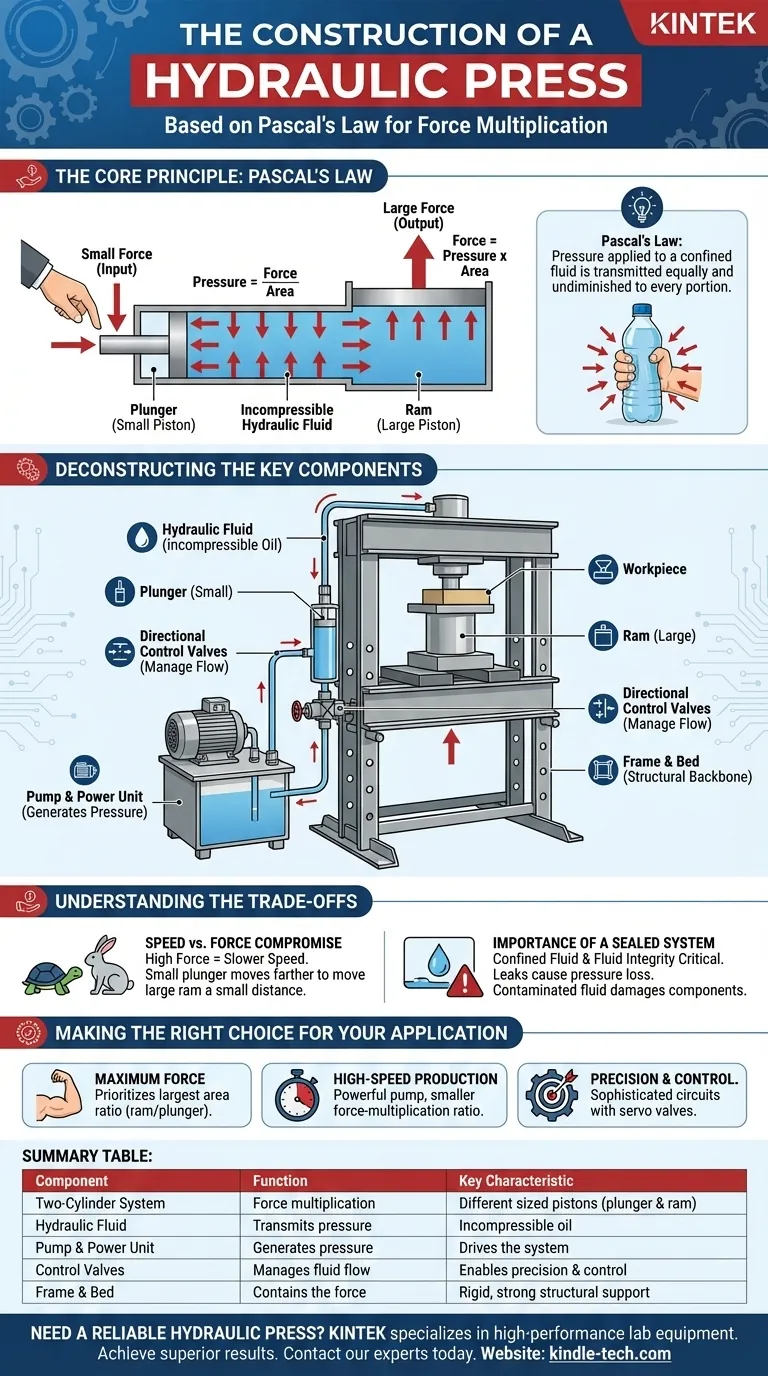
At its core, the construction of a hydraulic press is based on a fundamental physics principle known as Pascal's Law. This principle allows the machine to achieve immense force multiplication by applying pressure to a confined fluid. The essential components enabling this are two interconnected cylinders of different sizes, a pump to create pressure, and a rigid frame to contain the resulting force.
A hydraulic press is not just a collection of strong parts; it is a system deliberately engineered to exploit Pascal's Law. Its construction translates a small, manageable force applied over a small area into a massive output force over a larger area, all transmitted through an incompressible fluid.
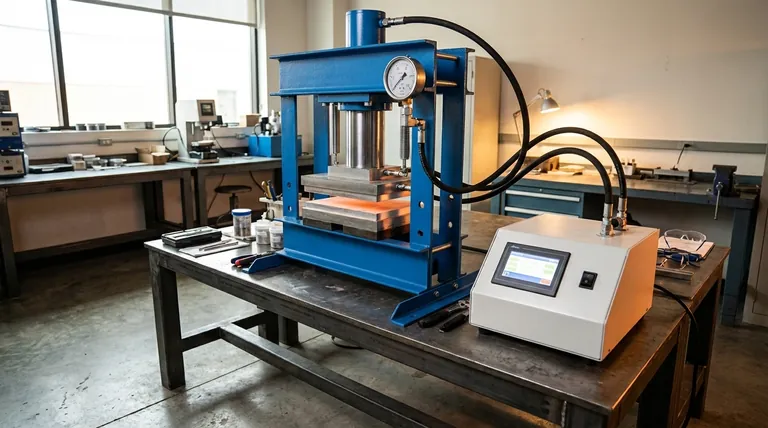

The Core Principle: Pascal's Law
The entire design of a hydraulic press hinges on one elegant concept. Understanding this principle is key to understanding how the machine functions.
