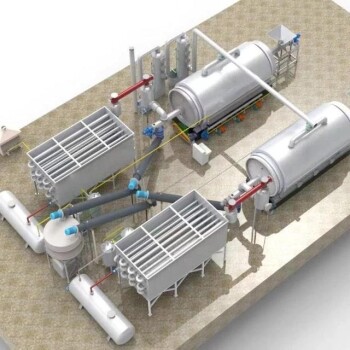
Waste tire recycling is a multi-faceted process that transforms discarded tires into valuable materials such as fuel, rubber powder, carbon black, and industrial raw materials. The process involves several key methods, including restructuring, retreading, pyrolysis, and grinding, each tailored to produce specific end products. Advanced technologies like devulcanization and pyrolysis have further enhanced the efficiency and sustainability of tire recycling, enabling the conversion of resilient waste into reusable resources. The recycling process typically includes steps such as shredding, magnetic separation, depolymerization, and heat exchange, ensuring that waste tires are repurposed into high-quality materials for industrial use or energy production.
Key Points Explained:
-
Methods of Waste Tire Recycling:
- Restructuring and Retreading: Waste tires can be reused in their original form or retreaded for extended use. This method is cost-effective and reduces the need for new tire production.
- Energy Recovery: Tires are used as fuel through high-temperature heating and thermal decomposition, converting them into oil, combustible gas, or carbon. This method is particularly useful for energy generation in industrial settings.
- Powder Production: Waste tires are ground into powder using methods like dry grinding, cryogenic grinding, or wet grinding. The resulting rubber powder is used in various applications, including asphalt, concrete, and polymeric matrices.
-
Advanced Recycling Technologies:
- Devulcanization: This process breaks down the vulcanized rubber in tires, making it possible to recycle the material into new rubber products. It is an environmentally friendly method that reduces waste and conserves resources.
- Pyrolysis: A thermal decomposition process that converts waste tires into oil, gas, and carbon black. Pyrolysis is highly efficient and produces valuable by-products for industrial use.
-
Carbon Black Production:
- Waste tires are processed into carbon black, a primary raw material used in manufacturing industrial products. The process involves fine processing equipment, with costs ranging from 70,000 to 100,000 yuan per ton of tires. Refined carbon black can be sold for approximately 4,000 yuan per ton, making it a profitable recycling option.
-
Grinding Technologies:
- Ambient Grinding: A cost-effective method that produces rubber powder at room temperature. The resulting powder has a larger specific surface area, making it suitable for blending with other materials.
- Cryogenic Grinding: Involves freezing the tires with liquid nitrogen before grinding, producing fine rubber powder with uniform particle sizes. This method is ideal for high-quality applications.
- Wet Grinding: Uses water to cool and lubricate the grinding process, resulting in smooth rubber powder with minimal heat generation.
-
Applications of Recycled Tire Products:
- Civil Engineering: Recycled tire rubber is used as a filler in concrete and asphalt, enhancing durability and reducing material costs.
- Polymeric Matrices: Rubber powder is blended with thermoplastics, thermosets, or virgin rubber to create composite materials for industrial use.
- Fuel and Energy: Pyrolysis-derived oil and gas are used as alternative energy sources, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
-
Process Steps in Tire Recycling:
- Shredding: Waste tires are cut into smaller pieces to facilitate further processing.
- Magnetic Separation: Metal components, such as steel belts, are removed using magnets.
- Depolymerization: The rubber is broken down into smaller molecules through heating and evaporation.
- Cracking and Heat Exchange: The rubber undergoes thermal cracking to produce oil and gas, followed by heat exchange to recover energy.
- Automatic Slag Discharge: Residual materials, such as carbon black, are automatically discharged for further processing.
By employing these methods and technologies, waste tire recycling not only addresses environmental concerns but also creates economic opportunities through the production of valuable materials and energy.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Methods | Restructuring, retreading, pyrolysis, grinding |
| Advanced Technologies | Devulcanization, pyrolysis |
| Key Products | Fuel, rubber powder, carbon black, industrial raw materials |
| Grinding Methods | Ambient, cryogenic, wet grinding |
| Applications | Civil engineering, polymeric matrices, fuel and energy |
| Process Steps | Shredding, magnetic separation, depolymerization, cracking, heat exchange, automatic discharge |
Discover how waste tire recycling can benefit your business—contact us today to learn more!