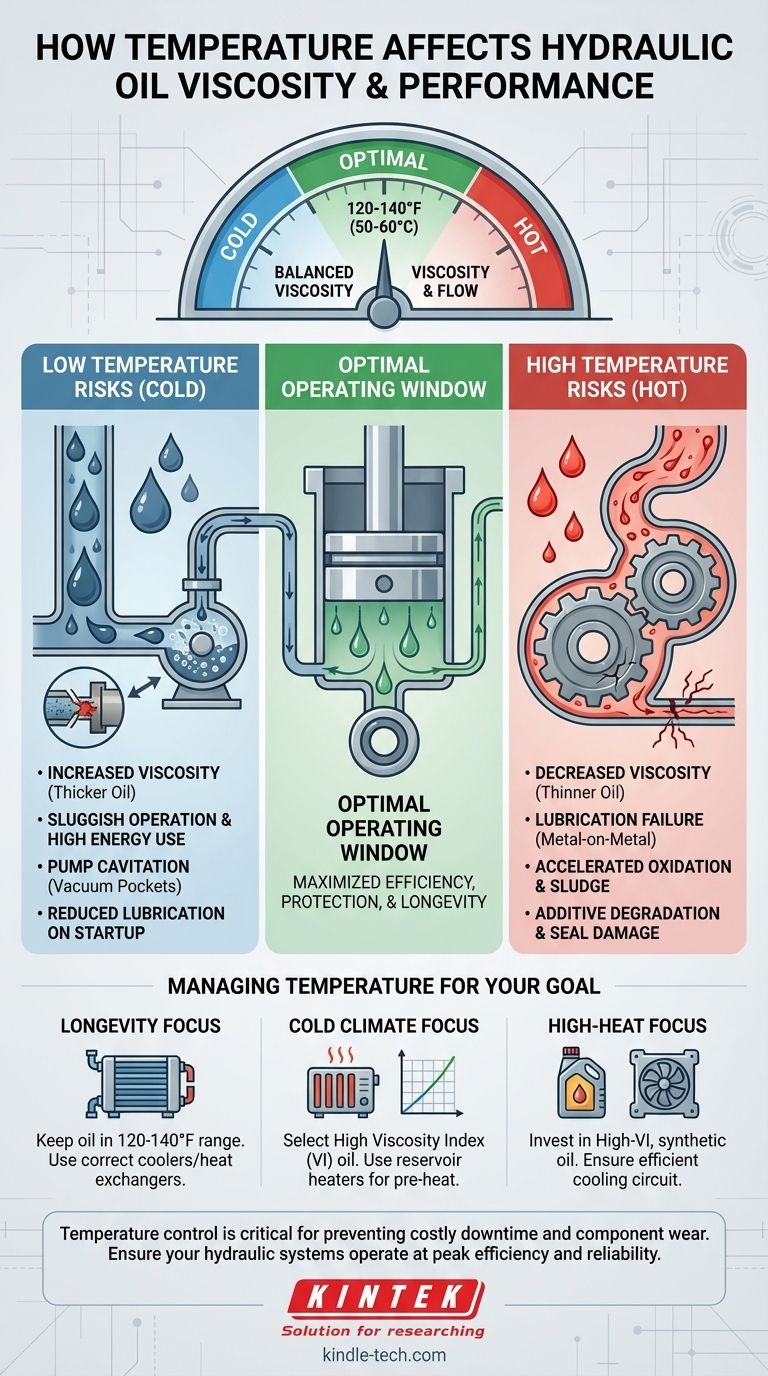
Hydraulic system performance, efficiency, and longevity are directly tied to maintaining the oil's temperature within its optimal operating window. Deviating from this range—either too hot or too cold—introduces distinct risks that degrade both the oil and the machinery.

The Dangers of High Temperatures
Operating a hydraulic system with oil that is too hot is one of the most common causes of premature component failure. The damage is often gradual but irreversible.
Decreased Viscosity and Lubrication Failure
As oil thins, the protective film between moving parts can break down. This leads to metal-on-metal contact, accelerated wear, and eventual failure of critical components like pumps, motors, and valves.