What is Pascal's Law?
Pascal's Law states that when pressure is applied to an enclosed, incompressible fluid, that pressure is transmitted equally and undiminished to every portion of the fluid and the walls of the containing vessel.
Imagine squeezing a sealed water bottle. The pressure you apply with your hand isn't just felt where your fingers are; it increases throughout the entire bottle.
How a Press Exploits This Principle
A hydraulic press uses this law by connecting two pistons of different sizes with a pipe filled with hydraulic fluid.
A small force is applied to the small piston (the plunger). This creates pressure in the fluid (Pressure = Force / Area). Because of Pascal's Law, this exact same pressure is transmitted to the large piston (the ram).
Since the ram has a much larger surface area, that same pressure results in a much larger output force (Force = Pressure x Area). This is the secret to the press's incredible power.
Deconstructing the Key Components
Each part of a hydraulic press has a distinct and critical role in applying this principle safely and effectively.
The Two-Cylinder System
The heart of the press is its two-cylinder system. The smaller cylinder, known as the plunger, is where the initial force is applied. The much larger cylinder, the ram, is what delivers the multiplied force to the workpiece. The ratio of their areas determines the machine's force multiplication factor.
The Hydraulic Fluid
This is the medium that transmits the pressure. It is typically a specialized, incompressible oil. Its incompressibility is crucial; it ensures that the energy applied to the plunger is efficiently transferred to the ram without being wasted on compressing the fluid itself.
The Pump and Power Unit
A pump, driven by a hydraulic power unit, is what actually generates the high-pressure oil and applies force to the plunger. This system is responsible for moving the fluid into the cylinder to create the pressure needed for operation.
Directional Control Valves
Modern presses use directional control valves to manage the flow of hydraulic fluid. These valves allow the operator to precisely control the extension and retraction of the ram, making the press a controllable tool rather than just a brute-force machine.
The Frame and Bed
The mainframe and bed (or bolster) are the structural backbone of the press. They must be incredibly strong and rigid to hold all components in alignment and safely withstand the immense forces generated by the ram without bending or failing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the design of a hydraulic press involves fundamental compromises that dictate its performance.
The Speed vs. Force Compromise
There is a direct trade-off between force and speed. To move the large ram a small distance, the small plunger must travel a much greater distance. This means that machines designed for extremely high force are often inherently slow.
The Importance of a Sealed System
The entire principle relies on a confined fluid. Any leak in the cylinders, pipes, or seals will cause a loss of pressure and a dramatic drop in efficiency. Similarly, any trapped air in the fluid (which is compressible) can lead to spongy, inconsistent operation.
Fluid Integrity is Non-Negotiable
The condition of the hydraulic fluid is critical. Contaminated or degraded oil can damage the pump, wear out seals, and reduce performance. Using the correct type of fluid ensures proper lubrication, heat dissipation, and resistance to compression.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The specific construction of a press is always tailored to its intended task. Understanding this allows you to evaluate a machine based on its design.
- If your primary focus is maximum pressing force: The design will prioritize the largest possible area ratio between the ram and the plunger, even at the cost of speed.
- If your primary focus is high-speed production: The design will likely feature a more powerful pump and a smaller force-multiplication ratio to cycle the ram quickly.
- If your primary focus is precision and control: The design will incorporate sophisticated hydraulic circuits with proportional and servo valves for exact control over speed, force, and position.
Ultimately, the construction of every hydraulic press is a physical demonstration of using fluid pressure to create powerful and controllable mechanical force.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Two-Cylinder System | Force multiplication | Different sized pistons (plunger & ram) |
| Hydraulic Fluid | Transmits pressure | Incompressible oil |
| Pump & Power Unit | Generates pressure | Drives the system |
| Control Valves | Manages fluid flow | Enables precision and control |
| Frame & Bed | Contains the force | Rigid, strong structural support |
Need a reliable hydraulic press for your laboratory or production line?
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment, including hydraulic presses engineered for precision, durability, and maximum force output. Our machines are designed to meet the rigorous demands of material testing, sample preparation, and industrial production.
Let us help you achieve superior results. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application needs and find the perfect press for your workflow.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual Lab Heat Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What are the parts of a manual hydraulic press? A Guide to Its Core Components and Operation
- What is the conclusion of a hydraulic press? Unmatched Force for Industrial Applications
- What is a hydraulic press in simple words? Harness Immense Force for Shaping and Crushing
- What is the efficiency of a hydraulic press? Harness Unmatched Force Multiplication for Your Lab
- What are the potential hazards in a hydraulic press? Understanding the Risks of Crushing, Injection, and Failure



















