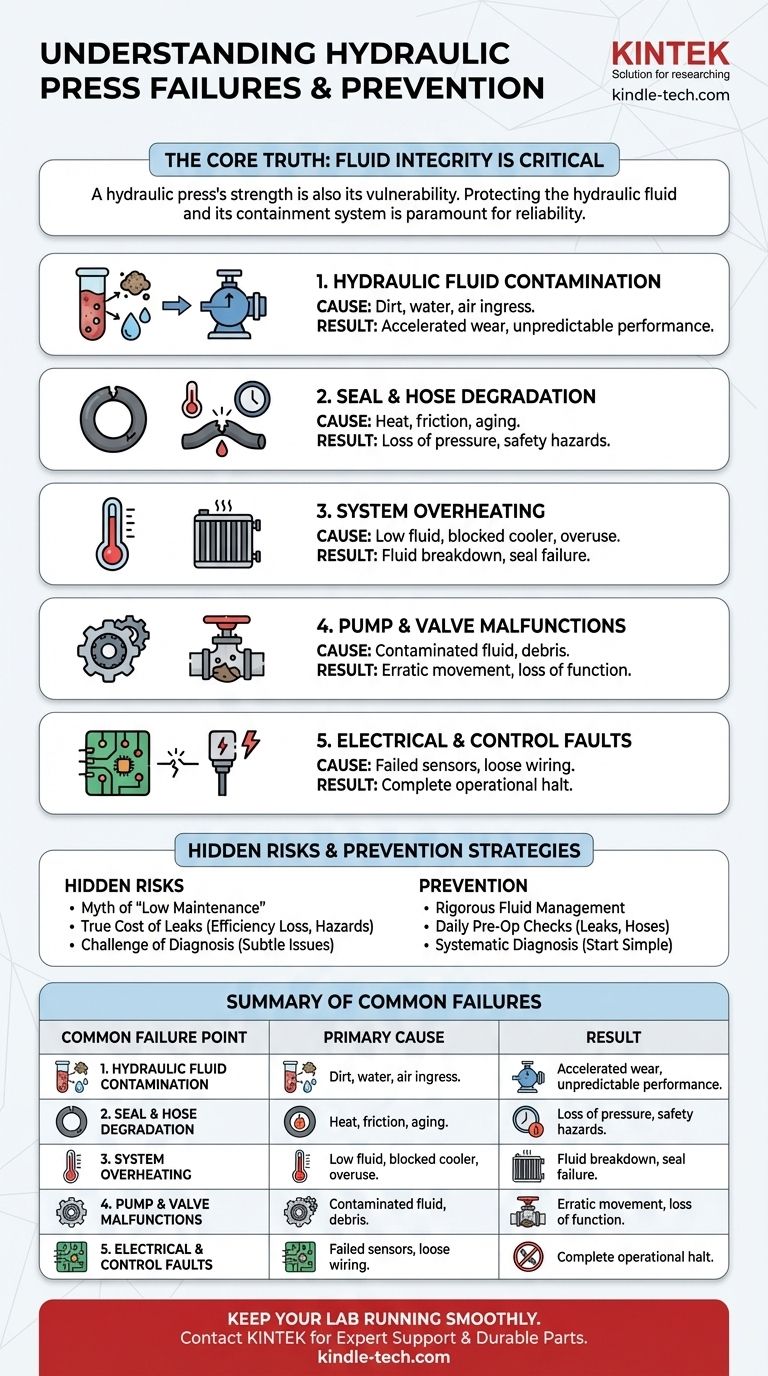
While known for their durability, hydraulic press failures almost always trace back to a few core areas: the hydraulic fluid itself, the seals and hoses containing it, or the electrical systems that control it. Issues like fluid contamination, leaks, and overheating are the most frequent culprits that lead to a loss of pressure or complete operational failure.
The central truth is that a hydraulic press's greatest strength—its reliance on pressurized fluid—is also the source of its most common vulnerabilities. Protecting the integrity of the hydraulic fluid and its containment system is the single most critical factor in ensuring long-term reliability.

Unpacking the Core Failure Points
A hydraulic press is a system of interconnected components. A problem in one area will inevitably cascade and affect others. Understanding these primary failure modes is the first step toward prevention.
Hydraulic Fluid Contamination
The hydraulic fluid is the lifeblood of the press. When it becomes contaminated with dirt, water, or air, it can no longer lubricate and transfer power effectively.