Accelerated Oil Oxidation
Heat acts as a catalyst for oxidation, a chemical reaction between the oil and oxygen. This process permanently degrades the oil, creating sludge and varnish that can clog filters, stick valves, and coat internal surfaces, impeding heat dissipation.
Additive Degradation
Hydraulic oil contains a sophisticated package of additives, including anti-wear agents, rust inhibitors, and anti-foam agents. High temperatures cause these additives to break down and deplete at a much faster rate, stripping the oil of its protective qualities.
Seal and Hose Damage
Excessive heat can cause seals and hoses to harden, become brittle, and lose their flexibility. This leads to both internal and external leaks, reducing system efficiency and creating safety hazards.
The Problems with Low Temperatures
While less common in many industrial settings, operating a hydraulic system in cold conditions presents its own set of challenges, primarily related to increased viscosity.
Increased Viscosity and Sluggish Operation
Extremely thick oil is difficult to pump. This results in slow, sluggish machine operation on startup and places immense strain on the system's pump and motor, increasing energy consumption.
Risk of Pump Cavitation
Pumps struggle to pull thick, cold oil from the reservoir. This can create vacuum pockets, or cavities, that collapse violently at the pump outlet, a destructive phenomenon known as cavitation that can quickly destroy a pump.
Reduced Lubrication on Startup
Before the system reaches its operating temperature, the thick oil may not flow quickly enough to properly lubricate all components. This brief period of lubricant starvation during every cold start can contribute to significant wear over time.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Managing temperature is not about running the system as cold as possible; it is about maintaining a stable temperature within a specific, engineered range.
Efficiency vs. Protection
While cooler oil is thicker and offers a robust protective film, it requires more energy to pump, reducing overall system efficiency. The goal is to find the balance point where the oil is thin enough for efficient flow but thick enough for complete protection.
The Ideal Operating Window
Most standard hydraulic systems are designed to operate most effectively with oil temperatures between 120°F and 140°F (50-60°C). Within this range, the oil achieves the optimal balance of viscosity and flow characteristics.
The Role of Viscosity Index (VI)
The Viscosity Index (VI) is a crucial metric that measures how much an oil's viscosity changes with temperature. An oil with a high VI maintains a more stable viscosity across a wider temperature range, making it superior for applications with significant temperature swings.
How to Manage Temperature for Your Goal
Your strategy for managing oil temperature should align directly with your operational environment and priorities.
- If your primary focus is maximum system longevity: Your goal is to keep the oil within the 120-140°F (50-60°C) window at all times using correctly sized heat exchangers or coolers.
- If your primary focus is performance in cold climates: Select a hydraulic oil with a high Viscosity Index (VI) and consider using reservoir heaters to pre-heat the oil before startup.
- If your primary focus is reliability in high-heat applications: Invest in a high-VI, synthetic-based hydraulic oil and ensure your system has an oversized or highly efficient cooling circuit.
By actively managing oil temperature, you move from a reactive to a proactive state, ensuring the long-term health and reliability of your hydraulic systems.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Condition | Key Effect on Oil | Primary Risk to System |
|---|---|---|
| High Temperature | Decreased Viscosity (Thinner Oil) | Lubrication Failure, Oxidation, Additive Depletion |
| Low Temperature | Increased Viscosity (Thicker Oil) | Pump Cavitation, Sluggish Operation, Startup Wear |
| Optimal Range (120-140°F / 50-60°C) | Balanced Viscosity & Flow | Maximized Efficiency, Protection, and Longevity |
Ensure your hydraulic systems operate at peak efficiency and reliability. Temperature control is critical for preventing costly downtime and component wear. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for fluid analysis and testing, helping you monitor and maintain optimal hydraulic oil conditions.
Contact our experts today to discuss solutions for your specific laboratory and maintenance needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual Lab Heat Press
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Integrated Manual Heated Plates for Lab Use
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the parts of a manual hydraulic press? A Guide to Its Core Components and Operation
- How much force can a hydraulic press exert? Understanding its immense power and design limits.
- What is the efficiency of a hydraulic press? Harness Unmatched Force Multiplication for Your Lab
- What is the conclusion of a hydraulic press? Unmatched Force for Industrial Applications
- What is the construction of a hydraulic press based on? Unlocking the Power of Pascal's Law





