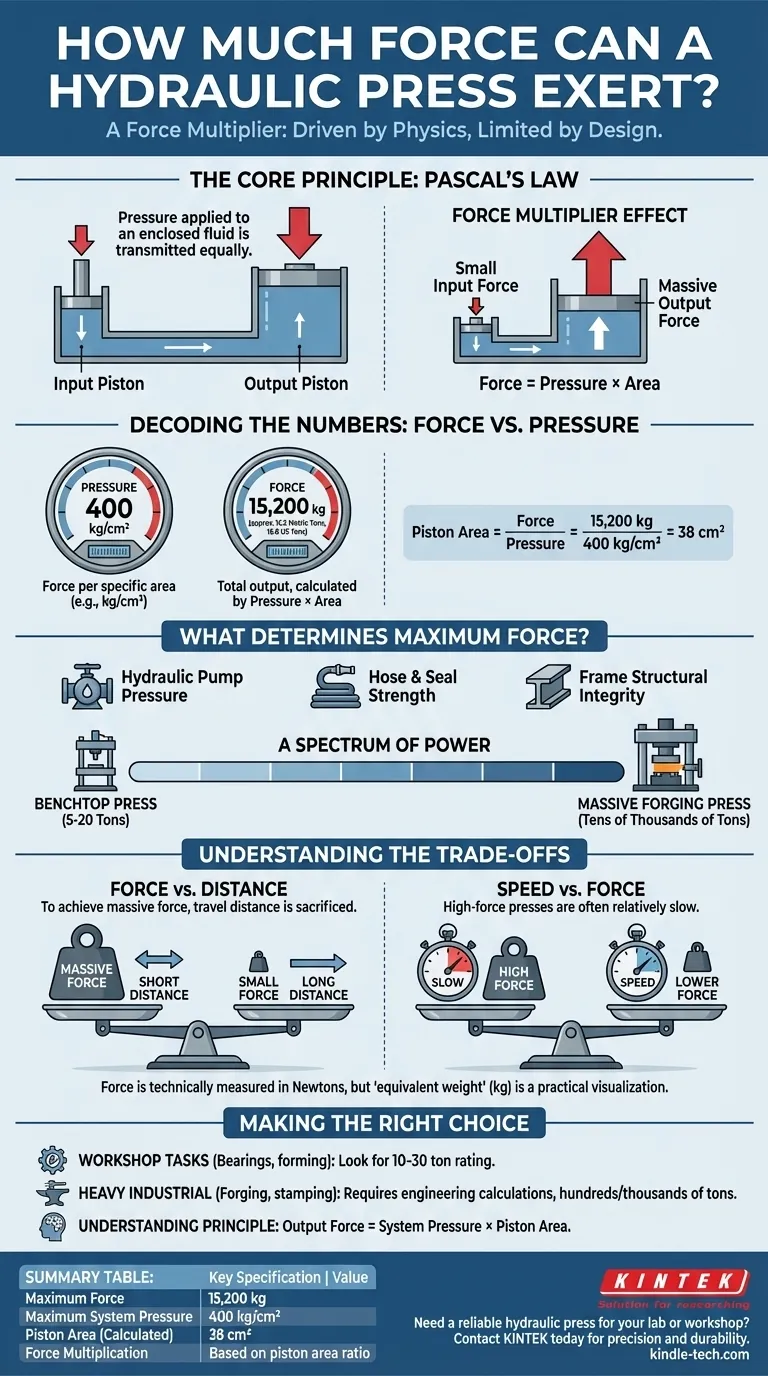
A hydraulic press is a force multiplier, capable of exerting immense force that is limited only by its design and the strength of its components. Based on the provided specifications, the press in question can exert a maximum force equivalent to the weight of 15,200 kilograms (approximately 15.2 metric tons or 16.8 US tons).
The true power of a hydraulic press doesn't come from its motor, but from a fundamental principle of physics: Pascal's Law. This law allows a small initial force to be multiplied into a massive output force, making these machines essential for tasks requiring extreme pressure.
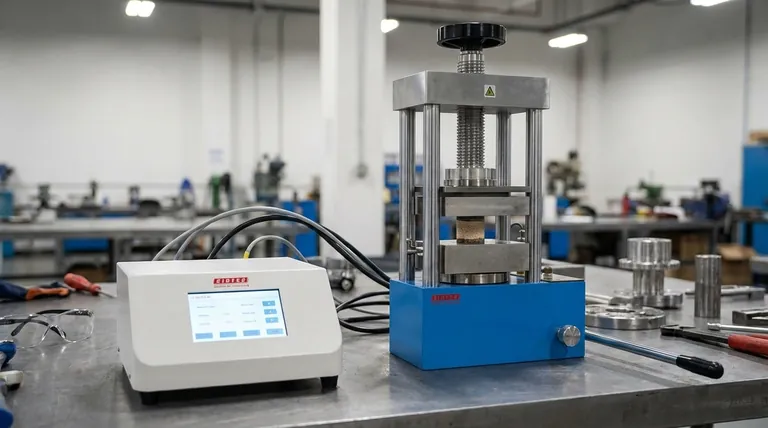

The Core Principle: How Force is Multiplied
The operation of a hydraulic press is a direct application of Pascal's Law, which states that pressure applied to an enclosed, incompressible fluid is transmitted equally to every portion of the fluid and the walls of the containing vessel.