This contamination accelerates wear on every component it touches, particularly the pump and valves, leading to premature failure and unpredictable performance.
Seal and Hose Degradation
Seals and hoses are responsible for containing the immense pressure of the hydraulic system. Over time, they degrade from heat, friction, and age.
A leaking seal or a burst hose is one of the most common and visible failures. This results in a direct loss of pressure, wasted fluid, and a significant safety hazard.
System Overheating
Excessive heat is a primary enemy of any hydraulic system. It can be caused by low fluid levels, a blocked cooler, or operating the press beyond its duty cycle.
Overheating rapidly breaks down the hydraulic fluid, reducing its viscosity and lubricating properties. It also causes seals to harden and crack, leading to leaks and system failure.
Pump and Valve Malfunctions
The pump generates the flow, and the valves direct it. These are precision components that are highly sensitive to contaminated fluid.
Debris can cause a valve to stick open or closed, leading to erratic ram movement or a complete loss of function. A failing pump will be unable to generate the required pressure, rendering the press useless.
Electrical and Control System Faults
Modern automatic presses rely on a complex system of sensors, relays, PLCs, and solenoids to control valve operation and monitor the system.
A single failed sensor or a loose wire can halt the entire operation. Troubleshooting these electrical issues can often be more complex than diagnosing a purely mechanical or hydraulic fault.
Understanding the Hidden Risks
The references rightly praise hydraulic presses for their efficiency and power. However, this performance comes with specific risks that must be managed proactively.
The Myth of "Low Maintenance"
While durable, "low maintenance" should never be interpreted as "no maintenance." Ignoring the system invites catastrophic failure.
The most critical maintenance task is managing the hydraulic fluid. Regular fluid analysis, filter changes, and system checks are not optional—they are essential for reliable operation.
The True Cost of a Leak
A hydraulic fluid leak is more than just a mess. It represents a loss of efficiency, a direct cost in replacement fluid, a serious slip-and-fall hazard for personnel, and a potential environmental issue.
Ignoring a small leak is a common mistake. It is often an early warning sign of a more significant impending failure, such as a compromised seal or a failing hose.
The Challenge of Diagnosis
Unlike a simple mechanical press, where a failure is often visibly obvious, a hydraulic issue can be subtle.
A loss of pressure or slow operation could be caused by a failing pump, a bypassing cylinder seal, a sticking relief valve, or a clog in the system. Proper diagnosis often requires specialized gauges and a clear understanding of the hydraulic circuit.
How to Prevent Common Failures
A proactive approach is the most effective way to ensure the safety, reliability, and longevity of your hydraulic press.
- If your primary focus is maximum uptime: Implement a rigorous preventative maintenance schedule centered on hydraulic fluid quality, including regular fluid analysis and filter changes.
- If your primary focus is operator safety: Mandate daily pre-operation checks for any visible leaks, damaged hoses, and the proper function of all safety guards.
- If you are diagnosing a problem: Always start with the simplest potential causes—check the fluid level, look for leaks, and listen for unusual pump noises before assuming a major component has failed.
Ultimately, understanding these potential points of failure transforms maintenance from a reactive chore into a strategic investment in performance and safety.
Summary Table:
| Common Failure Point | Primary Cause | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Hydraulic Fluid Contamination | Dirt, water, or air in the system | Accelerated wear, unpredictable performance |
| Seal and Hose Degradation | Heat, friction, age | Loss of pressure, safety hazards |
| System Overheating | Low fluid, blocked cooler, overuse | Fluid breakdown, seal failure |
| Pump/Valve Malfunctions | Contaminated fluid, debris | Erratic movement, loss of function |
| Electrical Control Faults | Failed sensors, loose wiring | Complete operational halt |
Keep your lab running smoothly and safely. The reliability of your hydraulic press is critical to your research and production. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, offering expert maintenance support and durable replacement parts to prevent common failures. Don't let hydraulic issues cause costly downtime—contact our experts today for a consultation and ensure your press operates at peak performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual Lab Heat Press
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What is a hydraulic press in simple words? Harness Immense Force for Shaping and Crushing
- What is the efficiency of a hydraulic press? Harness Unmatched Force Multiplication for Your Lab
- What is the conclusion of a hydraulic press? Unmatched Force for Industrial Applications
- What is the construction of a hydraulic press based on? Unlocking the Power of Pascal's Law
- What are the parts of a manual hydraulic press? A Guide to Its Core Components and Operation



