The Force Multiplier Effect
A hydraulic system uses two pistons of different sizes in a shared, sealed container of hydraulic fluid (typically oil).
When a small force is applied to the small input piston, it creates pressure in the fluid. This same pressure then acts on the much larger output piston. Because the area of the output piston is significantly larger, the resulting force is proportionally multiplied.
Decoding the Numbers: Force vs. Pressure
It's crucial to distinguish between the concepts of force and pressure.
- Pressure is the amount of force applied over a specific area (e.g., kilograms per square centimeter, or kg/cm²). In your example, the maximum system pressure is 400 kg/cm².
- Force is the total output, calculated by multiplying the pressure by the area it acts upon (
Force = Pressure × Area). The maximum output force is 15,200 kg.
From these two figures, we can deduce that the press's large piston has a surface area of 38 square centimeters (15,200 kg / 400 kg/cm²).
What Determines a Press's Maximum Force?
The 15,200 kg figure is not a universal constant for all hydraulic presses; it's the specific design limit for one particular machine. The actual force a press can exert is determined by several engineering factors.
Key Limiting Factors
The ultimate force is constrained by the weakest link in the system. This includes the maximum pressure the hydraulic pump can generate, the bursting strength of the hoses and seals, and, most importantly, the structural integrity of the press's frame.
A Spectrum of Power
The capabilities of hydraulic presses vary enormously based on their intended use. A small benchtop press used for installing bearings might exert 5 to 20 tons of force. In contrast, massive industrial forging presses can exert forces in the tens of thousands of tons.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The immense force multiplication of a hydraulic press does not come for free. There are inherent physical trade-offs to consider.
The Force vs. Distance Relationship
To achieve massive force, you sacrifice travel distance. The large output piston will move a very short distance for every long stroke of the small input piston. The work done remains the same (ignoring friction), but it's expressed as a high force over a short distance.
Speed is the Counterpart to Force
Because the large piston travels such a small distance with each pump stroke, high-force hydraulic presses are often relatively slow. Achieving higher speeds requires much more powerful pumps capable of moving a larger volume of fluid quickly, which increases system complexity and cost.
Common Misinterpretations
Expressing force in kilograms (a unit of mass) is common in industrial settings but is technically imprecise. Force is properly measured in Newtons or Pounds-force. However, thinking of it as the "equivalent weight it can lift or crush" is a practical way to visualize its capability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the relationship between pressure, area, and force allows you to select the right tool for the job.
- If your primary focus is on workshop tasks (like pressing bearings or small metal forming): Look for the press's "tonnage" rating; a 10- to 30-ton press is typically sufficient for most automotive and fabrication needs.
- If your primary focus is on heavy industrial applications (like forging or stamping): The required force will be determined by engineering calculations based on the material and process, often requiring presses rated in the hundreds or thousands of tons.
- If you are simply trying to understand the principle: Remember that the output force is always the system's pressure multiplied by the piston's area (F = P × A).
By grasping this core principle, you can effectively assess the power and suitability of any hydraulic press.
Summary Table:
| Key Specification | Value |
|---|---|
| Maximum Force | 15,200 kg (15.2 metric tons) |
| Maximum System Pressure | 400 kg/cm² |
| Piston Area (Calculated) | 38 cm² |
| Force Multiplication | Based on piston area ratio |
Need a reliable hydraulic press for your lab or workshop? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, offering hydraulic presses designed for precision and durability. Whether you're pressing samples, molding materials, or performing other lab tasks, our equipment ensures consistent performance and safety. Contact us today to find the perfect press for your specific needs and experience the KINTEK difference in quality and support!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual Lab Heat Press
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What does a manual press do? Understand the Two Key Types for Your Lab or Industrial Needs
- What is the conclusion of a hydraulic press? Unmatched Force for Industrial Applications
- What is an automatic press machine? High-Precision Force for Modern Manufacturing
- What are the failures of a hydraulic press? Prevent Downtime and Ensure Safety in Your Lab
- What are the parts of a manual hydraulic press? A Guide to Its Core Components and Operation



















